A new (heat) shocking player in cardiac hypertrophy
- PMID: 19028916
- PMCID: PMC2903428
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.189118
A new (heat) shocking player in cardiac hypertrophy
Abstract
Hypertrophic growth of cardiac myocytes is a common result of different physiological and pathological stresses. It remains a subject of considerable debate whether hypertrophy is a compensatory process that becomes maladaptive in diseased hearts or a direct contributor to the pathogenesis of heart failure. Nevertheless, many types of stressors, mechanical or neural/hormonal, induce hypertrophy and this phenoytpe is an independent risk factor in heart failure. Therefore, much effort has been devoted to uncovering mechanisms of hypertrophic growth with the expectation that intercepting this process clinically may halt the disease progression of heart failure. It is firmly established that hypertrophic growth involves alterations in gene regulation, excitation-contractile coupling, extracellular matrix remodeling and energy metabolism.
Figures
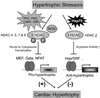
Comment on
-
Activation of histone deacetylase 2 by inducible heat shock protein 70 in cardiac hypertrophy.Circ Res. 2008 Nov 21;103(11):1259-69. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000338570.27156.84. Epub 2008 Oct 10. Circ Res. 2008. PMID: 18849323
Similar articles
-
Activation of histone deacetylase 2 by inducible heat shock protein 70 in cardiac hypertrophy.Circ Res. 2008 Nov 21;103(11):1259-69. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000338570.27156.84. Epub 2008 Oct 10. Circ Res. 2008. PMID: 18849323
-
miR-21: a star player in cardiac hypertrophy.Cardiovasc Res. 2015 Mar 1;105(3):235-7. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvv026. Epub 2015 Feb 2. Cardiovasc Res. 2015. PMID: 25644540 No abstract available.
-
miR-21-3p regulates cardiac hypertrophic response by targeting histone deacetylase-8.Cardiovasc Res. 2015 Mar 1;105(3):340-52. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvu254. Epub 2014 Dec 10. Cardiovasc Res. 2015. PMID: 25504627
-
[The mechanism underlying histone deacetylases regulating cardiac hypertrophy].Yi Chuan. 2020 Jun 20;42(6):536-547. doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.19-346. Yi Chuan. 2020. PMID: 32694112 Review. Chinese.
-
CAMTA in cardiac hypertrophy.Cell. 2006 May 5;125(3):427-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.04.015. Cell. 2006. PMID: 16678087 Review.
Cited by
-
Decreased PGC1- α levels and increased apoptotic protein signaling are associated with the maladaptive cardiac hypertrophy in hyperthyroidism.J Biosci. 2018 Dec;43(5):887-895. J Biosci. 2018. PMID: 30541949
-
Cardiac Dysfunction in the BACHD Mouse Model of Huntington's Disease.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 25;11(1):e0147269. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147269. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26807590 Free PMC article.
-
Hold me tight: Role of the heat shock protein family of chaperones in cardiac disease.Circulation. 2010 Oct 26;122(17):1740-51. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.942250. Circulation. 2010. PMID: 20975010 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- McKinsey TA, Olson EN. Dual roles of histone deacetylases in the control of cardiac growth. Novartis Found Symp. 2004;259:132–141. discussion 141-135, 163-139. - PubMed
-
- Olson EN, Backs J, McKinsey TA. Control of cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure by histone acetylation/deacetylation. Novartis Found Symp. 2006;274:3–12. discussion 13-19, 152-155, 272-156. - PubMed
-
- Trivedi CM, Luo Y, Yin Z, Zhang M, Zhu W, Wang T, Floss T, Goettlicher M, Noppinger PR, Wurst W, Ferrari VA, Abrams CS, Gruber PJ, Epstein JA. Hdac2 regulates the cardiac hypertrophic response by modulating Gsk3 beta activity. Nat Med. 2007;13(3):324–331. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL108186/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL070709-050003/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL080111/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL080111/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL103205/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL070709/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL080111-050003/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL062311/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070079/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087132/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL087132/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL062311/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL062311-09/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

