Agonist and antagonist recognition by RIG-I, a cytoplasmic innate immunity receptor
- PMID: 19019822
- PMCID: PMC2613625
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M806219200
Agonist and antagonist recognition by RIG-I, a cytoplasmic innate immunity receptor
Abstract
Cytoplasmic RNA receptors are important in the detection of and response to viral infections. We analyzed ligand recognition by the retinoic acid-inducible protein I (RIG-I) protein in biochemical assays and in transiently transfected cells and characterized the requirements for both single- and double-stranded RNA agonists for RIG-I activation of signaling. RIG-I mutants such as K270A and T409A/S411A that were defective in signaling with triphosphorylated single-stranded RNAs were perfectly capable of signaling with dsRNAs. Furthermore, phosphorothioated oligodeoxynucleotides were found to antagonize RIG-I signaling. Both agonists and antagonist bind purified RIG-I protein and a truncated RIG-I protein that lacked the signaling domain. The agonists were necessary to activate RIG-I ATPase activity in vitro, whereas antagonist inhibited ATPase activity. Differential scanning fluorometry showed that RIG-I bound to agonists, and antagonists have different denaturation properties, suggesting a difference in protein conformations. Last, single particle reconstruction was used to generate three-dimensional models of the RIG-I dimers in complex with an agonist and an antagonist. The two complexes exhibited dramatically different structures.
Figures


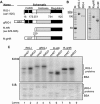
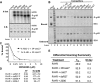
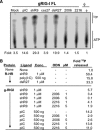

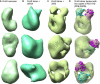
Similar articles
-
Structural basis of RNA recognition and activation by innate immune receptor RIG-I.Nature. 2011 Sep 25;479(7373):423-7. doi: 10.1038/nature10537. Nature. 2011. PMID: 21947008 Free PMC article.
-
Visualizing the determinants of viral RNA recognition by innate immune sensor RIG-I.Structure. 2012 Nov 7;20(11):1983-8. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2012.08.029. Epub 2012 Sep 27. Structure. 2012. PMID: 23022350 Free PMC article.
-
The regulatory domain of the RIG-I family ATPase LGP2 senses double-stranded RNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Apr;37(6):2014-25. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp059. Epub 2009 Feb 10. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 19208642 Free PMC article.
-
Approaching the RNA ligand for RIG-I?Immunol Rev. 2009 Jan;227(1):66-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00724.x. Immunol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19120476 Review.
-
Activation and regulation of pathogen sensor RIG-I.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014 Oct;25(5):513-23. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2014.08.005. Epub 2014 Aug 23. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014. PMID: 25212896 Review.
Cited by
-
Functional characterizations of RIG-I to GCRV and viral/bacterial PAMPs in grass carp Ctenopharyngodon idella.PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e42182. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042182. Epub 2012 Jul 31. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22860079 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis C virus nonstructural protein 5A: biochemical characterization of a novel structural class of RNA-binding proteins.J Virol. 2010 Dec;84(24):12480-91. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01319-10. Epub 2010 Oct 6. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20926572 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of chemical modification on the potency, serum stability, and immunostimulatory properties of short shRNAs.RNA. 2010 Jan;16(1):118-30. doi: 10.1261/rna.1901810. Epub 2009 Nov 30. RNA. 2010. PMID: 19948766 Free PMC article.
-
The RIG-I-like receptor LGP2 recognizes the termini of double-stranded RNA.J Biol Chem. 2009 May 15;284(20):13881-13891. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M900818200. Epub 2009 Mar 11. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19278996 Free PMC article.
-
Norovirus RNA synthesis is modulated by an interaction between the viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase and the major capsid protein, VP1.J Virol. 2012 Sep;86(18):10138-49. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01208-12. Epub 2012 Jul 11. J Virol. 2012. Retraction in: J Virol. 2017 Nov 30;91(24):e01708-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01708-17. PMID: 22787222 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- Akira, S., Uematsu, S., and Takeuchi, O. (2006) Cell 124 783-801 - PubMed
-
- Gaspari, A. A. (2006) J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 54 Suppl. 2, 67-80 - PubMed
-
- Kobayashi, T., Takaesu, G., and Yoshimura, A. (2006) Nat. Immunol. 7 123-124 - PubMed
-
- Underhill, D. M. (2004) Curr. Opin. Immunol. 16 483-487 - PubMed
-
- Yoneyama, M., Kikuchi, M., Natsukawa, T., Shinobu, N., Imaizumi, T., Miyagishi, M., Taira, K., Akira, S., and Fujita, T. (2004) Nat. Immunol. 5 730-737 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

