The antioxidant defense system Keap1-Nrf2 comprises a multiple sensing mechanism for responding to a wide range of chemical compounds
- PMID: 19001094
- PMCID: PMC2612520
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01080-08
The antioxidant defense system Keap1-Nrf2 comprises a multiple sensing mechanism for responding to a wide range of chemical compounds
Abstract
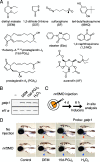
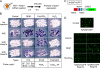
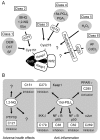
Animals have evolved defense systems for surviving in a chemically diverse environment. Such systems should demonstrate plasticity, such as adaptive immunity, enabling a response to even unknown chemicals. The antioxidant transcription factor Nrf2 is activated in response to various electrophiles and induces cytoprotective enzymes that detoxify them. We report here the discovery of a multiple sensing mechanism for Nrf2 activation using zebrafish and 11 Nrf2-activating compounds. First, we showed that six of the compounds tested specifically target Cys-151 in Keap1, the ubiquitin ligase for Nrf2, while two compounds target Cys-273. Second, in addition to Nrf2 and Keap1, a third factor was deemed necessary for responding to three of the compounds. Finally, we isolated a zebrafish mutant defective in its response to seven compounds but not in response to the remaining four. These results led us to categorize Nrf2 activators into six classes and hypothesize that multiple sensing allows enhanced plasticity in the system.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Nitro-fatty acids and cyclopentenone prostaglandins share strategies to activate the Keap1-Nrf2 system: a study using green fluorescent protein transgenic zebrafish.Genes Cells. 2011 Jan;16(1):46-57. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2443.2010.01466.x. Epub 2010 Dec 9. Genes Cells. 2011. PMID: 21143560 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of compounds that inhibit the binding of Keap1a/Keap1b Kelch DGR domain with Nrf2 ETGE/DLG motifs in zebrafish.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2019 Sep;125(3):259-270. doi: 10.1111/bcpt.13222. Epub 2019 Apr 15. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 30861618
-
Cellular mechanisms of redox cell signalling: role of cysteine modification in controlling antioxidant defences in response to electrophilic lipid oxidation products.Biochem J. 2004 Mar 1;378(Pt 2):373-82. doi: 10.1042/BJ20031049. Biochem J. 2004. PMID: 14616092 Free PMC article.
-
Nrf2 and Nrf2-related proteins in development and developmental toxicity: Insights from studies in zebrafish (Danio rerio).Free Radic Biol Med. 2015 Nov;88(Pt B):275-289. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.06.022. Epub 2015 Jun 28. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015. PMID: 26130508 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanism activating Nrf2-Keap1 pathway in regulation of adaptive response to electrophiles.Free Radic Biol Med. 2004 May 15;36(10):1208-13. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2004.02.075. Free Radic Biol Med. 2004. PMID: 15110385 Review.
Cited by
-
Oxidative Stress in Cataract Formation: Is There a Treatment Approach on the Horizon?Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Oct 16;13(10):1249. doi: 10.3390/antiox13101249. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39456502 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of activation of the transcription factor Nrf2 by redox stressors, nutrient cues, and energy status and the pathways through which it attenuates degenerative disease.Free Radic Biol Med. 2015 Nov;88(Pt B):108-146. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.06.021. Epub 2015 Jun 27. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015. PMID: 26122708 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glutathione redox dynamics and expression of glutathione-related genes in the developing embryo.Free Radic Biol Med. 2013 Dec;65:89-101. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.06.011. Epub 2013 Jun 13. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013. PMID: 23770340 Free PMC article.
-
KEAP1, a cysteine-based sensor and a drug target for the prevention and treatment of chronic disease.Open Biol. 2020 Jun;10(6):200105. doi: 10.1098/rsob.200105. Epub 2020 Jun 24. Open Biol. 2020. PMID: 32574549 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lactobacilli Modulate Epithelial Cytoprotection through the Nrf2 Pathway.Cell Rep. 2015 Aug 25;12(8):1217-25. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.07.042. Epub 2015 Aug 13. Cell Rep. 2015. PMID: 26279578 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cernuda-Morollón, E., E. Pineda-Molina, F. J. Cañada, and D. Pérez-Sala. 2001. 15-Deoxy-Δ12,14-prostaglandin J2 inhibition of NF-κB-DNA binding through covalent modification of the p50 subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 27635530-35536. - PubMed
-
- Dinkova-Kostova, A. T., W. D. Holtzclaw, R. N. Cole, K. Itoh, N. Wakabayashi, Y. Katoh, M. Yamamoto, and P. Talalay. 2002. Direct evidence that sulfhydryl groups of Keap1 are the sensors regulating induction of phase 2 enzymes that protect against carcinogens and oxidants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 9911908-11913. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Driever, W., L. Solnica-Krezel, A. F. Schier, S. C. Neuhauss, J. Malicki, D. L. Stemple, D. Y. Stainier, F. Zwartkruis, S. Abdelilah, Z. Rangini, J. Belak, and C. Boggs. 1996. A genetic screen for mutations affecting embryogenesis in zebrafish. Development 12337-46. - PubMed
-
- Eggler, A. L., Y. Luo, R. B. van Breemen, and A. D. Mesecar. 2007. Identification of the highly reactive cysteine 151 in the chemopreventive agent-sensor Keap1 protein is method-dependent. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 20:1878-1884. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
