Enhanced immune stimulation by a therapeutic lymphoma tumor antigen vaccine produced in insect cells involves mannose receptor targeting to antigen presenting cells
- PMID: 19000731
- PMCID: PMC2683685
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2008.10.055
Enhanced immune stimulation by a therapeutic lymphoma tumor antigen vaccine produced in insect cells involves mannose receptor targeting to antigen presenting cells
Abstract
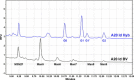
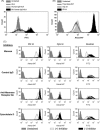
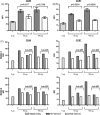
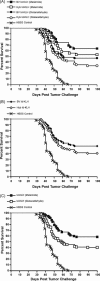
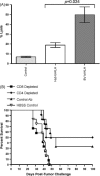
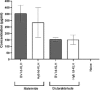
Therapeutic vaccination of lymphoma patients with tumor-specific immunoglobulin (idiotype, Id) coupled to the carrier protein keyhole limpet hemocyanin (Id-KLH) is undergoing clinical investigation, and methods to improve the immunogenicity of these and other protein tumor antigen vaccines are being sought. Id proteins can be produced via tumor-myeloma hybridomas or recombinant methods in mammalian, bacteria, or insect cells. We now demonstrate that terminal mannose residues, characteristic of recombinant proteins produced in insect cells, yield Id proteins with significantly enhanced immunostimulatory properties compared to Id proteins derived from mammalian cells. Recombinant baculovirus-infected insect cell-derived Id showed higher binding to and activation of human dendritic cells mediated by mannose receptors. In vivo, insect cell-derived Id elicited higher levels of tumor-specific CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) and improved eradication of pre-established murine lymphoma. Insect cell and mammalian Id generated similar levels of tumor-specific antibodies, showing no impairment in antibody responses to native tumor antigen despite the glycoslylation differences in the immunogen. Combining insect cell production and maleimide-based KLH conjugation offered the highest levels of anti-tumor immunity. Our data comparing sources of recombinant Id protein tumor antigens used in therapeutic cancer vaccines demonstrate that insect cell-derived antigens can offer several immunologic advantages over proteins derived from mammalian sources.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sulfhydryl-based tumor antigen-carrier protein conjugates stimulate superior antitumor immunity against B cell lymphomas.J Immunol. 2008 Sep 15;181(6):4131-40. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.6.4131. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18768870
-
Linkage of foreign carrier protein to a self-tumor antigen enhances the immunogenicity of a pulsed dendritic cell vaccine.J Immunol. 2000 May 1;164(9):4797-803. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.164.9.4797. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10779787
-
Tumor cell lysate-pulsed dendritic cells are more effective than TCR Id protein vaccines for active immunotherapy of T cell lymphoma.J Immunol. 2002 Nov 1;169(9):5227-35. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.9.5227. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12391241
-
Idiotypic vaccination for B-cell malignancies as a model for therapeutic cancer vaccines: from prototype protein to second generation vaccines.Haematologica. 2002 Sep;87(9):989-1001. Haematologica. 2002. PMID: 12217812 Review.
-
Translational development of active immunotherapy for hematologic malignancies.Semin Oncol. 2003 Jun;30(3 Suppl 8):17-22. doi: 10.1016/s0093-7754(03)00232-x. Semin Oncol. 2003. PMID: 12881808 Review.
Cited by
-
Designing the optimal vaccine: the importance of cytokines and dendritic cells.Open Vaccine J. 2010;3:7-17. doi: 10.2174/1875035401003010007. Open Vaccine J. 2010. PMID: 21822455 Free PMC article.
-
Convergent chemo-enzymatic synthesis of mannosylated glycopeptides; targeting of putative vaccine candidates to antigen presenting cells.Chem Sci. 2015 Aug 1;6(8):4636-4642. doi: 10.1039/c5sc00952a. Epub 2015 May 19. Chem Sci. 2015. PMID: 28717478 Free PMC article.
-
1-MT enhances potency of tumor cell lysate-pulsed dendritic cells against pancreatic adenocarcinoma by downregulating the percentage of Tregs.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2010 Jun;30(3):344-8. doi: 10.1007/s11596-010-0354-3. Epub 2010 Jun 17. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2010. PMID: 20556579
-
Producing recombinant therapeutic glycoproteins with enhanced sialylation using CHO-gmt4 glycosylation mutant cells.Bioengineered. 2014 Jul-Aug;5(4):269–73. doi: 10.4161/bioe.29490. Epub 2014 Jun 9. Bioengineered. 2014. PMID: 24911584 Free PMC article.
-
The specialized roles of immature and mature dendritic cells in antigen cross-presentation.Immunol Res. 2012 Sep;53(1-3):91-107. doi: 10.1007/s12026-012-8300-z. Immunol Res. 2012. PMID: 22450675 Review.
References
-
- Timmerman J.M. Therapeutic idiotype vaccines for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Adv Pharmacol (San Diego, Calif) 2004;51:271–293. - PubMed
-
- Rosenberg S.A. Progress in human tumour immunology and immunotherapy. Nature. 2001;411(May(6835)):380–384. - PubMed
-
- Timmerman J.M., Levy R.L. The history of the development of vaccines for lymphoma. Clin Lymph. 2000;1:129–139. - PubMed
-
- Kwak L.W., Campbell M.J., Czerwinski D.K., Hart S., Miller R.A., Levy R. Induction of immune responses in patients with B-cell lymphoma against the surface-immunoglobulin idiotype expressed by their tumors. N Engl J Med. 1992;327(17):1209–1215. - PubMed
-
- Hsu F.J., Caspar C.B., Czerwinski D., Kwak L.W., Liles T.M., Syrengelas A. Tumor-specific idiotype vaccines in the treatment of patients with B-cell lymphoma—long-term results of a clinical trial. Blood. 1997;89(9):3129–3135. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

