Sunlight triggers cutaneous lupus through a CSF-1-dependent mechanism in MRL-Fas(lpr) mice
- PMID: 18981160
- PMCID: PMC2607048
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.10.7367
Sunlight triggers cutaneous lupus through a CSF-1-dependent mechanism in MRL-Fas(lpr) mice
Abstract
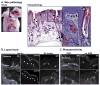
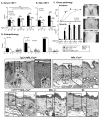
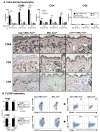
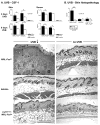
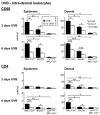
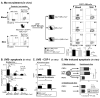
Sunlight (UVB) triggers cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CLE) and systemic lupus through an unknown mechanism. We tested the hypothesis that UVB triggers CLE through a CSF-1-dependent, macrophage (Mø)-mediated mechanism in MRL-Fas(lpr) mice. By constructing mutant MRL-Fas(lpr) strains expressing varying levels of CSF-1 (high, intermediate, none), and use of an ex vivo gene transfer to deliver CSF-1 intradermally, we determined that CSF-1 induces CLE in lupus-susceptible MRL-Fas(lpr) mice, but not in lupus-resistant BALB/c mice. UVB incites an increase in Møs, apoptosis in the skin, and CLE in MRL-Fas(lpr), but not in CSF-1-deficient MRL-Fas(lpr) mice. Furthermore, UVB did not induce CLE in BALB/c mice. Probing further, UVB stimulates CSF-1 expression by keratinocytes leading to recruitment and activation of Møs that, in turn, release mediators, which induce apoptosis in keratinocytes. Thus, sunlight triggers a CSF-1-dependent, Mø-mediated destructive inflammation in the skin leading to CLE in lupus-susceptible MRL-Fas(lpr) but not lupus-resistant BALB/c mice. Taken together, CSF-1 is envisioned as the match and lupus susceptibility as the tinder leading to CLE.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Aberrant macrophages mediate defective kidney repair that triggers nephritis in lupus-susceptible mice.J Immunol. 2012 May 1;188(9):4568-80. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1102154. Epub 2012 Mar 30. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22467656 Free PMC article.
-
Negative role of colony-stimulating factor-1 in macrophage, T cell, and B cell mediated autoimmune disease in MRL-Fas(lpr) mice.J Immunol. 2004 Oct 1;173(7):4744-54. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.173.7.4744. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15383612
-
IFN-gamma limits macrophage expansion in MRL-Fas(lpr) autoimmune interstitial nephritis: a negative regulatory pathway.J Immunol. 1998 Apr 15;160(8):4074-81. J Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9558118
-
Murine models of cutaneous involvement in lupus erythematosus.Autoimmun Rev. 2009 May;8(6):484-7. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2009.02.028. Epub 2009 Feb 23. Autoimmun Rev. 2009. PMID: 19239927 Review.
-
The central and multiple roles of B cells in lupus pathogenesis.Immunol Rev. 1999 Jun;169:107-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1999.tb01310.x. Immunol Rev. 1999. PMID: 10450512 Review.
Cited by
-
Epidermal injury promotes nephritis flare in lupus-prone mice.J Autoimmun. 2015 Dec;65:38-48. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2015.08.005. Epub 2015 Aug 21. J Autoimmun. 2015. PMID: 26305061 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal α6β4 integrin stimulates the influx of immunosuppressive cells during skin tumor promotion.J Dermatol Sci. 2012 May;66(2):108-18. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2012.02.009. Epub 2012 Feb 27. J Dermatol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22464766 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Involvement of Heme Oxygenase-1 Expression in Discoid Lupus Erythematosus Lesions.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Jun 27;12(7):1352. doi: 10.3390/antiox12071352. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37507892 Free PMC article.
-
The interferon-rich skin environment regulates Langerhans cell ADAM17 to promote photosensitivity in lupus.Elife. 2024 Jun 11;13:e85914. doi: 10.7554/eLife.85914. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38860651 Free PMC article.
-
Lymphocytes Change Their Phenotype and Function in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Lupus Nephritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 10;25(20):10905. doi: 10.3390/ijms252010905. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456692 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lin JH, Dutz JP, Sontheimer RD, Werth VP. Pathophysiology of cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2007;33:85–106. - PubMed
-
- Furukawa F, Yoshimasu T. Animal models of spontaneous and drug-induced cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Autoimmun Rev. 2005;4:345–350. - PubMed
-
- Werth VP. Cutaneous lupus: insights into pathogenesis and disease classification. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2007;65:200–204. - PubMed
-
- Synkowski DR, Provost TT. Characterization of the inflammatory infiltrate in lupus erythematosus lesions using monoclonal antibodies. J Rheumatol. 1983;10:920–924. - PubMed
-
- Kanauchi H, Furukawa F, Imamura S. Characterization of cutaneous infiltrates in MRL/lpr mice monitored from onset to the full development of lupus erythematosus-like skin lesions. J Invest Dermatol. 1991;96:478–483. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

