Excitatory local connections of superficial neurons in rat auditory cortex
- PMID: 18971460
- PMCID: PMC2610470
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2093-08.2008
Excitatory local connections of superficial neurons in rat auditory cortex
Abstract
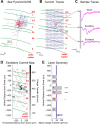
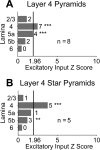
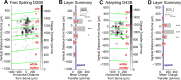
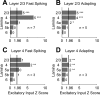
The mammalian cerebral cortex consists of multiple areas specialized for processing information for many different sensory modalities. Although the basic structure is similar for each cortical area, specialized neural connections likely mediate unique information processing requirements. Relative to primary visual (V1) and somatosensory (S1) cortices, little is known about the intrinsic connectivity of primary auditory cortex (A1). To better understand the flow of information from the thalamus to and through rat A1, we made use of a rapid, high-throughput screening method exploiting laser-induced uncaging of glutamate to construct excitatory input maps of individual neurons. We found that excitatory inputs to layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons were similar to those in V1 and S1; these cells received strong excitation primarily from layers 2-4. Both anatomical and physiological observations, however, indicate that inputs and outputs of layer 4 excitatory neurons in A1 contrast with those in V1 and S1. Layer 2/3 pyramids in A1 have substantial axonal arbors in layer 4, and photostimulation demonstrates that these pyramids can connect to layer 4 excitatory neurons. Furthermore, most or all of these layer 4 excitatory neurons project out of the local cortical circuit. Unlike S1 and V1, where feedback to layer 4 is mediated exclusively by indirect local circuits involving layer 2/3 projections to deep layers and deep feedback to layer 4, layer 4 of A1 integrates thalamic and strong layer 4 recurrent excitatory input with relatively direct feedback from layer 2/3 and provides direct cortical output.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Possible anatomical pathways for short-latency multisensory integration processes in primary sensory cortices.Brain Struct Funct. 2015 Mar;220(2):955-77. doi: 10.1007/s00429-013-0694-4. Epub 2014 Jan 3. Brain Struct Funct. 2015. PMID: 24384580
-
Indirect pathway between the primary auditory and visual cortices through layer V pyramidal neurons in V2L in mouse and the effects of bilateral enucleation.Eur J Neurosci. 2011 Jul;34(1):65-78. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2011.07732.x. Epub 2011 Jun 16. Eur J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21676038
-
Layer-specific input to distinct cell types in layer 6 of monkey primary visual cortex.J Neurosci. 2001 May 15;21(10):3600-8. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-10-03600.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11331389 Free PMC article.
-
Cell type specificity of local cortical connections.J Neurocytol. 2002 Mar-Jun;31(3-5):231-7. doi: 10.1023/a:1024165824469. J Neurocytol. 2002. PMID: 12815242 Review.
-
Local connections of excitatory neurons in motor-associated cortical areas of the rat.Front Neural Circuits. 2013 May 28;7:75. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2013.00075. eCollection 2013. Front Neural Circuits. 2013. PMID: 23754982 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A role for silent synapses in the development of the pathway from layer 2/3 to 5 pyramidal cells in the neocortex.J Neurosci. 2012 Sep 19;32(38):13085-99. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1262-12.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22993426 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Receptive Field Properties of Parvalbumin and Somatostatin Inhibitory Neurons in Mouse Auditory Cortex.Cereb Cortex. 2015 Jul;25(7):1782-91. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bht417. Epub 2014 Jan 14. Cereb Cortex. 2015. PMID: 24425250 Free PMC article.
-
Parallel processing strategies of the primate visual system.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2009 May;10(5):360-72. doi: 10.1038/nrn2619. Epub 2009 Apr 8. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19352403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Top-down beta rhythms support selective attention via interlaminar interaction: a model.PLoS Comput Biol. 2013;9(8):e1003164. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003164. Epub 2013 Aug 8. PLoS Comput Biol. 2013. PMID: 23950699 Free PMC article.
-
A feedforward inhibitory circuit mediates lateral refinement of sensory representation in upper layer 2/3 of mouse primary auditory cortex.J Neurosci. 2014 Oct 8;34(41):13670-83. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1516-14.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25297094 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Atzori M, Lei S, Evans DI, Kanold PO, Phillips-Tansey E, McIntyre O, McBain CJ. Differential synaptic processing separates stationary from transient inputs to the auditory cortex. Nat Neurosci. 2001;4:1230–1237. - PubMed
-
- Barbour DL, Callaway EM. Excitatory connections in superficial rat primary auditory cortex. Soc Neurosci Abs. 2004;30:987–12.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
