Targeted screening of cis-regulatory variation in human haplotypes
- PMID: 18971308
- PMCID: PMC2612965
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.084798.108
Targeted screening of cis-regulatory variation in human haplotypes
Abstract
Regulatory cis-acting variants account for a large proportion of gene expression variability in populations. Cis-acting differences can be specifically measured by comparing relative levels of allelic transcripts within a sample. Allelic expression (AE) mapping for cis-regulatory variant discovery has been hindered by the requirements of having informative or heterozygous single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) within genes in order to assign the allelic origin of each transcript. In this study we have developed an approach to systematically screen for heritable cis-variants in common human haplotypes across >1,000 genes. In order to achieve the highest level of information per haplotype studied, we carried out allelic expression measurements by using both intronic and exonic SNPs in primary transcripts. We used a novel RNA pooling strategy in immortalized lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCLs) and primary human osteoblast cell lines (HObs) to allow for high-throughput AE. Screening hits from RNA pools were further validated by performing allelic expression mapping in individual samples. Our results indicate that >10% of expressed genes in human LCLs show genotype-linked AE. In addition, we have validated cis-acting variants in over 20 genes linked with common disease susceptibility in recent genome-wide studies. More generally, our results indicate that RNA pooling coupled with AE read-out by second generation sequencing or by other methods provides a high-throughput tool for cataloging the impact of common noncoding variants in the human genome.
Figures

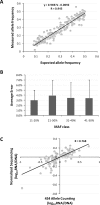
Similar articles
-
Mapping common regulatory variants to human haplotypes.Hum Mol Genet. 2005 Dec 15;14(24):3963-71. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddi420. Epub 2005 Nov 21. Hum Mol Genet. 2005. PMID: 16301213
-
A survey of genetic and epigenetic variation affecting human gene expression.Physiol Genomics. 2004 Jan 15;16(2):184-93. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00163.2003. Physiol Genomics. 2004. PMID: 14583597
-
Allele-specific transcript quantification detects haplotypic variation in the levels of the SDF-1 transcripts.Hum Mol Genet. 2005 Jun 15;14(12):1579-85. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddi166. Epub 2005 Apr 20. Hum Mol Genet. 2005. PMID: 15843397
-
Cis-acting regulatory variation in the human genome.Science. 2004 Oct 22;306(5696):647-50. doi: 10.1126/science.1101659. Science. 2004. PMID: 15499010 Review.
-
Influence of human genome polymorphism on gene expression.Hum Mol Genet. 2006 Apr 15;15 Spec No 1:R9-16. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddl044. Hum Mol Genet. 2006. PMID: 16651375 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide association reveals genetic effects on human Aβ42 and τ protein levels in cerebrospinal fluids: a case control study.BMC Neurol. 2010 Oct 8;10:90. doi: 10.1186/1471-2377-10-90. BMC Neurol. 2010. PMID: 20932310 Free PMC article.
-
Next-generation DNA sequencing-based assay for measuring allelic expression imbalance (AEI) of candidate neuropsychiatric disorder genes in human brain.BMC Genomics. 2011 Oct 20;12:518. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-518. BMC Genomics. 2011. PMID: 22013986 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the genetics of Bti resistance using mRNA tag sequencing: application on laboratory strains and natural populations of the dengue vector Aedes aegypti.Evol Appl. 2013 Nov;6(7):1012-27. doi: 10.1111/eva.12082. Epub 2013 Aug 31. Evol Appl. 2013. PMID: 24187584 Free PMC article.
-
Ethnic-specific associations of rare and low-frequency DNA sequence variants with asthma.Nat Commun. 2015 Jan 16;6:5965. doi: 10.1038/ncomms6965. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 25591454 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding mechanisms underlying human gene expression variation with RNA sequencing.Nature. 2010 Apr 1;464(7289):768-72. doi: 10.1038/nature08872. Epub 2010 Mar 10. Nature. 2010. PMID: 20220758 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bouatia-Naji N., Rocheleau G., Van Lommel L., Lemaire K., Schuit F., Cavalcanti-Proenca C., Marchand M., Hartikainen A.L., Sovio U., De Graeve F., et al. A polymorphism within the G6PC2 gene is associated with fasting plasma glucose levels. Science. 2008;320:1085–1088. - PubMed
-
- Bray N.J., Buckland P.R., Owen M.J., O'Donovan M.C. Cis-acting variation in the expression of a high proportion of genes in human brain. Hum. Genet. 2003;113:149–153. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
