Epac and phospholipase Cepsilon regulate Ca2+ release in the heart by activation of protein kinase Cepsilon and calcium-calmodulin kinase II
- PMID: 18957419
- PMCID: PMC2615515
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M806994200
Epac and phospholipase Cepsilon regulate Ca2+ release in the heart by activation of protein kinase Cepsilon and calcium-calmodulin kinase II
Abstract
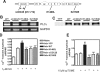
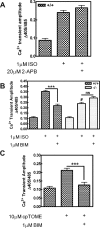
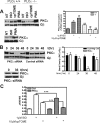
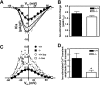
Recently, we identified a novel signaling pathway involving Epac, Rap, and phospholipase C (PLC)epsilon that plays a critical role in maximal beta-adrenergic receptor (betaAR) stimulation of Ca2+-induced Ca2+ release (CICR) in cardiac myocytes. Here we demonstrate that PLCepsilon phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate hydrolytic activity and PLCepsilon-stimulated Rap1 GEF activity are both required for PLCepsilon-mediated enhancement of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ release and that PLCepsilon significantly enhances Rap activation in response to betaAR stimulation in the heart. Downstream of PLCepsilon hydrolytic activity, pharmacological inhibition of PKC significantly inhibited both betaAR- and Epac-stimulated increases in CICR in PLCepsilon+/+ myocytes but had no effect in PLCepsilon-/- myocytes. betaAR and Epac activation caused membrane translocation of PKCepsilon in PLCepsilon+/+ but not PLCepsilon-/- myocytes and small interfering RNA-mediated PKCepsilon knockdown significantly inhibited both betaAR and Epac-mediated CICR enhancement. Further downstream, the Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CamKII) inhibitor, KN93, inhibited betaAR- and Epac-mediated CICR in PLCepsilon+/+ but not PLCepsilon-/- myocytes. Epac activation increased CamKII Thr286 phosphorylation and enhanced phosphorylation at CamKII phosphorylation sites on the ryanodine receptor (RyR2) (Ser2815) and phospholamban (Thr17) in a PKC-dependent manner. Perforated patch clamp experiments revealed that basal and betaAR-stimulated peak L-type current density are similar in PLCepsilon+/+ and PLCepsilon-/- myocytes suggesting that control of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ release, rather than Ca2+ influx through L-type Ca2+ channels, is the target of regulation of a novel signal transduction pathway involving sequential activation of Epac, PLCepsilon, PKCepsilon, and CamKII downstream of betaAR activation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Epac-mediated activation of phospholipase C(epsilon) plays a critical role in beta-adrenergic receptor-dependent enhancement of Ca2+ mobilization in cardiac myocytes.J Biol Chem. 2007 Feb 23;282(8):5488-95. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M608495200. Epub 2006 Dec 17. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17178726
-
Calcium-calmodulin kinase II mediates digitalis-induced arrhythmias.Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2011 Dec;4(6):947-57. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.111.964908. Epub 2011 Oct 18. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2011. PMID: 22009705
-
The cAMP binding protein Epac modulates Ca2+ sparks by a Ca2+/calmodulin kinase signalling pathway in rat cardiac myocytes.J Physiol. 2007 Sep 1;583(Pt 2):685-94. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.133066. Epub 2007 Jun 28. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17599964 Free PMC article.
-
Epac in cardiac calcium signaling.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2013 May;58:162-71. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2012.11.021. Epub 2012 Dec 7. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23220153 Review.
-
Cardiac ryanodine receptor phosphorylation by CaM Kinase II: keeping the balance right.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2009 Jun 1;14(13):5134-56. doi: 10.2741/3591. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2009. PMID: 19482609 Review.
Cited by
-
cAMP and mitochondria.Physiology (Bethesda). 2013 May;28(3):199-209. doi: 10.1152/physiol.00004.2013. Physiology (Bethesda). 2013. PMID: 23636265 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NAADP)-mediated calcium signaling and arrhythmias in the heart evoked by β-adrenergic stimulation.J Biol Chem. 2013 May 31;288(22):16017-30. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.441246. Epub 2013 Apr 5. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23564460 Free PMC article.
-
Functional and structural characterization of allosteric activation of phospholipase Cε by Rap1A.J Biol Chem. 2020 Dec 4;295(49):16562-16571. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.015685. Epub 2020 Sep 18. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32948655 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol ameliorates aging-related metabolic phenotypes by inhibiting cAMP phosphodiesterases.Cell. 2012 Feb 3;148(3):421-33. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.01.017. Cell. 2012. PMID: 22304913 Free PMC article.
-
Calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II: linking heart failure and arrhythmias.Circ Res. 2012 Jun 8;110(12):1661-77. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.243956. Circ Res. 2012. PMID: 22679140 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jin, T. G., Satoh, T., Liao, Y., Song, C., Gao, X., Kariya, K., Hu, C. D., and Kataoka, T. (2001) J. Biol. Chem. 276 30301–30307 - PubMed
-
- Lopez, I., Mak, E. C., Ding, J., Hamm, H. E., and Lomasney, J. W. (2001) J. Biol. Chem. 276 2758–2765 - PubMed
-
- Shibatohge, M., Kariya, K., Liao, Y., Hu, C. D., Watari, Y., Goshima, M., Shima, F., and Kataoka, T. (1998) J. Biol. Chem. 273 6218–6222 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

