Structure-based design, synthesis, evaluation, and crystallographic studies of conformationally constrained Smac mimetics as inhibitors of the X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP)
- PMID: 18954041
- PMCID: PMC2688463
- DOI: 10.1021/jm8006849
Structure-based design, synthesis, evaluation, and crystallographic studies of conformationally constrained Smac mimetics as inhibitors of the X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP)
Abstract
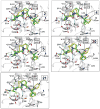
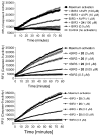
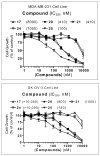
Small molecules designed to mimic the binding of Smac protein to X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP) are being pursued as a promising new class of anticancer drugs. Herein, we report the design, synthesis, and comprehensive structure-activity relationship studies of a series of conformationally constrained bicyclic Smac mimetics. Our studies led to the discovery of a number of highly potent and cell-permeable Smac mimetics and yielded important new insights into their structure-activity relationship for their binding to XIAP and for their activity in inhibition of cancer cell growth. Determination of the crystal structure of one potent Smac mimetic, compound 21, in complex with XIAP BIR3 provides the structural basis for its high-affinity binding to XIAP and for the design of highly potent Smac mimetics.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Design, synthesis, and characterization of a potent, nonpeptide, cell-permeable, bivalent Smac mimetic that concurrently targets both the BIR2 and BIR3 domains in XIAP.J Am Chem Soc. 2007 Dec 12;129(49):15279-94. doi: 10.1021/ja074725f. Epub 2007 Nov 14. J Am Chem Soc. 2007. PMID: 17999504 Free PMC article.
-
Rational design, synthesis and characterization of potent, non-peptidic Smac mimics/XIAP inhibitors as proapoptotic agents for cancer therapy.Bioorg Med Chem. 2009 Aug 15;17(16):5834-56. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2009.07.009. Epub 2009 Jul 10. Bioorg Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 19620011
-
Structure-activity based study of the Smac-binding pocket within the BIR3 domain of XIAP.Bioorg Med Chem. 2007 Apr 15;15(8):2935-43. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2007.02.010. Epub 2007 Feb 11. Bioorg Med Chem. 2007. PMID: 17336535
-
Small-molecule SMAC mimetics as new cancer therapeutics.Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Oct;144(1):82-95. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2014.05.007. Epub 2014 May 16. Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24841289 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bivalent SMAC Mimetics for Treating Cancer by Antagonizing Inhibitor of Apoptosis Proteins.ChemMedChem. 2019 Dec 4;14(23):1951-1962. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201900410. Epub 2019 Nov 19. ChemMedChem. 2019. PMID: 31692274 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms of drug sensitization to TRA-8, an agonistic death receptor 5 antibody, involve modulation of the intrinsic apoptotic pathway in human breast cancer cells.Mol Cancer Res. 2011 Apr;9(4):403-17. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-10-0133. Epub 2011 Feb 25. Mol Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21357440 Free PMC article.
-
X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein - a critical death resistance regulator and therapeutic target for personalized cancer therapy.Front Oncol. 2014 Jul 28;4:197. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2014.00197. eCollection 2014. Front Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25120954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design of novel potent selective survivin inhibitors using 2D-QSAR modeling, molecular docking, molecular dynamics, and ADMET properties of new MX-106 hydroxyquinoline scaffold derivatives.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 26;10(19):e38383. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38383. eCollection 2024 Oct 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39397921 Free PMC article.
-
XIAP as a Target of New Small Organic Natural Molecules Inducing Human Cancer Cell Death.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Sep 9;11(9):1336. doi: 10.3390/cancers11091336. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31505859 Free PMC article.
-
Current Computational Methods for Protein-peptide Complex Structure Prediction.Curr Med Chem. 2024;31(26):4058-4078. doi: 10.2174/0109298673263447230920151524. Curr Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 37888817 Review.
References
-
- Thompson CB. Apoptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of disease. Science. 1995;267:1456–1462. - PubMed
-
- Nicholson DW. From bench to clinic with apoptosis-based therapeutic agents. Nature. 2000;407:810–816. - PubMed
-
- Reed JC. Apoptosis-based therapies. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2002;1:111–121. - PubMed
-
- Deveraux QL, Reed JC. IAP family proteins--suppressors of apoptosis. Genes Dev. 1999;1:239–252. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information

