Formation of nucleoprotein filaments by mammalian DNA methyltransferase Dnmt3a in complex with regulator Dnmt3L
- PMID: 18945701
- PMCID: PMC2588524
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkn747
Formation of nucleoprotein filaments by mammalian DNA methyltransferase Dnmt3a in complex with regulator Dnmt3L
Abstract
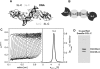
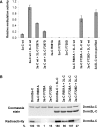
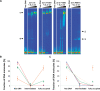
The C-terminal domains of Dnmt3a and Dnmt3L form elongated heterotetramers (3L-3a-3a-3L). Analytical ultracentrifugation confirmed the Dnmt3a-C/3L-C complex exists as a 2:2 heterotetramer in solution. The 3a-3a interface is the DNA-binding site, while both interfaces are essential for AdoMet binding and catalytic activity. Hairpin bisulfite analysis shows correlated methylation of two CG sites in a distance of approximately 8-10 bp in the opposite DNA strands, which corresponds to the geometry of the two active sites in one Dnmt3a-C/3L-C tetramer. Correlated methylation was also observed for two CG sites at similar distances in the same DNA strand, which can be attributed to the binding of two tetramers next to each other. DNA-binding experiments show that Dnmt3a-C/3L-C complexes multimerize on the DNA. Scanning force microscopy demonstrates filament formation rather than binding of single tetramers and shows that protein-DNA filament formation leads to a 1.5-fold shortening of the DNA length.
Figures

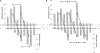
Similar articles
-
Multimerization of the dnmt3a DNA methyltransferase and its functional implications.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2013;117:445-64. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-386931-9.00016-7. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2013. PMID: 23663978 Review.
-
Structure of Dnmt3a bound to Dnmt3L suggests a model for de novo DNA methylation.Nature. 2007 Sep 13;449(7159):248-51. doi: 10.1038/nature06146. Epub 2007 Aug 22. Nature. 2007. PMID: 17713477 Free PMC article.
-
Function and disruption of DNA methyltransferase 3a cooperative DNA binding and nucleoprotein filament formation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Jan;40(2):569-80. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr753. Epub 2011 Sep 16. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 21926161 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted methylation and gene silencing of VEGF-A in human cells by using a designed Dnmt3a-Dnmt3L single-chain fusion protein with increased DNA methylation activity.J Mol Biol. 2013 Feb 8;425(3):479-91. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2012.11.038. Epub 2012 Dec 4. J Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23220192
-
Structure and function of mammalian DNA methyltransferases.Chembiochem. 2011 Jan 24;12(2):206-22. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201000195. Epub 2010 Nov 29. Chembiochem. 2011. PMID: 21243710 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular coupling of DNA methylation and histone methylation.Epigenomics. 2010 Oct;2(5):657-69. doi: 10.2217/epi.10.44. Epigenomics. 2010. PMID: 21339843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The DNMT3A R882H mutation does not cause dominant negative effects in purified mixed DNMT3A/R882H complexes.Sci Rep. 2018 Sep 5;8(1):13242. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-31635-8. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30185810 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin methylation activity of Dnmt3a and Dnmt3a/3L is guided by interaction of the ADD domain with the histone H3 tail.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Jul;38(13):4246-53. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq147. Epub 2010 Mar 11. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20223770 Free PMC article.
-
Mammalian DNA methyltransferases: new discoveries and open questions.Biochem Soc Trans. 2018 Oct 19;46(5):1191-1202. doi: 10.1042/BST20170574. Epub 2018 Aug 28. Biochem Soc Trans. 2018. PMID: 30154093 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dissect the DNMT3A- and DNMT3B-mediated DNA Co-methylation through a Covalent Complex Approach.J Mol Biol. 2020 Jan 17;432(2):569-575. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2019.11.004. Epub 2019 Nov 11. J Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31726062 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jeltsch A. Beyond Watson and Crick: DNA methylation and molecular enzymology of DNA methyltransferases. Chembiochem. 2002;3:274–293. - PubMed
-
- Goll MG, Bestor TH. Eukaryotic cytosine methyltransferases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2005;74:481–514. - PubMed
-
- Hermann A, Gowher H, Jeltsch A. Biochemistry and biology of mammalian DNA methyltransferases. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2004;61:2571–2587. - PubMed
-
- Robertson KD. DNA methylation and human disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2005;6:597–610. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

