A role for the Dicer helicase domain in the processing of thermodynamically unstable hairpin RNAs
- PMID: 18927112
- PMCID: PMC2582626
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkn687
A role for the Dicer helicase domain in the processing of thermodynamically unstable hairpin RNAs
Abstract
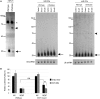
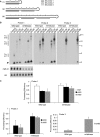
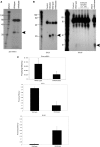
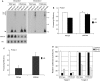
In humans a single species of the RNAseIII enzyme Dicer processes both microRNA precursors into miRNAs and long double-stranded RNAs into small interfering RNAs (siRNAs). An interesting but poorly understood domain of the mammalian Dicer protein is the N-terminal helicase-like domain that possesses a signature DExH motif. Cummins et al. created a human Dicer mutant cell line by inserting an AAV targeting cassette into the helicase domain of both Dicer alleles in HCT116 cells generating an in-frame 43-amino-acid insertion immediately adjacent to the DExH box. This insertion creates a Dicer mutant protein with defects in the processing of most, but not all, endogenous pre-miRNAs into mature miRNA. Using both biochemical and computational approaches, we provide evidence that the Dicer helicase mutant is sensitive to the thermodynamic properties of the stems in microRNAs and short-hairpin RNAs, with thermodynamically unstable stems resulting in poor processing and a reduction in the levels of functional mi/siRNAs. Paradoxically, this mutant exhibits enhanced processing efficiency and concomitant RNA interference when thermodynamically stable, long-hairpin RNAs are used. These results suggest an important function for the Dicer helicase domain in the processing of thermodynamically unstable hairpin structures.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Single processing center models for human Dicer and bacterial RNase III.Cell. 2004 Jul 9;118(1):57-68. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.06.017. Cell. 2004. PMID: 15242644
-
Dicer's helicase domain is required for accumulation of some, but not all, C. elegans endogenous siRNAs.RNA. 2010 May;16(5):893-903. doi: 10.1261/rna.2122010. Epub 2010 Mar 30. RNA. 2010. PMID: 20354150 Free PMC article.
-
Cryo-EM structures of human DICER dicing a pre-miRNA substrate.FEBS J. 2024 Jul;291(14):3072-3079. doi: 10.1111/febs.17048. Epub 2024 Jan 10. FEBS J. 2024. PMID: 38151772 Review.
-
In vivo structure-function analysis of human Dicer reveals directional processing of precursor miRNAs.RNA. 2012 Jun;18(6):1116-22. doi: 10.1261/rna.032680.112. Epub 2012 Apr 30. RNA. 2012. PMID: 22546613 Free PMC article.
-
Production of small RNAs by mammalian Dicer.Pflugers Arch. 2016 Jun;468(6):1089-102. doi: 10.1007/s00424-016-1817-6. Epub 2016 Apr 6. Pflugers Arch. 2016. PMID: 27048428 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of MicroRNA Biogenesis: A miRiad of mechanisms.Cell Commun Signal. 2009 Aug 10;7:18. doi: 10.1186/1478-811X-7-18. Cell Commun Signal. 2009. PMID: 19664273 Free PMC article.
-
Deriving four functional anti-HIV siRNAs from a single Pol III-generated transcript comprising two adjacent long hairpin RNA precursors.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Oct;38(19):6652-63. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq460. Epub 2010 Jun 4. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20525791 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of microRNA biogenesis confers resistance to ER stress-induced cell death upstream of the mitochondrion.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 19;8(8):e73870. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073870. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23977393 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of Add3 impairs the myogenic response of renal afferent arterioles and middle cerebral arteries.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2017 Jun 1;312(6):F971-F981. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00529.2016. Epub 2016 Dec 7. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2017. PMID: 27927653 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms of Dicer: endonuclease and enzymatic activity.Biochem J. 2017 May 4;474(10):1603-1618. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20160759. Biochem J. 2017. PMID: 28473628 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gan J, Tropea JE, Austin BP, Court DL, Waugh DS, Ji X. Structural insight into the mechanism of double-stranded RNA processing by ribonuclease III. Cell. 2006;124:355–366. - PubMed
-
- Gregory RI, Yan KP, Amuthan G, Chendrimada T, Doratotaj B, Cooch N, Shiekhattar R. The Microprocessor complex mediates the genesis of microRNAs. Nature. 2004;432:235–240. - PubMed
-
- MacRae IJ, Doudna JA. Ribonuclease revisited: structural insights into ribonuclease III family enzymes. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2007;17:138–145. - PubMed
-
- Carmell MA, Hannon GJ. RNase III enzymes and the initiation of gene silencing. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2004;11:214–218. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein E, Caudy AA, Hammond SM, Hannon GJ. Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step of RNA interference. Nature. 2001;409:363–366. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

