Regulated release of ERdj3 from unfolded proteins by BiP
- PMID: 18923428
- PMCID: PMC2580786
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2008.207
Regulated release of ERdj3 from unfolded proteins by BiP
Abstract
DnaJ proteins often bind to unfolded substrates and recruit their Hsp70 partners. This induces a conformational change in the Hsp70 that stabilizes its binding to substrate. By some unknown mechanism, the DnaJ protein is released. We examined the requirements for the release of ERdj3, a mammalian ER DnaJ, from substrates and found that BiP promoted the release of ERdj3 only in the presence of ATP. Mutations in ERdj3 or BiP that disrupted their interaction interrupted the release of ERdj3. BiP mutants that were defective in any step of the ATPase cycle were also unable to release ERdj3. These results demonstrate that a functional interaction between ERdj3 and BiP, including both a direct interaction and the ability to stimulate BiP's ATPase activity are required to release ERdj3 from substrate and support a model where ERdj3 must recruit BiP and stimulate its high-affinity association with the substrate through activation of ATP hydrolysis to trigger its own release from substrates. On the basis of similarities among DnaJs and Hsp70s, this is likely to be applicable to other Hsp70-DnaJ pairs.
Figures
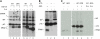
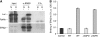
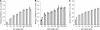
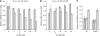
Similar articles
-
ERdj3 regulates BiP occupancy in living cells.J Cell Sci. 2013 Mar 15;126(Pt 6):1429-39. doi: 10.1242/jcs.118182. Epub 2013 Feb 1. J Cell Sci. 2013. PMID: 23378021 Free PMC article.
-
ERdj3, a stress-inducible endoplasmic reticulum DnaJ homologue, serves as a cofactor for BiP's interactions with unfolded substrates.Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Jan;16(1):40-50. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-05-0434. Epub 2004 Nov 3. Mol Biol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15525676 Free PMC article.
-
Dissection of structural and functional requirements that underlie the interaction of ERdj3 protein with substrates in the endoplasmic reticulum.J Biol Chem. 2014 Oct 3;289(40):27504-12. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.587147. Epub 2014 Aug 20. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25143379 Free PMC article.
-
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) chaperone BiP is a master regulator of ER functions: Getting by with a little help from ERdj friends.J Biol Chem. 2019 Feb 8;294(6):2098-2108. doi: 10.1074/jbc.REV118.002804. Epub 2018 Dec 18. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30563838 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BiP and its nucleotide exchange factors Grp170 and Sil1: mechanisms of action and biological functions.J Mol Biol. 2015 Apr 10;427(7):1589-608. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2015.02.011. Epub 2015 Feb 16. J Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25698114 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
J domain independent functions of J proteins.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2016 Jul;21(4):563-70. doi: 10.1007/s12192-016-0697-1. Epub 2016 May 4. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2016. PMID: 27145962 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ERdj3 regulates BiP occupancy in living cells.J Cell Sci. 2013 Mar 15;126(Pt 6):1429-39. doi: 10.1242/jcs.118182. Epub 2013 Feb 1. J Cell Sci. 2013. PMID: 23378021 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing the functional properties of the Hsp70 chaperones, DnaK and BiP.Biophys Chem. 2010 Jun;149(1-2):58-66. doi: 10.1016/j.bpc.2010.04.001. Epub 2010 Apr 10. Biophys Chem. 2010. PMID: 20435400 Free PMC article.
-
Control of the pattern-recognition receptor EFR by an ER protein complex in plant immunity.EMBO J. 2009 Nov 4;28(21):3428-38. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2009.262. Epub 2009 Sep 17. EMBO J. 2009. PMID: 19763086 Free PMC article.
-
The Grp170 nucleotide exchange factor executes a key role during ERAD of cellular misfolded clients.Mol Biol Cell. 2016 May 15;27(10):1650-62. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E16-01-0033. Epub 2016 Mar 30. Mol Biol Cell. 2016. PMID: 27030672 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brightman SE, Blatch GL, Zetter BR (1995) Isolation of a mouse cDNA encoding MTJ1, a new murine member of the DnaJ family of proteins. Gene 153: 249–254 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

