Arx is a direct target of Dlx2 and thereby contributes to the tangential migration of GABAergic interneurons
- PMID: 18923043
- PMCID: PMC3844830
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1283-08.2008
Arx is a direct target of Dlx2 and thereby contributes to the tangential migration of GABAergic interneurons
Abstract
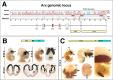
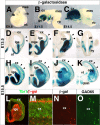
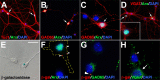
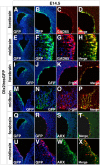
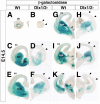
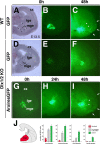
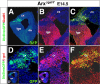
The Arx transcription factor is expressed in the developing ventral telencephalon and subsets of its derivatives. Mutation of human ARX ortholog causes neurological disorders including epilepsy, lissencephaly, and mental retardation. We have isolated the mouse Arx endogenous enhancer modules that control its tightly compartmentalized forebrain expression. Interestingly, they are scattered downstream of its coding region and partially included within the introns of the downstream PolA1 gene. These enhancers are ultraconserved noncoding sequences that are highly conserved throughout the vertebrate phylum. Functional characterization of the Arx GABAergic enhancer element revealed its strict dependence on the activity of Dlx transcription factors. Dlx overexpression induces ectopic expression of endogenous Arx and its isolated enhancer, whereas loss of Dlx expression results in reduced Arx expression, suggesting that Arx is a key mediator of Dlx function. To further elucidate the mechanisms involved, a combination of gain-of-function studies in mutant Arx or Dlx tissues was pursued. This analysis provided evidence that, although Arx is necessary for the Dlx-dependent promotion of interneuron migration, it is not required for the GABAergic cell fate commitment mediated by Dlx factors. Although Arx has additional functions independent of the Dlx pathway, we have established a direct genetic relationship that controls critical steps in the development of telencephalic GABAergic neurons. These findings contribute elucidating the genetic hierarchy that likely underlies the etiology of a variety of human neurodevelopmental disorders.
Figures



Similar articles
-
GABAergic Interneuron Differentiation in the Basal Forebrain Is Mediated through Direct Regulation of Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase Isoforms by Dlx Homeobox Transcription Factors.J Neurosci. 2017 Sep 6;37(36):8816-8829. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2125-16.2017. Epub 2017 Aug 8. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28821666 Free PMC article.
-
The vertebrate ortholog of Aristaless is regulated by Dlx genes in the developing forebrain.J Comp Neurol. 2005 Mar 14;483(3):292-303. doi: 10.1002/cne.20405. J Comp Neurol. 2005. PMID: 15682394
-
Dlx homeobox genes promote cortical interneuron migration from the basal forebrain by direct repression of the semaphorin receptor neuropilin-2.J Biol Chem. 2007 Jun 29;282(26):19071-81. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M607486200. Epub 2007 Jan 26. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17259176
-
[Topics of brain malformation and epilepsy--age-dependent epileptic encephalopathies and interneuronopathies].No To Hattatsu. 2010 Sep;42(5):333-8. No To Hattatsu. 2010. PMID: 20845763 Review. Japanese.
-
A new paradigm for West syndrome based on molecular and cell biology.Epilepsy Res. 2006 Aug;70 Suppl 1:S87-95. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2006.02.008. Epub 2006 Jun 23. Epilepsy Res. 2006. PMID: 16806828 Review.
Cited by
-
Role for TGF-beta superfamily signaling in telencephalic GABAergic neuron development.J Neurodev Disord. 2010 Mar;2(1):48-60. doi: 10.1007/s11689-009-9035-6. Epub 2009 Nov 27. J Neurodev Disord. 2010. PMID: 20339443 Free PMC article.
-
Shh activation restores interneurons and cognitive function in newborns with intraventricular haemorrhage.Brain. 2023 Feb 13;146(2):629-644. doi: 10.1093/brain/awac271. Brain. 2023. PMID: 35867870 Free PMC article.
-
A new mouse model of ARX dup24 recapitulates the patients' behavioral and fine motor alterations.Hum Mol Genet. 2018 Jun 15;27(12):2138-2153. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddy122. Hum Mol Genet. 2018. PMID: 29659809 Free PMC article.
-
Arx expansion mutation perturbs cortical development by augmenting apoptosis without activating innate immunity in a mouse model of X-linked infantile spasms syndrome.Dis Model Mech. 2020 Mar 30;13(3):dmm042515. doi: 10.1242/dmm.042515. Dis Model Mech. 2020. PMID: 32033960 Free PMC article.
-
Prox1 Regulates the Subtype-Specific Development of Caudal Ganglionic Eminence-Derived GABAergic Cortical Interneurons.J Neurosci. 2015 Sep 16;35(37):12869-89. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1164-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26377473 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson SA, Qiu M, Bulfone A, Eisenstat DD, Meneses J, Pedersen R, Rubenstein JL. Mutations of the homeobox genes Dlx-1 and Dlx-2 disrupt the striatal subventricular zone and differentiation of late born striatal neurons. Neuron. 1997a;19:27–37. - PubMed
-
- Anderson SA, Eisenstat DD, Shi L, Rubenstein JL. Interneuron migration from basal forebrain to neocortex: dependence on Dlx genes. Science. 1997b;278:474–476. - PubMed
-
- Anderson SA, Marín O, Horn C, Jennings K, Rubenstein JL. Distinct cortical migrations from the medial and lateral ganglionic eminences. Development. 2001;128:353–363. - PubMed
-
- Banker GA, Cowan WM. Rat hippocampal neurons in dispersed cell culture. Brain Res. 1977;126:397–442. - PubMed
-
- Bejerano G, Pheasant M, Makunin I, Stephen S, Kent WJ, Mattick JS, Haussler D. Ultraconserved elements in the human genome. Science. 2004;304:1321–1325. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
