The Bet v 1 fold: an ancient, versatile scaffold for binding of large, hydrophobic ligands
- PMID: 18922149
- PMCID: PMC2577659
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2148-8-286
The Bet v 1 fold: an ancient, versatile scaffold for binding of large, hydrophobic ligands
Abstract
Background: The major birch pollen allergen, Bet v 1, is a member of the ubiquitous PR-10 family of plant pathogenesis-related proteins. In recent years, a number of diverse plant proteins with low sequence similarity to Bet v 1 was identified. In addition, determination of the Bet v 1 structure revealed the existence of a large superfamily of structurally related proteins. In this study, we aimed to identify and classify all Bet v 1-related structures from the Protein Data Bank and all Bet v 1-related sequences from the Uniprot database.
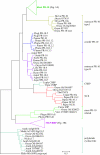
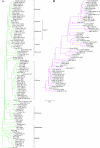
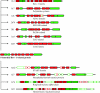
Results: Structural comparisons of representative members of already known protein families structurally related to Bet v 1 with all entries of the Protein Data Bank yielded 47 structures with non-identical sequences. They were classified into eleven families, five of which were newly identified and not included in the Structural Classification of Proteins database release 1.71. The taxonomic distribution of these families extracted from the Pfam protein family database showed that members of the polyketide cyclase family and the activator of Hsp90 ATPase homologue 1 family were distributed among all three superkingdoms, while members of some bacterial families were confined to a small number of species. Comparison of ligand binding activities of Bet v 1-like superfamily members revealed that their functions were related to binding and metabolism of large, hydrophobic compounds such as lipids, hormones, and antibiotics. Phylogenetic relationships within the Bet v 1 family, defined as the group of proteins with significant sequence similarity to Bet v 1, were determined by aligning 264 Bet v 1-related sequences. A distance-based phylogenetic tree yielded a classification into 11 subfamilies, nine exclusively containing plant sequences and two subfamilies of bacterial proteins. Plant sequences included the pathogenesis-related proteins 10, the major latex proteins/ripening-related proteins subfamily, and polyketide cyclase-like sequences.
Conclusion: The ubiquitous distribution of Bet v 1-related proteins among all superkingdoms suggests that a Bet v 1-like protein was already present in the last universal common ancestor. During evolution, this protein diversified into numerous families with low sequence similarity but with a common fold that succeeded as a versatile scaffold for binding of bulky ligands.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Crystal structure of a hypoallergenic isoform of the major birch pollen allergen Bet v 1 and its likely biological function as a plant steroid carrier.J Mol Biol. 2003 Jan 3;325(1):123-33. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(02)01197-x. J Mol Biol. 2003. PMID: 12473456
-
Seven different genes encode a diverse mixture of isoforms of Bet v 1, the major birch pollen allergen.BMC Genomics. 2006 Jul 4;7:168. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-7-168. BMC Genomics. 2006. PMID: 16820045 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and bioinformatic analysis of the kiwifruit allergen Act d 11, a member of the family of ripening-related proteins.Mol Immunol. 2013 Dec;56(4):794-803. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2013.07.004. Epub 2013 Aug 23. Mol Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23969108 Free PMC article.
-
The History and Science of the Major Birch Pollen Allergen Bet v 1.Biomolecules. 2023 Jul 19;13(7):1151. doi: 10.3390/biom13071151. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37509186 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Molecular aspects of allergy to plant products. Part II. Pathogenesis-related proteins (PRs), apple allergenicity governed by Mal d 1 gene].Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2012 Mar;32(189):176-81. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2012. PMID: 22568184 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
The major birch pollen allergen Bet v 1 induces different responses in dendritic cells of birch pollen allergic and healthy individuals.PLoS One. 2015 Jan 30;10(1):e0117904. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117904. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25635684 Free PMC article.
-
Post-translational control of ABA signalling: the roles of protein phosphorylation and ubiquitination.Plant Biotechnol J. 2017 Jan;15(1):4-14. doi: 10.1111/pbi.12652. Epub 2016 Dec 6. Plant Biotechnol J. 2017. PMID: 27767245 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mammalian START-like phosphatidylinositol transfer proteins - Physiological perspectives and roles in cancer biology.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2024 Oct;1869(7):159529. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2024.159529. Epub 2024 Jun 28. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2024. PMID: 38945251 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel rubber tree PR-10 protein involved in host-defense response against the white root rot fungus Rigidoporus microporus.BMC Plant Biol. 2023 Mar 22;23(1):157. doi: 10.1186/s12870-023-04149-3. BMC Plant Biol. 2023. PMID: 36944945 Free PMC article.
-
Ozone-induced inhibition of kiwifruit ripening is amplified by 1-methylcyclopropene and reversed by exogenous ethylene.BMC Plant Biol. 2018 Dec 17;18(1):358. doi: 10.1186/s12870-018-1584-y. BMC Plant Biol. 2018. PMID: 30558543 Free PMC article.
References
-
- van Loon LC, van Kammen A. Polyacrylamide disc electrophoresis of the soluble leaf proteins from Nicotiana tabacum var. "Samsun" and "Samsun NN". II. Changes in protein constitution after infection with tobacco mosaic virus. Virology. 1970;40:190–211. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90395-8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Liu JJ, Ekramoddoullah AKM. The family 10 of plant pathogenesis-related proteins: Their structure, regulation, and function in response to biotic and abiotic stresses. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol. 2006;68:3–13. doi: 10.1016/j.pmpp.2006.06.004. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

