Mre11 nuclease activity has essential roles in DNA repair and genomic stability distinct from ATM activation
- PMID: 18854157
- PMCID: PMC2645868
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.08.015
Mre11 nuclease activity has essential roles in DNA repair and genomic stability distinct from ATM activation
Abstract
The Mre11/Rad50/NBS1 (MRN) complex maintains genomic stability by bridging DNA ends and initiating DNA damage signaling through activation of the ATM kinase. Mre11 possesses DNA nuclease activities that are highly conserved in evolution but play unknown roles in mammals. To define the functions of Mre11, we engineered targeted mouse alleles that either abrogate nuclease activities or inactivate the entire MRN complex. Mre11 nuclease deficiency causes a striking array of phenotypes indistinguishable from the absence of MRN, including early embryonic lethality and dramatic genomic instability. We identify a crucial role for the nuclease activities in homology-directed double-strand-break repair and a contributing role in activating the ATR kinase. However, the nuclease activities are not required to activate ATM after DNA damage or telomere deprotection. Therefore, nucleolytic processing by Mre11 is an essential function of fundamental importance in DNA repair, distinct from MRN control of ATM signaling.
Figures
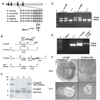
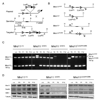
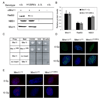
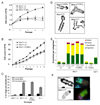
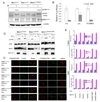
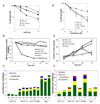
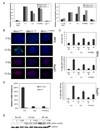
Comment in
-
DNA repair by the MRN complex: break it to make it.Cell. 2008 Oct 3;135(1):14-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.09.027. Cell. 2008. PMID: 18854148
Similar articles
-
Multiple roles for MRE11 at uncapped telomeres.Nature. 2009 Aug 13;460(7257):914-8. doi: 10.1038/nature08196. Epub 2009 Jul 26. Nature. 2009. PMID: 19633651 Free PMC article.
-
Ataxia telangiectasia-mutated (ATM) kinase activity is regulated by ATP-driven conformational changes in the Mre11/Rad50/Nbs1 (MRN) complex.J Biol Chem. 2013 May 3;288(18):12840-51. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.460378. Epub 2013 Mar 22. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23525106 Free PMC article.
-
Mre11 ATLD17/18 mutation retains Tel1/ATM activity but blocks DNA double-strand break repair.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Dec;40(22):11435-49. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks954. Epub 2012 Oct 17. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 23080121 Free PMC article.
-
Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1 is a keystone complex connecting DNA repair machinery, double-strand break signaling, and the chromatin template.Biochem Cell Biol. 2007 Aug;85(4):509-20. doi: 10.1139/O07-069. Biochem Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17713585 Review.
-
MRE11/RAD50/NBS1: complex activities.Chromosoma. 2004 Oct;113(4):157-66. doi: 10.1007/s00412-004-0306-4. Epub 2004 Aug 10. Chromosoma. 2004. PMID: 15309560 Review.
Cited by
-
Enhanced cellular radiosensitivity induced by cofilin-1 over-expression is associated with reduced DNA repair capacity.Int J Radiat Biol. 2013 Jun;89(6):433-44. doi: 10.3109/09553002.2013.767992. Epub 2013 Mar 19. Int J Radiat Biol. 2013. PMID: 23362981 Free PMC article.
-
Disease-associated MRE11 mutants impact ATM/ATR DNA damage signaling by distinct mechanisms.Hum Mol Genet. 2013 Dec 20;22(25):5146-59. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt368. Epub 2013 Aug 2. Hum Mol Genet. 2013. PMID: 23912341 Free PMC article.
-
Absolute quantification of DNA damage response proteins.Genes Environ. 2023 Dec 18;45(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s41021-023-00295-0. Genes Environ. 2023. PMID: 38111058 Free PMC article.
-
CtIP-BRCA1 complex and MRE11 maintain replication forks in the presence of chain terminating nucleoside analogs.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Apr 8;47(6):2966-2980. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz009. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 30657944 Free PMC article.
-
Ataxia-telangiectasia-like disorder in a family deficient for MRE11A, caused by a MRE11 variant.Neurol Genet. 2018 Dec 3;4(6):e295. doi: 10.1212/NXG.0000000000000295. eCollection 2018 Dec. Neurol Genet. 2018. PMID: 30584599 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bakkenist CJ, Kastan MB. DNA damage activates ATM through intermolecular autophosphorylation and dimer dissociation. Nature. 2003;421:499–506. - PubMed
-
- Berkovich E, Monnat RJ, Jr, Kastan MB. Roles of ATM and NBS1 in chromatin structure modulation and DNA double-strand break repair. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9:683–690. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 5-P30-CA46592/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016672/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL067580/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL079118-02/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL067580-03/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 1K01CA124461-01/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA046592/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI063058-04/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL067580-05/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL079118-03/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 CA124461/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL079118/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- CA129037/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HL079118/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AG028888/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL067580-04/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL079118-04/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI063058/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL067580-01/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG028888/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AI063058/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009676/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL067580-02/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL079118-01/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- CA016672)/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA129037/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

