Role of homodimerization of human cytomegalovirus DNA polymerase accessory protein UL44 in origin-dependent DNA replication in cells
- PMID: 18842734
- PMCID: PMC2593364
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01193-08
Role of homodimerization of human cytomegalovirus DNA polymerase accessory protein UL44 in origin-dependent DNA replication in cells
Abstract
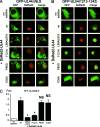
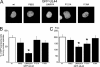
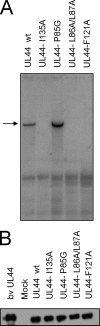
The presumed processivity subunit of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) DNA polymerase, UL44, forms homodimers. The dimerization of UL44 is important for binding to DNA in vitro; however, whether it is also important for DNA replication in a cellular context is unknown. Here we show that UL44 point mutants that are impaired for dimerization, but not for nuclear localization or interaction with the C terminus of the polymerase catalytic subunit, are not capable of supporting HCMV oriLyt-dependent DNA replication in cells. These data suggest that the disruption of UL44 homodimers could represent a novel anti-HCMV strategy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of the specific interaction of UL112-113 p84 with UL44 DNA polymerase processivity factor in promoting DNA replication of human cytomegalovirus.J Virol. 2010 Sep;84(17):8409-21. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00189-10. Epub 2010 Jun 10. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20538862 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the association of the human cytomegalovirus DNA polymerase subunit UL44 with the viral DNA replication factor UL84.J Virol. 2009 Aug;83(15):7581-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00663-09. Epub 2009 May 20. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19457994 Free PMC article.
-
The human cytomegalovirus DNA polymerase processivity factor UL44 is modified by SUMO in a DNA-dependent manner.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e49630. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049630. Epub 2012 Nov 15. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23166733 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic analysis and putative role in resistance to antivirals of the human cytomegalovirus DNA polymerase UL44 processivity factor.Antivir Ther. 2009;14(6):847-52. doi: 10.3851/IMP1299. Antivir Ther. 2009. PMID: 19812447
-
Nuts and bolts of human cytomegalovirus lytic DNA replication.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008;325:153-66. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-77349-8_9. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18637505 Review.
Cited by
-
The flexible loop of the human cytomegalovirus DNA polymerase processivity factor ppUL44 is required for efficient DNA binding and replication in cells.J Virol. 2009 Sep;83(18):9567-76. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00669-09. Epub 2009 Jul 1. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19570866 Free PMC article.
-
Antiviral drug resistance of human cytomegalovirus.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2010 Oct;23(4):689-712. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00009-10. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2010. PMID: 20930070 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Requirements for Self-Interaction of the Respiratory Syncytial Virus Matrix Protein in Living Mammalian Cells.Viruses. 2018 Mar 3;10(3):109. doi: 10.3390/v10030109. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 29510513 Free PMC article.
-
Divide et impera: An In Silico Screening Targeting HCMV ppUL44 Processivity Factor Homodimerization Identifies Small Molecules Inhibiting Viral Replication.Viruses. 2021 May 20;13(5):941. doi: 10.3390/v13050941. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34065234 Free PMC article.
-
The carboxy-terminal segment of the human cytomegalovirus DNA polymerase accessory subunit UL44 is crucial for viral replication.J Virol. 2010 Nov;84(21):11563-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01033-10. Epub 2010 Aug 25. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20739543 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agulnick, A. D., J. R. Thompson, S. Iyengar, G. Pearson, D. Ablashi, and R. P. Ricciardi. 1993. Identification of a DNA-binding protein of human herpesvirus 6, a putative DNA polymerase stimulatory factor. J. Gen. Virol. 741003-1009. - PubMed
-
- Alvisi, G., D. A. Jans, J. Guo, L. A. Pinna, and A. Ripalti. 2005. A protein kinase CK2 site flanking the nuclear targeting signal enhances nuclear transport of human cytomegalovirus ppUL44. Traffic 61002-1013. - PubMed
-
- Alvisi, G., D. A. Jans, and A. Ripalti. 2006. Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) DNA polymerase processivity factor ppUL44 dimerizes in the cytosol before translocation to the nucleus. Biochemistry 456866-6872. - PubMed
-
- Alvisi, G., A. Ripalti, A. Ngankeu, M. Giannandrea, S. G. Caraffi, M. M. Dias, and D. A. Jans. 2006. Human cytomegalovirus DNA polymerase catalytic subunit pUL54 possesses independently acting nuclear localization and ppUL44 binding motifs. Traffic 71322-1332. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

