The accuracy of the Guardian RT continuous glucose monitor in children with type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 18828242
- PMCID: PMC2587171
- DOI: 10.1089/dia.2007.0279
The accuracy of the Guardian RT continuous glucose monitor in children with type 1 diabetes
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to determine the accuracy of the Guardian RT system (Medtronic Minimed, Northridge, CA) in young children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes (T1D) during different scenarios of glucose levels and sensor age.
Methods: At five clinical centers, 30 subjects between 4 and 17 years old with T1D were recruited. All subjects had a glycosylated hemoglobin level of <or=10.0% and were using an insulin pump. Subjects initially used a Guardian RT for approximately 1 week at home. Each subject was then hospitalized overnight for about 18 h in a clinical research center, during which time insulin-induced hypoglycemia occurred, along with frequently sampled glucose.
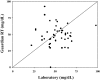
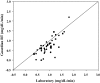
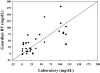
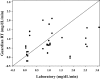
Results: There were 1,511 laboratory glucose measurements paired with glucose measurements from 48 Guardian RT sensors. Overall, the median absolute difference (AD) was 21 mg/dL, and the median relative AD (RAD) was 14%, with 64% of sensor values meeting International Organization for Standardization home glucose meter criteria. The median AD was 27 mg/dL for reference glucose values<or=60 mg/dL and 25 mg/dL for reference glucose values<or=70 mg/dL. The median RAD was 19% for reference glucose values 71-120 mg/dL, 14% for reference glucose values 121-180 mg/dL, and 10% for reference glucose values>180 mg/dL.
Conclusions: The Guardian RT appears to perform as well in children with T1D as it has been reported to perform in adults with diabetes. The Guardian RT has an accuracy similar to that of other available continuous glucose monitors and can give important and useful clinical information.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The accuracy and efficacy of real-time continuous glucose monitoring sensor in patients with type 1 diabetes.Diabetes Technol Ther. 2008 Oct;10(5):385-90. doi: 10.1089/dia.2007.0291. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2008. PMID: 18715215
-
Accuracy of a Fourth-Generation Continuous Glucose Monitoring System in Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes.Diabetes Technol Ther. 2018 Sep;20(9):576-584. doi: 10.1089/dia.2018.0109. Epub 2018 Jul 31. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2018. PMID: 30063162 Clinical Trial.
-
Performance comparison of the medtronic sof-sensor and enlite glucose sensors in inpatient studies of individuals with type 1 diabetes.Diabetes Technol Ther. 2013 Sep;15(9):758-61. doi: 10.1089/dia.2013.0042. Epub 2013 May 31. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23725474 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetes technology and treatments in the paediatric age group.Int J Clin Pract Suppl. 2011 Feb;(170):76-82. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-1241.2010.02582.x. Int J Clin Pract Suppl. 2011. PMID: 21323816 Review.
-
Delays in minimally invasive continuous glucose monitoring devices: a review of current technology.J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2009 Sep 1;3(5):1207-14. doi: 10.1177/193229680900300528. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2009. PMID: 20144438 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical Performance Evaluation of Continuous Glucose Monitoring Systems: A Scoping Review and Recommendations for Reporting.J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2023 Nov;17(6):1506-1526. doi: 10.1177/19322968231190941. Epub 2023 Aug 20. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2023. PMID: 37599389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glucose Profiles Assessed by Intermittently Scanned Continuous Glucose Monitoring System during the Perioperative Period of Metabolic Surgery.Diabetes Metab J. 2022 Sep;46(5):713-721. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2021.0164. Epub 2022 Jan 24. Diabetes Metab J. 2022. PMID: 35067012 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and feasibility of a factory-calibrated continuous glucose monitoring system in term and near-term infants at risk of hypoglycemia.Turk Arch Pediatr. 2021 Jan 12;56(2):115-120. doi: 10.5152/TurkArchPediatr.2020.20183. eCollection 2021 Mar. Turk Arch Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34286319 Free PMC article.
-
Automated closed-loop control of diabetes: the artificial pancreas.Bioelectron Med. 2018 Nov 7;4:14. doi: 10.1186/s42234-018-0015-6. eCollection 2018. Bioelectron Med. 2018. PMID: 32232090 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blood Glucose Level Prediction for Diabetics Based on Nutrition and Insulin Administration Logs Using Personalized Mathematical Models.J Healthc Eng. 2019 Jan 10;2019:8605206. doi: 10.1155/2019/8605206. eCollection 2019. J Healthc Eng. 2019. PMID: 30774850 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Neese JW. Duncan P. Bayse D. Robinson M. Cooper T. Stewart C. Development, Evaluation of a Hexokinase/Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Procedure for Use as a National Glucose Reference Method. Atlanta: Centers for Disease Control; 1976.
-
- Passey RB. Gillum RL. Fuller JB. Urry FM. Giles ML. Evaluation and comparison of 10 glucose methods and the reference method recommended in the proposed product class standard (1974) Clin Chem. 1977;23:131–139. - PubMed
-
- Diabetes Research in Children Network (DirecNet) Study Group. A multicenter study of the accuracy of the OneTouch Ultra home glucose meter in children with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2003;5:933–941. - PubMed
-
- International Organization for Standardization. Vitro Diagnostic Test Systems—Requirements for Blood-Glucose Monitoring Systems for Self-Testing in Managing Diabetes Mellitus. Geneva: Switzerland: 2003.
-
- Efron B. Tibshirani R. An introduction to the Bootstrap. New York: Chapman & Hall; 1993.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- RR 06022/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD041906/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD041918/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD041890-01/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD041918-01/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD041890/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD041915/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD041919-01/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD041908/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR00069/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- RR00059/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD041906-01/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD041890/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD041915-01/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- RR00070-41/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD041908-01/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

