The von Hippel-Lindau gene: turning discovery into therapy
- PMID: 18800388
- PMCID: PMC2963103
- DOI: 10.1002/cncr.23645
The von Hippel-Lindau gene: turning discovery into therapy
Abstract
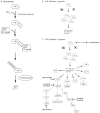
Mutations or aberrations of the von Hippel-Lindau gene are responsible for the hereditary neoplastic syndrome that bears the same name, as well as for the majority of sporadic clear cell renal cell carcinomas. The discovery of this gene and subsequent clarification of its mechanism of action have led to a series of targeted treatments for advanced kidney cancer and have dramatically changed how we manage this disease. The discovery of the VHL gene is a prime example of how discoveries at the bench can inform and revolutionize therapeutics at the bedside. In this review, the authors trace this illuminating tale, from the cloning of the VHL gene, to elucidating its biologic function, to the development of novel therapeutics that have dramatically changed the paradigm of managing advanced renal cell carcinoma.
Figures
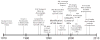
Similar articles
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1-dependent repression of E-cadherin in von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor-null renal cell carcinoma mediated by TCF3, ZFHX1A, and ZFHX1B.Cancer Res. 2006 Mar 1;66(5):2725-31. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-3719. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16510593
-
Up-regulation of hypoxia-inducible factors HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha under normoxic conditions in renal carcinoma cells by von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor gene loss of function.Oncogene. 2000 Nov 16;19(48):5435-43. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203938. Oncogene. 2000. PMID: 11114720
-
[The expression of hypoxia inducible factor-1,2 alpha in sporadic clear cell renal cell carcinoma and their relationships to the mutations of von Hippel-Lindau gene].Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2005 Mar 15;43(6):390-3. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2005. PMID: 15854350 Chinese.
-
Von Hippel-Lindau disease and sporadic renal cell carcinoma.Cancer Surv. 1995;25:219-32. Cancer Surv. 1995. PMID: 8718521 Review.
-
The von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor gene and kidney cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2004 Sep 15;10(18 Pt 2):6290S-5S. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-sup-040025. Clin Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15448019 Review.
Cited by
-
The von Hippel-Lindau tumour suppressor gene: uncovering the expression of the pVHL172 isoform.Br J Cancer. 2015 Jul 14;113(2):336-44. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2015.189. Epub 2015 Jun 2. Br J Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26035699 Free PMC article.
-
Von Hippel-Lindau Disease Presenting as Obstructive Jaundice.ACG Case Rep J. 2020 Feb 19;7(2):e00324. doi: 10.14309/crj.0000000000000324. eCollection 2020 Feb. ACG Case Rep J. 2020. PMID: 32309512 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Immunogenicity in renal cell carcinoma: shifting focus to alternative sources of tumour-specific antigens.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2023 Jul;19(7):440-450. doi: 10.1038/s41581-023-00700-5. Epub 2023 Mar 27. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 36973495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Obstructive jaundice due to von Hippel-Lindau disease-associated pancreatic lesions: A case report.Oncol Lett. 2014 Jul;8(1):446-448. doi: 10.3892/ol.2014.2098. Epub 2014 Apr 28. Oncol Lett. 2014. PMID: 24959293 Free PMC article.
-
Antitumor effect and biological pathways of a recombinant adeno-associated virus as a human renal cell carcinoma suppressor.Tumour Biol. 2014 Nov;35(11):10993-1003. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-2393-z. Epub 2014 Aug 5. Tumour Biol. 2014. PMID: 25091575 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lonser RR, Glenn GM, Walther M, Chew EY, Libutti SK, Linehan WM, et al. von Hippel-Lindau disease. Lancet. 2003;361:2059–2067. - PubMed
-
- Grubb RL, III, Choyke PL, Pinto PA, Linehan WM, Walther MM. Management of von Hippel-Lindau-associated kidney cancer. Nat Clin Pract Urol. 2005;2:248–255. - PubMed
-
- Neumann HP, Wiestler OD. Clustering of features of von Hippel-Lindau syndrome: evidence for a complex genetic locus. Lancet. 1991;337:1052–1054. - PubMed
-
- Maher ER, Yates JR, Harries R, et al. Clinical features and natural history of von Hippel-Lindau disease. Q J Med. 1990;77:1151–1163. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

