Engineering and optimization of the miR-106b cluster for ectopic expression of multiplexed anti-HIV RNAs
- PMID: 18800151
- PMCID: PMC3155610
- DOI: 10.1038/gt.2008.147
Engineering and optimization of the miR-106b cluster for ectopic expression of multiplexed anti-HIV RNAs
Abstract
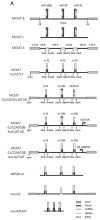
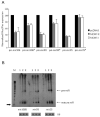
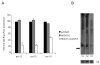
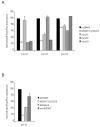
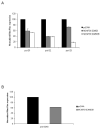
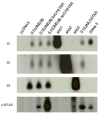
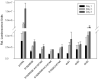
Many microRNAs (miRNAs) are encoded within the introns of RNA Pol II transcripts, often as polycistronic precursors. Here, we demonstrate the optimization of an intron encoding three endogenous miRNAs for the ectopic expression of heterologous anti-HIV-1 small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) processed from a single RNA polymerase II primary miRNA. Our expression system, designated as MCM7, is engineered from the intron-embedded, tri-cistronic miR-106b cluster that endogenously expresses miR-106b, miR-93 and miR-25. Manipulation of the miR-106b cluster demonstrated a strict requirement for maintenance of the native flanking primary miRNA (pri-miRNA) sequences and key structural features of the native miRNAs for efficient siRNA processing. As a model for testing the efficacy of this approach, we have replaced the three endogenous miRNAs with siRNAs targeting the tat and rev transcripts of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1). This study has enabled us to establish guidelines for optimal processing of the engineered miRNA mimics into functional siRNAs. In addition, we demonstrate that the incorporation of a small nucleolar RNA TAR chimeric decoy (snoRNA) inserted within the MCM7 intron resulted in a substantial enhancement of HIV suppression in long-term acute infectious HIV-1 challenges.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

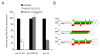

Similar articles
-
Endogenous MCM7 microRNA cluster as a novel platform to multiplex small interfering and nucleolar RNAs for combinational HIV-1 gene therapy.Hum Gene Ther. 2012 Nov;23(11):1200-8. doi: 10.1089/hum.2012.011. Epub 2012 Sep 18. Hum Gene Ther. 2012. PMID: 22834872 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of HIV-1 replication with designed miRNAs expressed from RNA polymerase II promoters.Gene Ther. 2007 Nov;14(21):1503-12. doi: 10.1038/sj.gt.3303011. Epub 2007 Sep 6. Gene Ther. 2007. PMID: 17805304
-
A multiplexed miRNA and transgene expression platform for simultaneous repression and expression of protein coding sequences.Mol Biosyst. 2016 Jan;12(1):295-312. doi: 10.1039/c5mb00506j. Mol Biosyst. 2016. PMID: 26617199
-
Cloning and detection of HIV-1-encoded microRNA.Methods Mol Biol. 2006;342:255-65. doi: 10.1385/1-59745-123-1:255. Methods Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16957380 Review.
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
Cited by
-
Foamy combinatorial anti-HIV vectors with MGMTP140K potently inhibit HIV-1 and SHIV replication and mediate selection in vivo.Gene Ther. 2010 Jan;17(1):37-49. doi: 10.1038/gt.2009.118. Epub 2009 Sep 10. Gene Ther. 2010. PMID: 19741733 Free PMC article.
-
Short non-coding RNA biology and neurodegenerative disorders: novel disease targets and therapeutics.Hum Mol Genet. 2009 Apr 15;18(R1):R27-39. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddp070. Hum Mol Genet. 2009. PMID: 19297399 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Subretinal AAV delivery of RNAi-therapeutics targeting VEGFA reduces choroidal neovascularization in a large animal model.Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2024 Mar 22;32(2):101242. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2024.101242. eCollection 2024 Jun 13. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2024. PMID: 38605811 Free PMC article.
-
Improved knockdown from artificial microRNAs in an enhanced miR-155 backbone: a designer's guide to potent multi-target RNAi.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Mar 18;44(5):e48. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1246. Epub 2015 Nov 17. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 26582923 Free PMC article.
-
Deriving four functional anti-HIV siRNAs from a single Pol III-generated transcript comprising two adjacent long hairpin RNA precursors.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Oct;38(19):6652-63. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq460. Epub 2010 Jun 4. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20525791 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fire A, et al. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1998;391:806–811. - PubMed
-
- Elbashir SM, et al. Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature. 2001;411:494–498. - PubMed
-
- Hannon GJ, Rossi JJ. Unlocking the potential of the human genome with RNA interference. Nature. 2004;431:371–378. - PubMed
-
- Kim DH, Rossi JJ. Strategies for silencing human disease using RNA interference. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8:173–184. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

