Limbic and cortical information processing in the nucleus accumbens
- PMID: 18786735
- PMCID: PMC2884964
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tins.2008.08.002
Limbic and cortical information processing in the nucleus accumbens
Abstract
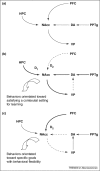
The nucleus accumbens regulates goal-directed behaviors by integrating information from limbic structures and the prefrontal cortex. Here, we review recent studies in an attempt to provide an integrated view of the control of information processing in the nucleus accumbens in terms of the regulation of goal-directed behaviors and how disruption of these functions might underlie the pathological states in drug addiction and other psychiatric disorders. We propose a model that could account for the results of several studies investigating limbic-system interactions in the nucleus accumbens and their modulation by dopamine and provide testable hypotheses for how these might relate to the pathophysiology of major psychiatric disorders.
Figures
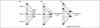
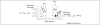
Similar articles
-
Dopamine-dependent interactions between limbic and prefrontal cortical plasticity in the nucleus accumbens: disruption by cocaine sensitization.Neuron. 2005 Jul 21;47(2):255-66. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2005.06.017. Neuron. 2005. PMID: 16039567
-
Is the dopaminergic mesocorticolimbic system necessary for intracranial self-stimulation? Biochemical and behavioral studies from A10 cell bodies and terminals.Behav Neural Biol. 1979 Oct;27(2):125-45. doi: 10.1016/s0163-1047(79)91745-x. Behav Neural Biol. 1979. PMID: 508212 No abstract available.
-
Modulation of cell firing in the nucleus accumbens.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999 Jun 29;877:157-75. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1999.tb09267.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999. PMID: 10415649 Review.
-
The modulation of corticoaccumbens transmission by limbic afferents and dopamine: a model for the pathophysiology of schizophrenia.Adv Pharmacol. 1998;42:721-4. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(08)60849-2. Adv Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9328000 No abstract available.
-
Redefining the Role of Limbic Areas in Cortical Processing.Trends Cogn Sci. 2016 Feb;20(2):96-106. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2015.11.005. Epub 2015 Dec 15. Trends Cogn Sci. 2016. PMID: 26704857 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Synaptic and behavioral profile of multiple glutamatergic inputs to the nucleus accumbens.Neuron. 2012 Nov 21;76(4):790-803. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.09.040. Neuron. 2012. PMID: 23177963 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in studying phasic dopamine signaling in brain reward mechanisms.Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2013 Jun 1;5(3):982-99. doi: 10.2741/e678. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2013. PMID: 23747914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brain activity and transcriptional profiling in mice under chronic jet lag.Sci Data. 2020 Oct 21;7(1):361. doi: 10.1038/s41597-020-00709-6. Sci Data. 2020. PMID: 33087702 Free PMC article.
-
Morphological elucidation of basal ganglia circuits contributing reward prediction.Front Neurosci. 2015 Feb 5;9:6. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2015.00006. eCollection 2015. Front Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25698913 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ventral striatal dopamine reflects behavioral and neural signatures of model-based control during sequential decision making.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Feb 3;112(5):1595-600. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1417219112. Epub 2015 Jan 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25605941 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Groenewegen HJ, et al. Convergence and segregation of ventral striatal inputs and outputs. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1999;877:49–63. - PubMed
-
- Grace AA. Gating of information flow within the limbic system and the pathophysiology of schizophrenia. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 2000;31:330–341. - PubMed
-
- Cassaday HJ, et al. Electrolytic lesions to nucleus accumbens core and shell have dissociable effects on conditioning to discrete and contextual cues in aversive and appetitive procedures respectively. Behav. Brain Res. 2005;160:222–235. - PubMed
-
- Cardinal RN, et al. Impulsive choice induced in rats by lesions of the nucleus accumbens core. Science. 2001;292:2499–2501. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

