Functional copy-number alterations in cancer
- PMID: 18784837
- PMCID: PMC2527508
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003179
Functional copy-number alterations in cancer
Abstract
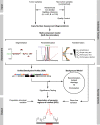
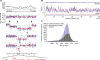
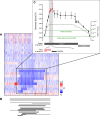
Understanding the molecular basis of cancer requires characterization of its genetic defects. DNA microarray technologies can provide detailed raw data about chromosomal aberrations in tumor samples. Computational analysis is needed (1) to deduce from raw array data actual amplification or deletion events for chromosomal fragments and (2) to distinguish causal chromosomal alterations from functionally neutral ones. We present a comprehensive computational approach, RAE, designed to robustly map chromosomal alterations in tumor samples and assess their functional importance in cancer. To demonstrate the methodology, we experimentally profile copy number changes in a clinically aggressive subtype of soft-tissue sarcoma, pleomorphic liposarcoma, and computationally derive a portrait of candidate oncogenic alterations and their target genes. Many affected genes are known to be involved in sarcomagenesis; others are novel, including mediators of adipocyte differentiation, and may include valuable therapeutic targets. Taken together, we present a statistically robust methodology applicable to high-resolution genomic data to assess the extent and function of copy-number alterations in cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
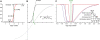

Similar articles
-
"Lineage addiction" in human cancer: lessons from integrated genomics.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2005;70:25-34. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2005.70.016. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2005. PMID: 16869735
-
Integrative genomics identifies distinct molecular classes of neuroblastoma and shows that multiple genes are targeted by regional alterations in DNA copy number.Cancer Res. 2006 Jun 15;66(12):6050-62. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-4618. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16778177
-
TAFFYS: An Integrated Tool for Comprehensive Analysis of Genomic Aberrations in Tumor Samples.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 25;10(6):e0129835. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0129835. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26111017 Free PMC article.
-
Existing and emerging technologies for tumor genomic profiling.J Clin Oncol. 2013 May 20;31(15):1815-24. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.46.5948. Epub 2013 Apr 15. J Clin Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23589546 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Patterns of Chromosomal Aberrations in Solid Tumors.Recent Results Cancer Res. 2015;200:115-42. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-20291-4_6. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26376875 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Five decades of sarcoma care at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center.J Surg Oncol. 2022 Oct;126(5):896-901. doi: 10.1002/jso.27032. J Surg Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36087086 Free PMC article.
-
TRIM3, a tumor suppressor linked to regulation of p21(Waf1/Cip1.).Oncogene. 2014 Jan 16;33(3):308-15. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.596. Epub 2013 Jan 14. Oncogene. 2014. PMID: 23318451 Free PMC article.
-
Soft tissue sarcoma subtypes exhibit distinct patterns of acquired uniparental disomy.BMC Med Genomics. 2012 Dec 5;5:60. doi: 10.1186/1755-8794-5-60. BMC Med Genomics. 2012. PMID: 23217126 Free PMC article.
-
Interactive analysis of large cancer copy number studies with Copy Number Explorer.Bioinformatics. 2015 Sep 1;31(17):2874-6. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv298. Epub 2015 May 7. Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 25957352 Free PMC article.
-
New treatments for bladder cancer: when will we make progress?Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2014 Mar;15(1):99-114. doi: 10.1007/s11864-013-0271-3. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24415439 Review.
References
-
- Albertson DG, Collins C, McCormick F, Gray JW. Chromosome aberrations in solid tumors. Nat Genet. 2003;34:369–376. - PubMed
-
- Druker BJ, Talpaz M, Resta DJ, Peng B, Buchdunger E, et al. Efficacy and safety of a specific inhibitor of the BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase in chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:1031–1037. - PubMed
-
- Engelman JA, Zejnullahu K, Mitsudomi T, Song Y, Hyland C, et al. MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung cancer by activating ERBB3 signaling. Science. 2007;316:1039–1043. - PubMed
-
- Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2129–2139. - PubMed
-
- Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S, Greulich H, et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 2004;304:1497–1500. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

