Identification of chromatin remodeling genes Arid4a and Arid4b as leukemia suppressor genes
- PMID: 18728284
- PMCID: PMC2528019
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djn253
Identification of chromatin remodeling genes Arid4a and Arid4b as leukemia suppressor genes
Abstract
Background: Leukemia evolves through a multistep process from premalignancy to malignancy. Epigenetic alterations, including histone modifications, have been proposed to play an important role in tumorigenesis. The involvement of two chromatin remodeling genes, retinoblastoma-binding protein 1 (Rbbp1/Arid4a) and Rbbp1-like 1 (Rbbp1l1/Arid4b), in leukemogenesis was not characterized.
Methods: The leukemic phenotype of mice deficient for Arid4a with or without haploinsufficiency for Arid4b was investigated by serially monitoring complete blood counts together with microscopic histologic analysis and flow cytometric analysis of bone marrow and spleen from the Arid4a(-/-) mice or Arid4a(-/-)Arid4b(+/-) mice. Regulation in bone marrow cells of downstream genes important for normal hematopoiesis was analyzed by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. Genotypic effects on histone modifications were examined by western blotting and immunofluorescence analysis. All statistical tests were two-sided.
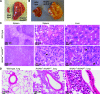
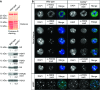
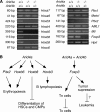
Results: Young (2-5 months old) Arid4a-deficient mice had ineffective blood cell production in all hematopoietic lineages. Beyond 5 months of age, the Arid4a(-/-) mice manifested monocytosis, accompanied by severe anemia and thrombocytopenia. These sick Arid4a(-/-) mice showed bone marrow failure with myelofibrosis associated with splenomegaly and hepatomegaly. Five of 42 Arid4a(-/-) mice and 10 of 12 Arid4a(-/-)Arid4b(+/-) mice progressed to acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and had rapid further increases of leukocyte counts. Expression of Hox genes (Hoxb3, Hoxb5, Hoxb6, and Hoxb8) was decreased in Arid4a-deficient bone marrow cells with or without Arid4b haploinsufficiency, and FoxP3 expression was reduced in Arid4a(-/-)Arid4b(+/-) bone marrow. Increases of histone trimethylation of H3K4, H3K9, and H4K20 (fold increases in trimethylation = 32, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 27 to 32; 45, 95% CI = 41 to 49; and 2.2, 95% CI = 1.7 to 2.7, respectively) were observed in the bone marrow of Arid4a-deficient mice.
Conclusions: Arid4a-deficient mice initially display ineffective hematopoiesis, followed by transition to chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML)-like myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative disorder, and then transformation to AML. The disease processes in the Arid4a-deficient mice are very similar to the course of events in humans with CMML and AML. This mouse model has the potential to furnish additional insights into the role of epigenetic alterations in leukemogenesis, and it may be useful in developing novel pharmacological approaches to treatment of preleukemic and leukemic states.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ARID4A and ARID4B regulate male fertility, a functional link to the AR and RB pathways.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Mar 19;110(12):4616-21. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1218318110. Epub 2013 Mar 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23487765 Free PMC article.
-
Deficiency of Rbbp1/Arid4a and Rbbp1l1/Arid4b alters epigenetic modifications and suppresses an imprinting defect in the PWS/AS domain.Genes Dev. 2006 Oct 15;20(20):2859-70. doi: 10.1101/gad.1452206. Genes Dev. 2006. PMID: 17043311 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of ARID4A and ARID4B promote tumor progression and directly regulated by microRNA-30d in patient with prostate cancer.J Cell Biochem. 2018 Sep;119(9):7245-7255. doi: 10.1002/jcb.26913. Epub 2018 May 24. J Cell Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29797600
-
The AML1 gene: a transcription factor involved in the pathogenesis of myeloid and lymphoid leukemias.Haematologica. 1997 May-Jun;82(3):364-70. Haematologica. 1997. PMID: 9234595 Review.
-
Homeobox genes in hematopoiesis and leukemogenesis.Int J Hematol. 1998 Jun;67(4):339-50. doi: 10.1016/s0925-5710(98)00024-3. Int J Hematol. 1998. PMID: 9695407 Review.
Cited by
-
ARID4A and ARID4B regulate male fertility, a functional link to the AR and RB pathways.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Mar 19;110(12):4616-21. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1218318110. Epub 2013 Mar 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23487765 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of genetic aberrations and novel transcripts involved in the pathogenesis of oligodendroglioma using array comparative genomic hybridization and next generation sequencing.Oncol Lett. 2019 Feb;17(2):1675-1687. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.9811. Epub 2018 Dec 7. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 30675227 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse models of myelodysplastic syndromes.Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2010 Apr;24(2):361-75. doi: 10.1016/j.hoc.2010.02.002. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2010. PMID: 20359631 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overexpression of HOXC11 homeobox gene in clear cell renal cell carcinoma induces cellular proliferation and is associated with poor prognosis.Tumour Biol. 2015 Apr;36(4):2821-9. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-2909-6. Epub 2014 Dec 5. Tumour Biol. 2015. PMID: 25476856
-
CALR mutational status identifies different disease subtypes of essential thrombocythemia showing distinct expression profiles.Blood Cancer J. 2017 Dec 8;7(12):638. doi: 10.1038/s41408-017-0010-2. Blood Cancer J. 2017. PMID: 29217833 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Defeo-Jones D, Huang PS, Jones RE, et al. Cloning of cDNAs for cellular proteins that bind to the retinoblastoma gene product. Nature. 1991;352(6332):251–254. - PubMed
-
- Fattaey AR, Helin K, Dembski MS, et al. Characterization of the retinoblastoma binding proteins RBP1 and RBP2. Oncogene. 1993;8(11):3149–3156. - PubMed
-
- Cao J, Gao T, Stanbridge EJ, Irie R. RBP1L1, a retinoblastoma-binding protein-related gene encoding an antigenic epitope abundantly expressed in human carcinomas and normal testis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2001;93(15):1159–1165. - PubMed
-
- Wilsker D, Probst L, Wain HM, Maltais L, Tucker PW, Moran E. Nomenclature of the ARID family of DNA-binding proteins. Genomics. 2005;86(2):242–251. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

