Prevention of axonal injury using calpain inhibitor in chronic progressive experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
- PMID: 18725211
- PMCID: PMC3193985
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.07.124
Prevention of axonal injury using calpain inhibitor in chronic progressive experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
Abstract
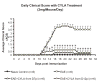
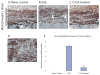
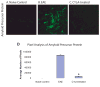
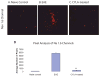
Axonal injury is the major correlate of permanent disability in neurodegenerative diseases such as multiple sclerosis (MS), especially in secondary-progressive MS which follows relapsing-remitting disease course. Proteolytic enzyme, calpain, is a potential candidate for causing axonal injury. Most current treatment options only target the inflammatory component of MS. Previous work using calpain inhibitor CYLA in our laboratory showed significant reduction in clinical sign, demyelination and tissue calpain content in acute experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). Here we evaluated markers of axonal injury (amyloid precursor protein, Na(v)1.6 channels), neuronal calpain content and the effect of CYLA on axonal protection using histological methods in chronic EAE [myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG)-induced disease model of MS]. Intraperitoneal application of CYLA (2 mg/mouse/day) significantly reduced the clinical signs, tissue calpain content, demyelination and inflammatory infiltration of EAE. Similarly, markers for axonal injury were barely detectable in the treated mice. Thus, this novel drug, which markedly suppresses the disease course, axonal injury and its progression, is a candidate for the treatment of a neurodegenerative disease such as multiple sclerosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Limiting multiple sclerosis related axonopathy by blocking Nogo receptor and CRMP-2 phosphorylation.Brain. 2012 Jun;135(Pt 6):1794-818. doi: 10.1093/brain/aws100. Epub 2012 Apr 28. Brain. 2012. PMID: 22544872 Free PMC article.
-
Pattern of axonal injury in murine myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein induced experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis: implications for multiple sclerosis.Neurobiol Dis. 2008 May;30(2):162-73. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2008.01.001. Epub 2008 Jan 26. Neurobiol Dis. 2008. PMID: 18342527
-
Activated microglia mediate axoglial disruption that contributes to axonal injury in multiple sclerosis.J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2010 Oct;69(10):1017-1033. doi: 10.1097/NEN.0b013e3181f3a5b1. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2010. PMID: 20838243 Free PMC article.
-
Phenytoin protects central axons in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.J Neurol Sci. 2008 Nov 15;274(1-2):57-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2008.04.001. Epub 2008 May 15. J Neurol Sci. 2008. PMID: 18485368 Review.
-
Axonal loss in the pathology of MS: consequences for understanding the progressive phase of the disease.J Neurol Sci. 2003 Feb 15;206(2):165-71. doi: 10.1016/s0022-510x(02)00069-2. J Neurol Sci. 2003. PMID: 12559505 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms of neurodegeneration and axonal dysfunction in multiple sclerosis.Nat Rev Neurol. 2014 Apr;10(4):225-38. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2014.37. Epub 2014 Mar 18. Nat Rev Neurol. 2014. PMID: 24638138 Review.
-
Altered Expression of Ion Channels in White Matter Lesions of Progressive Multiple Sclerosis: What Do We Know About Their Function?Front Cell Neurosci. 2021 Jun 25;15:685703. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.685703. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34276310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Animal models of multiple sclerosis--potentials and limitations.Prog Neurobiol. 2010 Nov;92(3):386-404. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2010.06.005. Epub 2010 Jun 15. Prog Neurobiol. 2010. PMID: 20558237 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Calpain and Proteasomes in the Degradation of Carbonylated Neuronal Cytoskeletal Proteins in Acute Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis.Neurochem Res. 2018 Dec;43(12):2277-2287. doi: 10.1007/s11064-018-2648-y. Epub 2018 Sep 24. Neurochem Res. 2018. PMID: 30251207
-
Effects of a novel orally administered calpain inhibitor SNJ-1945 on immunomodulation and neurodegeneration in a murine model of multiple sclerosis.J Neurochem. 2014 Jul;130(2):268-79. doi: 10.1111/jnc.12659. Epub 2014 Feb 12. J Neurochem. 2014. PMID: 24447070 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Banati RB, Gehrmann J, Schubert P, Kreutzberg GW. Cytotoxicity of microglia. Glia. 1993;7:111–118. - PubMed
-
- Banik NL, Hogan EL, Whetstine LJ, Balentine JD. Changes in myelin and axonal proteins in CaCl2-induced myelopathy in rat spinal cord. Cent Nerv Syst Trauma. 1984;1:131–137. - PubMed
-
- Bartus RT, Hayward NJ, Elliott PJ, Sawyer SD, Baker KL, Dean RL, Akiyama A, Straub JA, Harbeson SL, Li Z, et al. Calpain inhibitor AK295 protects neurons from focal brain ischemia. Effects of postocclusion intra-arterial administration. Stroke. 1994;25:2265–2270. - PubMed
-
- Benveniste EN. Role of macrophages/microglia in multiple sclerosis and experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Mol Med. 1997;75:165–173. - PubMed
-
- Bjartmar C, Battistuta J, Terada N, Dupree E, Trapp BD. N-acetylaspartate is an axon-specific marker of mature white matter in vivo: a biochemical and immunohistochemical study on the rat optic nerve. Ann Neurol. 2002;51:51–58. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

