SEL1L nucleates a protein complex required for dislocation of misfolded glycoproteins
- PMID: 18711132
- PMCID: PMC2527910
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0805371105
SEL1L nucleates a protein complex required for dislocation of misfolded glycoproteins
Abstract
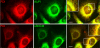
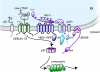
Membrane and secretory proteins that fail to pass quality control in the endoplasmic reticulum are discharged into the cytosol and degraded by the proteasome. Many of the mammalian components involved in this process remain to be identified. We performed a biochemical search for proteins that interact with SEL1L, a protein that is part of the mammalian HRD1 ligase complex and involved in substrate recognition. SEL1L is crucial for dislocation of Class I major histocompatibility complex heavy chains by the human cytomegalovirus US11 protein. We identified AUP1, UBXD8, UBC6e, and OS9 as functionally important components of this degradation complex in mammalian cells, as confirmed by mutagenesis and dominant negative versions of these proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


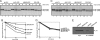
Similar articles
-
SEL1L, the homologue of yeast Hrd3p, is involved in protein dislocation from the mammalian ER.J Cell Biol. 2006 Oct 23;175(2):261-70. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200605196. Epub 2006 Oct 16. J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 17043138 Free PMC article.
-
Multiprotein complexes that link dislocation, ubiquitination, and extraction of misfolded proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum membrane.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Oct 4;102(40):14296-301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0505014102. Epub 2005 Sep 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 16186509 Free PMC article.
-
Association of the SEL1L protein transmembrane domain with HRD1 ubiquitin ligase regulates ERAD-L.FEBS J. 2016 Jan;283(1):157-72. doi: 10.1111/febs.13564. Epub 2015 Nov 6. FEBS J. 2016. PMID: 26471130
-
Identifying the ERAD ubiquitin E3 ligases for viral and cellular targeting of MHC class I.Mol Immunol. 2015 Dec;68(2 Pt A):106-11. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2015.07.005. Epub 2015 Jul 22. Mol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26210183 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of productive folding and endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation of glycoproteins and non-glycoproteins.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2021 Mar;1865(3):129812. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2020.129812. Epub 2020 Dec 11. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2021. PMID: 33316349 Review.
Cited by
-
SEL1L, an UPR response protein, a potential marker of colonic cell transformation.Dig Dis Sci. 2012 Apr;57(4):905-12. doi: 10.1007/s10620-011-2026-y. Epub 2012 Feb 16. Dig Dis Sci. 2012. PMID: 22350780 Free PMC article.
-
Subunit architecture of the Golgi Dsc E3 ligase required for sterol regulatory element-binding protein (SREBP) cleavage in fission yeast.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jul 19;288(29):21043-21054. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.468215. Epub 2013 Jun 12. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23760507 Free PMC article.
-
How Is the Fidelity of Proteins Ensured in Terms of Both Quality and Quantity at the Endoplasmic Reticulum? Mechanistic Insights into E3 Ubiquitin Ligases.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 19;22(4):2078. doi: 10.3390/ijms22042078. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33669844 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tay-Sachs disease mutations in HEXA target the α chain of hexosaminidase A to endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation.Mol Biol Cell. 2016 Dec 1;27(24):3813-3827. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E16-01-0012. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Mol Biol Cell. 2016. PMID: 27682588 Free PMC article.
-
SEL1L-HRD1 ER-associated degradation suppresses hepatocyte hyperproliferation and liver cancer.iScience. 2022 Sep 24;25(10):105183. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.105183. eCollection 2022 Oct 21. iScience. 2022. PMID: 36238898 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ellgaard L, Helenius A. Quality control in the endoplasmic reticulum. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003;4(3):181–191. - PubMed
-
- Tortorella D, Gewurz B, Schust D, Furman M, Ploegh H. Down-regulation of MHC class I antigen presentation by HCMV; lessons for tumor immunology. Immunol Invest. 2000;29(2):97–100. - PubMed
-
- Wiertz EJ, et al. The human cytomegalovirus US11 gene product dislocates MHC class I heavy chains from the endoplasmic reticulum to the cytosol. Cell. 1996;84(5):769–779. - PubMed
-
- Wiertz EJ, et al. Sec61-mediated transfer of a membrane protein from the endoplasmic reticulum to the proteasome for destruction. Nature. 1996;384(6608):432–438. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

