The histone acetyltransferase PCAF associates with actin and hnRNP U for RNA polymerase II transcription
- PMID: 18710935
- PMCID: PMC2577438
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00766-08
The histone acetyltransferase PCAF associates with actin and hnRNP U for RNA polymerase II transcription
Abstract
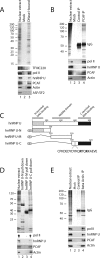
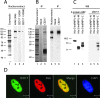
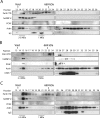
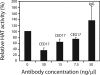
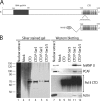
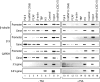
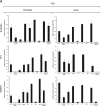
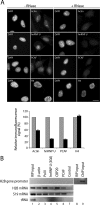
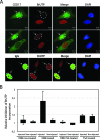
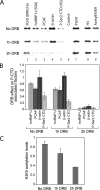
Actin is a key regulator of RNA polymerase (pol) II transcription. In complex with specific hnRNPs, it has been proposed that actin functions to recruit pol II coactivators during the elongation of nascent transcripts. Here, we show by affinity chromatography, protein-protein interaction assays, and biochemical fractionation of nuclear extracts that the histone acetyltransferase (HAT) PCAF associates with actin and hnRNP U. PCAF and the nuclear actin-associated HAT activity detected in the DNase I-bound protein fraction could be released by disruption of the actin-hnRNP U complex. In addition, actin, hnRNP U, and PCAF were found to be associated with the Ser2/5- and Ser2-phosphorylated pol II carboxy-terminal domain construct. Chromatin and RNA immunoprecipitation assays demonstrated that actin, hnRNP U, and PCAF are present at the promoters and coding regions of constitutively expressed pol II genes and that they are associated with ribonucleoprotein complexes. Finally, disruption of the actin-hnRNP U interaction repressed bromouridine triphosphate incorporation in living cells, suggesting that actin and hnRNP U cooperate with PCAF in the regulation of pol II transcription elongation.
Figures
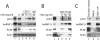

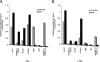
Similar articles
-
Actin and hnRNP U cooperate for productive transcription by RNA polymerase II.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2005 Mar;12(3):238-44. doi: 10.1038/nsmb904. Epub 2005 Feb 13. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2005. PMID: 15711563
-
H19 inhibits RNA polymerase II-mediated transcription by disrupting the hnRNP U-actin complex.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Oct;1830(10):4899-906. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.06.026. Epub 2013 Jun 27. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23811339
-
hnRNP U inhibits carboxy-terminal domain phosphorylation by TFIIH and represses RNA polymerase II elongation.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Oct;19(10):6833-44. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.10.6833. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10490622 Free PMC article.
-
The role of SAF-A/hnRNP U in regulating chromatin structure.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2022 Feb;72:38-44. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2021.10.008. Epub 2021 Nov 22. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2022. PMID: 34823151 Review.
-
Co-transcriptional nuclear actin dynamics.Nucleus. 2013 Jan-Feb;4(1):43-52. doi: 10.4161/nucl.22798. Epub 2012 Nov 8. Nucleus. 2013. PMID: 23138849 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Role for Nuclear Actin in HDAC 1 and 2 Regulation.Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 27;6:28460. doi: 10.1038/srep28460. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27345839 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear actin: ancient clue to evolution in eukaryotes?Histochem Cell Biol. 2018 Sep;150(3):235-244. doi: 10.1007/s00418-018-1693-6. Epub 2018 Jul 17. Histochem Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 30019087 Review.
-
Targeting of a Photosensitizer to the Mitochondrion Enhances the Potency of Photodynamic Therapy.ACS Omega. 2018 Jun 30;3(6):6066-6074. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.8b00692. Epub 2018 Jun 5. ACS Omega. 2018. PMID: 30023938 Free PMC article.
-
Flow-enhanced priming of hESCs through H2B acetylation and chromatin decondensation.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019 Nov 27;10(1):349. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1454-z. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31775893 Free PMC article.
-
Biological functions and clinic significance of SAF‑A (Review).Biomed Rep. 2024 Apr 10;20(6):88. doi: 10.3892/br.2024.1776. eCollection 2024 Jun. Biomed Rep. 2024. PMID: 38665420 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brand, M., K. Yamamoto, A. Staub, and L. Tora. 1999. Identification of TATA-binding protein-free TAFII-containing complex subunits suggests a role in nucleosome acetylation and signal transduction. J. Biol. Chem. 27418285-18289. - PubMed
-
- Fomproix, N., and P. Percipalle. 2004. An actin-myosin complex on actively transcribing genes. Exp. Cell Res. 294140-148. - PubMed
-
- Gilbert, C., A. Kristjuhan, G. S. Winkler, and J. Q. Svejstrup. 2004. Elongator interactions with nascent mRNA revealed by RNA immunoprecipitation. Mol. Cell 14:457-464. - PubMed
-
- Hofmann, W. A., L. Stojiljkovic, B. Fuchsova, G. M. Vargas, E. Mavrommatis, V. Philimonenko, K. Kysela, J. A. Goodrich, J. L. Lessard, T. J. Hope, P. Hozak, and P. de Lanerolle. 2004. Actin is part of pre-initiation complexes and is necessary for transcription by RNA polymerase II. Nat. Cell Biol. 6:1094-1101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
