Adenine nucleotide changes in the remnant liver: An early signal for regeneration after partial hepatectomy
- PMID: 18697206
- PMCID: PMC3348855
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.22421
Adenine nucleotide changes in the remnant liver: An early signal for regeneration after partial hepatectomy
Abstract
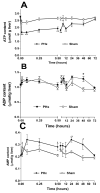
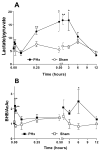
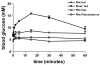
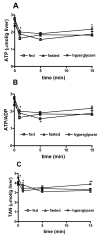
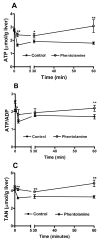
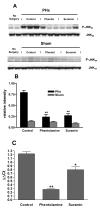
Liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy (PHx) is orchestrated by multiple signals from cytokines and growth factors. We investigated whether increased energy demand on the remnant liver after PHx contributes to regenerative signals. Changes in the tissue's energy state were determined from adenine nucleotide levels. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) levels in remnant livers decreased markedly and rapidly (to 48% of control by 30 seconds post-PHx) and remained significantly lower than those in sham-operated controls for 24 to 48 hours. The ATP decrease was not reflected in corresponding increases in adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and adenosine monophosphate (AMP), resulting in a marked decline in total adenine nucleotides (TAN). We found no evidence of mitochondrial damage or uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation. Multiple lines of evidence indicated that the decline in TAN was not caused by increased energy demand, but by ATP release from the liver. The extent of ATP loss was identical after 30% or 70% PHx, whereas fasting or hyperglycemia, conditions that greatly alter energy demand for gluconeogenesis, affected the ATP/ADP decline but not the loss of TAN. Presurgical treatment with the alpha-adrenergic antagonist phentolamine completely prevented loss of TAN, although changes in ATP/ADP were still apparent. Importantly, phentolamine treatment inhibited early signaling events associated with the priming stages of liver regeneration and suppressed the expression of c-fos. Pretreatment with the purinergic receptor antagonist suramin also partly suppressed early regenerative signals and c-fos expression, but without preventing TAN loss.
Conclusion: The rapid loss of adenine nucleotides after PHx generates early stress signals that contribute to the onset of liver regeneration.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Absence of mitochondrial enhancement in the remnant liver after partial hepatectomy in cirrhotic rats.Res Exp Med (Berl). 1992;192(2):89-97. doi: 10.1007/BF02576262. Res Exp Med (Berl). 1992. PMID: 1529168
-
Circulating hepatodepressant factors decreasing the energy charge levels of the remnant liver after hepatectomy.Eur Surg Res. 1981;13(6):444-57. doi: 10.1159/000128213. Eur Surg Res. 1981. PMID: 7338265
-
Regenerative activity and liver function following partial hepatectomy in the rat using (31)P-MR spectroscopy.Hepatology. 2002 Aug;36(2):345-53. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2002.34742. Hepatology. 2002. PMID: 12143042
-
Regulation of the mitochondrial adenine nucleotide pool size in liver: mechanism and metabolic role.FASEB J. 1988 Jul;2(10):2547-56. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.10.3290024. FASEB J. 1988. PMID: 3290024 Review.
-
Role of shear stress and immune responses in liver regeneration after a partial hepatectomy.Surg Today. 1999;29(1):1-9. doi: 10.1007/BF02482962. Surg Today. 1999. PMID: 9934824 Review.
Cited by
-
Longitudinal ultrasound imaging and network modeling in rats reveal sex-dependent suppression of liver regeneration after resection in alcoholic liver disease.Front Physiol. 2023 Mar 9;14:1102393. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1102393. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36969577 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological ceramide reduction alleviates alcohol-induced steatosis and hepatomegaly in adiponectin knockout mice.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014 Jun 1;306(11):G959-73. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00395.2013. Epub 2014 Apr 17. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24742988 Free PMC article.
-
P2Y2 purinergic receptor activation is essential for efficient hepatocyte proliferation in response to partial hepatectomy.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014 Dec 1;307(11):G1073-87. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00092.2014. Epub 2014 Oct 9. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25301185 Free PMC article.
-
Single-Cell Gene Expression Analysis Identifies Chronic Alcohol-Mediated Shift in Hepatocyte Molecular States After Partial Hepatectomy.Gene Expr. 2019 Apr 18;19(2):97-119. doi: 10.3727/105221618X15361728786767. Epub 2018 Sep 6. Gene Expr. 2019. PMID: 30189915 Free PMC article.
-
Purinergic signaling in liver disease.Dig Dis. 2014;32(5):516-24. doi: 10.1159/000360498. Epub 2014 Jul 14. Dig Dis. 2014. PMID: 25034284 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Michalopoulos GK, DeFrances MC. Liver regeneration. Science. 1997;276:60–66. - PubMed
-
- Taub R. Liver regeneration: from myth to mechanism. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2004;5:836–847. - PubMed
-
- Fausto N, Campbell JS, Riehle KJ. Liver regeneration. Hepatology. 2006;43:S45–53. - PubMed
-
- Higgins G, Anderson R. Experimental pathology of the liver: 1. Restoration of the liver of the white rat following partial surgical removal. Arch Pathol. 1931;12:186–202.
-
- Ngala Kenda JF, de Hemptinne B, Lambotte L. Role of metabolic overload in the initiation of DNA synthesis following partial hepatectomy in the rat. Eur Surg Res. 1984;16:294–302. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
