Structural basis for cargo regulation of COPII coat assembly
- PMID: 18692470
- PMCID: PMC2649882
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.06.024
Structural basis for cargo regulation of COPII coat assembly
Abstract
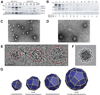
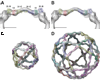
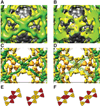
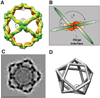
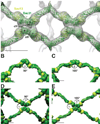
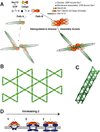
Using cryo-electron microscopy, we have solved the structure of an icosidodecahedral COPII coat involved in cargo export from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) coassembled from purified cargo adaptor Sec23-24 and Sec13-31 lattice-forming complexes. The coat structure shows a tetrameric assembly of the Sec23-24 adaptor layer that is well positioned beneath the vertices and edges of the Sec13-31 lattice. Fitting the known crystal structures of the COPII proteins into the density map reveals a flexible hinge region stemming from interactions between WD40 beta-propeller domains present in Sec13 and Sec31 at the vertices. The structure shows that the hinge region can direct geometric cage expansion to accommodate a wide range of bulky cargo, including procollagen and chylomicrons, that is sensitive to adaptor function in inherited disease. The COPII coat structure leads us to propose a mechanism by which cargo drives cage assembly and membrane curvature for budding from the ER.
Figures
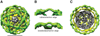
Comment in
-
Both layers of the COPII coat come into view.Cell. 2008 Aug 8;134(3):384-5. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.07.027. Cell. 2008. PMID: 18692460
Similar articles
-
Structure of the Sec13/31 COPII coat cage.Nature. 2006 Jan 12;439(7073):234-8. doi: 10.1038/nature04339. Nature. 2006. PMID: 16407955
-
Efficient coupling of Sec23-Sec24 to Sec13-Sec31 drives COPII-dependent collagen secretion and is essential for normal craniofacial development.J Cell Sci. 2008 Sep 15;121(Pt 18):3025-34. doi: 10.1242/jcs.031070. Epub 2008 Aug 19. J Cell Sci. 2008. PMID: 18713835
-
The structure of the Sec13/31 COPII cage bound to Sec23.J Mol Biol. 2012 Jul 20;420(4-5):324-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2012.04.024. Epub 2012 Apr 26. J Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22543240 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into the structural mechanisms of the COPII coat.Traffic. 2010 Mar;11(3):303-10. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2009.01026.x. Epub 2009 Dec 7. Traffic. 2010. PMID: 20070605 Review.
-
COPII coat assembly and selective export from the endoplasmic reticulum.J Biochem. 2004 Dec;136(6):755-60. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvh184. J Biochem. 2004. PMID: 15671485 Review.
Cited by
-
ER exit in physiology and disease.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Jan 18;11:1352970. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1352970. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38314136 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SEA you later alli-GATOR--a dynamic regulator of the TORC1 stress response pathway.J Cell Sci. 2015 Jun 15;128(12):2219-28. doi: 10.1242/jcs.168922. Epub 2015 May 1. J Cell Sci. 2015. PMID: 25934700 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Traffic of p24 Proteins and COPII Coat Composition Mutually Influence Membrane Scaffolding.Curr Biol. 2015 May 18;25(10):1296-305. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2015.03.029. Epub 2015 Apr 30. Curr Biol. 2015. PMID: 25936552 Free PMC article.
-
New putative chloroplast vesicle transport components and cargo proteins revealed using a bioinformatics approach: an Arabidopsis model.PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e59898. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059898. Epub 2013 Apr 1. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23573218 Free PMC article.
-
The highly conserved COPII coat complex sorts cargo from the endoplasmic reticulum and targets it to the golgi.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013 Feb 1;5(2):a013367. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a013367. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013. PMID: 23378591 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Antonny B, Bigay J, Casella JF, Drin G, Mesmin B, Gounon P. Membrane curvature and the control of GTP hydrolysis in Arf1 during COPI vesicle formation. Biochem Soc Trans. 2005;33:619–622. - PubMed
-
- Aridor M, Bannykh SI, Rowe T, Balch WE. Cargo can modulate COPII vesicle formation from the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:4389–4399. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 GM042336/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR017573/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- GM42336/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F32 GM073509/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR017573-07/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R33 EB000798-04/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R33 EB000798/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM042336-17S1/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM073509/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- RR17573/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- F32 GM073509-02/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R33EB00798/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

