Multifunctional hydrogels that promote osteogenic hMSC differentiation through stimulation and sequestering of BMP2
- PMID: 18688288
- PMCID: PMC2500208
- DOI: 10.1002/adfm.200700012
Multifunctional hydrogels that promote osteogenic hMSC differentiation through stimulation and sequestering of BMP2
Abstract
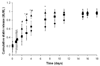
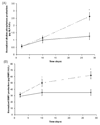
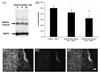
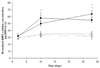
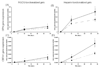
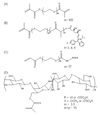
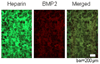
The extracellular environment controls many cellular activities thereby linking external material cues to internal cell function. By better understanding these processes, synthetic extracellular material niches can be tailored to present cells with highly regulated physical and/or chemical cues that promote or suppress selected cell functions. Here, poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) hydrogels were functionalized with fluvastatin-releasing grafts and growth factor binding heparin domains to enable the dynamic exchange of information between the material and cells from the outside-in and inside-out (i.e., bidirectional signaling). By incorporating a fluvastatin-releasing graft and carefully controlling the dose and temporal release, materials were designed to promote bone morphogenic protein (BMP2) and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) production by human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs). When the release of fluvastatin was controlled to occur over 2 weeks, BMP2 and ALP production was increased 2.2-fold and 1.7-fold, respectively, at day 28 compared to hMSCs cultured in the absence of fluvastatin. By introducing a heparin functionality into the gel to sequester and localize the hMSC-produced BMP2, the osteogenic differentiation of hMSCs was further augmented over fluvastatin delivery alone. Osteopontin and core binding factor α1 gene expression was 6-fold and 4-fold greater for hMSCs exposed to fluvastatin in the presence of the heparin functionalities, respectively. These results demonstrate how multifunctional gels that interact with cells in a bidirectional manner can efficiently promote selected cell functions, such as the osteogenic differentiation of hMSCs.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synthesis and characterization of a fluvastatin-releasing hydrogel delivery system to modulate hMSC differentiation and function for bone regeneration.Biomaterials. 2006 Dec;27(36):6102-10. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2006.06.031. Epub 2006 Jul 24. Biomaterials. 2006. PMID: 16860387
-
The effect of heparin-functionalized PEG hydrogels on three-dimensional human mesenchymal stem cell osteogenic differentiation.Biomaterials. 2007 Jan;28(1):66-77. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2006.08.033. Epub 2006 Sep 8. Biomaterials. 2007. PMID: 16963119
-
Osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells on α5 integrin binding peptide hydrogels is dependent on substrate elasticity.Biomater Sci. 2014 Mar 1;2(3):352-361. doi: 10.1039/C3BM60149H. Biomater Sci. 2014. PMID: 24660057 Free PMC article.
-
Spatiotemporal release of BMP-2 and VEGF enhances osteogenic and vasculogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells and endothelial colony-forming cells co-encapsulated in a patterned hydrogel.J Control Release. 2016 Feb 10;223:126-136. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.12.031. Epub 2015 Dec 22. J Control Release. 2016. PMID: 26721447 Free PMC article.
-
Dexamethasone-functionalized gels induce osteogenic differentiation of encapsulated hMSCs.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2006 Jan;76(1):183-95. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.30537. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2006. PMID: 16265650
Cited by
-
An improved cryosection method for polyethylene glycol hydrogels used in tissue engineering.Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2013 Oct;19(10):794-801. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEC.2012.0460. Epub 2013 Apr 19. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2013. PMID: 23448137 Free PMC article.
-
Migration of marrow stromal cells in response to sustained release of stromal-derived factor-1alpha from poly(lactide ethylene oxide fumarate) hydrogels.Int J Pharm. 2010 May 10;390(2):107-16. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2009.12.063. Epub 2010 Feb 26. Int J Pharm. 2010. PMID: 20219655 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of mesenchymal stem cells delivered via hydrogel-based tissue engineered periosteum on bone allograft healing.Biomaterials. 2013 Nov;34(35):8887-98. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.08.005. Epub 2013 Aug 16. Biomaterials. 2013. PMID: 23958029 Free PMC article.
-
Microwave-assisted functionalization of poly(ethylene glycol) and on-resin peptides for use in chain polymerizations and hydrogel formation.J Vis Exp. 2013 Oct 29;(80):e50890. doi: 10.3791/50890. J Vis Exp. 2013. PMID: 24193366 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging strategies for spatiotemporal control of stem cell fate and morphogenesis.Trends Biotechnol. 2013 Feb;31(2):78-84. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2012.11.001. Epub 2012 Dec 5. Trends Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 23219200 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
