The arthritis severity locus Cia5d is a novel genetic regulator of the invasive properties of synovial fibroblasts
- PMID: 18668563
- PMCID: PMC2714698
- DOI: 10.1002/art.23610
The arthritis severity locus Cia5d is a novel genetic regulator of the invasive properties of synovial fibroblasts
Abstract
Objective: The synovial fibroblast, or fibroblast-like synoviocyte (FLS), has a central role in pannus invasion and destruction of cartilage and bone in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). However, regulation of the FLS remains incompletely understood. The aim of this study was to determine whether the invasive properties of FLS are genetically regulated by arthritis severity loci.
Methods: DA rats (arthritis susceptible) and rat strains congenic for arthritis-protective intervals were studied. Primary FLS cell lines were generated from each strain and used in a well-established FLS invasion model through a collagen-rich barrier. Cells or culture supernatants were analyzed for gene expression, activity of different matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), cytoskeleton integrity, and cell proliferation.
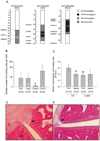
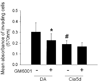
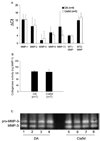
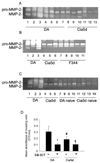
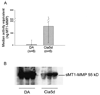
Results: The median number of FLS from DA.F344(Cia5d) rats that invaded through the collagen-rich barrier was reduced 86.5% compared with the median number of invading FLS from DA rats. Histologic examination showed that DA.F344(Cia5d) rats preserved a normal joint without pannus, hyperplasia, or erosions. FLS from DA.F344(Cia5d) rats produced significantly lower levels of active MMP-2 compared with FLS from DA rats, but the levels of proMMP-2 and MMP-2 messenger RNA in DA.F344(Cia5d) rats were similar to those in DA rats. Treatment of FLS from DA rats with an MMP-2 inhibitor reduced cell invasion to a level similar to that in DA.F344(Cia5d) rats, demonstrating that MMP-2 activity accounted for the difference between FLS from these 2 strains. Analysis of MMP-2-activating pathways revealed increased levels of soluble membrane type 1 (MT1)-MMP in DA rats compared with DA.F344(Cia5d) rats.
Conclusion: These data represent the first evidence for a genetic component in the regulation of FLS invasion. A gene located within the Cia5d interval accounts for this effect and operates via the regulation of soluble MT1-MMP production and MMP-2 activation. These observations suggest novel potential pathways for prognostication and therapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Liver X receptor regulates rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocyte invasiveness, matrix metalloproteinase 2 activation, interleukin-6 and CXCL10.Mol Med. 2012 Sep 7;18(1):1009-17. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2012.00173. Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22634718 Free PMC article.
-
CXCL10 and its receptor CXCR3 regulate synovial fibroblast invasion in rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2011 Nov;63(11):3274-83. doi: 10.1002/art.30573. Arthritis Rheum. 2011. PMID: 21811993 Free PMC article.
-
Cia5d regulates a new fibroblast-like synoviocyte invasion-associated gene expression signature.Arthritis Res Ther. 2008;10(4):R92. doi: 10.1186/ar2476. Epub 2008 Aug 15. Arthritis Res Ther. 2008. PMID: 18706093 Free PMC article.
-
The non-MHC quantitative trait locus Cia5 contains three major arthritis genes that differentially regulate disease severity, pannus formation, and joint damage in collagen- and pristane-induced arthritis.J Immunol. 2005 Jun 15;174(12):7894-903. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.12.7894. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15944295
-
Membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase is a crucial promoter of synovial invasion in human rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2009 Mar;60(3):686-97. doi: 10.1002/art.24331. Arthritis Rheum. 2009. PMID: 19248098 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Liver X receptor regulates rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocyte invasiveness, matrix metalloproteinase 2 activation, interleukin-6 and CXCL10.Mol Med. 2012 Sep 7;18(1):1009-17. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2012.00173. Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22634718 Free PMC article.
-
A review of the pleiotropic actions of the IFN-inducible CXC chemokine receptor 3 ligands in the synovial microenvironment.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023 Mar 2;80(3):78. doi: 10.1007/s00018-023-04715-w. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 36862204 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KCa1.1 and Kv1.3 channels regulate the interactions between fibroblast-like synoviocytes and T lymphocytes during rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2019 Jan 7;21(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s13075-018-1783-9. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 30612588 Free PMC article.
-
CXCL10 and its receptor CXCR3 regulate synovial fibroblast invasion in rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2011 Nov;63(11):3274-83. doi: 10.1002/art.30573. Arthritis Rheum. 2011. PMID: 21811993 Free PMC article.
-
KCa1.1 inhibition attenuates fibroblast-like synoviocyte invasiveness and ameliorates disease in rat models of rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015 Jan;67(1):96-106. doi: 10.1002/art.38883. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 25252152 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gregersen PK, Plenge RM, Gulko PS. Genetics of rheumatoid arthritis. In: Firestein G, Panayi G, Wollheim FA, editors. Rheumatoid arthritis. 2nd ed. New York: Oxford University Press; 2006. pp. 3–14.
-
- Gulko PS, Winchester RJ. Rheumatoid arthritis. In: Austen KF, Frank MM, Atkinson JP, Cantor H, editors. Samter’s immunologic diseases. 6th ed. Baltimore: Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins; 2001. pp. 427–463.
-
- Okada Y, Morodomi T, Enghild JJ, Suzuki K, Yasui A, Nakanishi I, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase 2 from human rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts: purification and activation of the precursor and enzymic properties. Eur J Biochem. 1990;194:721–730. - PubMed
-
- Hanemaaijer R, Sorsa T, Konttinen YT, Ding Y, Sutinen M, Visser H, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-8 is expressed in rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts and endothelial cells: regulation by tumor necrosis factor-α and doxycycline. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:31504–31509. - PubMed
-
- Lee DM, Kiener HP, Agarwal SK, Noss EH, Watts GF, Chisaka O, et al. Cadherin-11 in synovial lining formation and pathology in arthritis. Science. 2007;315:1006–1010. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AR046213-06/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR052439-02/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI054348/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR 46213/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI 54348/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR046213-04/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR046213/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR052439/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI054348-04/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR052439-04/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR052439-01A1/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI054348-05/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR046213-05/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR 052439/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR046213-07A2/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR052439-03/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR046213-08/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

