All translation elongation factors and the e, f, and h subunits of translation initiation factor 3 are encoded by 5'-terminal oligopyrimidine (TOP) mRNAs
- PMID: 18658124
- PMCID: PMC2525946
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.1037108
All translation elongation factors and the e, f, and h subunits of translation initiation factor 3 are encoded by 5'-terminal oligopyrimidine (TOP) mRNAs
Abstract
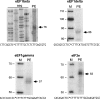
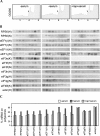
Terminal oligopyrimidine (TOP) mRNAs (encoded by the TOP genes) are identified by a sequence of 6-12 pyrimidines at the 5' end and by a growth-associated translational regulation. All vertebrate genes for the 80 ribosomal proteins and some other genes involved, directly or indirectly, in translation, are TOP genes. Among the numerous translation factors, only eEF1A and eEF2 are known to be encoded by TOP genes, most of the others having not been analyzed. Here, we report a systematic analysis of the human genes for translation factors. Our results show that: (1) all five elongation factors are encoded by TOP genes; and (2) among the initiation and termination factors analyzed, only eIF3e, eIF3f, and eIF3h exhibit the characteristics of TOP genes. Interestingly, these three polypeptides have been recently shown to constitute a specific subgroup among eIF3 subunits. In fact, eIF3e, eIF3f, and eIF3h are the part of the functional core of eIF3 that is not conserved in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. It has been hypothesized that they are regulatory subunits, and the fact that they are encoded by TOP genes may be relevant for their function.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of the cardiomyocyte transcriptome vs translatome by endothelin-1 and insulin: translational regulation of 5' terminal oligopyrimidine tract (TOP) mRNAs by insulin.BMC Genomics. 2010 May 29;11:343. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-343. BMC Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20509958 Free PMC article.
-
Translational regulation via 5' mRNA leader sequences revealed by mutational analysis of the Arabidopsis translation initiation factor subunit eIF3h.Plant Cell. 2004 Dec;16(12):3341-56. doi: 10.1105/tpc.104.026880. Epub 2004 Nov 17. Plant Cell. 2004. PMID: 15548739 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosomal stress activates eEF2K-eEF2 pathway causing translation elongation inhibition and recruitment of terminal oligopyrimidine (TOP) mRNAs on polysomes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Nov 10;42(20):12668-80. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku996. Epub 2014 Oct 20. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 25332393 Free PMC article.
-
Mitogenic and nutritional signals are transduced into translational efficiency of TOP mRNAs.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2001;66:477-84. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2001.66.477. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2001. PMID: 12762050 Review. No abstract available.
-
Ribosomal protein S6 kinase from TOP mRNAs to cell size.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2009;90:109-53. doi: 10.1016/S1877-1173(09)90003-5. Epub 2009 Oct 27. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2009. PMID: 20374740 Review.
Cited by
-
Non-Canonical Targets of MicroRNAs: Role in Transcriptional Regulation, Disease Pathogenesis and Potential for Therapeutic Targets.Microrna. 2024;13(2):83-95. doi: 10.2174/0122115366278651240105071533. Microrna. 2024. PMID: 38317474 Review.
-
Tau drives translational selectivity by interacting with ribosomal proteins.Acta Neuropathol. 2019 Apr;137(4):571-583. doi: 10.1007/s00401-019-01970-9. Epub 2019 Feb 13. Acta Neuropathol. 2019. PMID: 30759285 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis of CCHC-type zinc finger (ZCCHC) proteins in yeast, Arabidopsis, and humans.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020 Oct;77(20):3991-4014. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03518-7. Epub 2020 Apr 18. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32303790 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TORC1 and TORC2 work together to regulate ribosomal protein S6 phosphorylation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Biol Cell. 2016 Jan 15;27(2):397-409. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E15-08-0594. Epub 2015 Nov 18. Mol Biol Cell. 2016. PMID: 26582391 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorescently-tagged human eIF3 for single-molecule spectroscopy.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jan 25;46(2):e8. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1050. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29136179 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asano K., Vornlocher H.P., Richter-Cook N.J., Merrick W.C., Hinnebusch A.G., Hershey J.W. Structure of cDNAs encoding human eukaryotic initiation factor 3 subunits. Possible roles in RNA binding and macromolecular assembly. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:27042–27052. - PubMed
-
- Caldarola S., Amaldi F., Proud C.G., Loreni F. Translational regulation of terminal oligopyrimidine mRNAs induced by serum and amino acids involves distinct signaling events. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:13522–13531. - PubMed
-
- Cardinali B., Carissimi C., Gravina P., Pierandrei-Amaldi P. La protein is associated with terminal oligopyrimidine mRNAs in actively translating polysomes. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:35145–35151. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
