Design of compact, universal DNA microarrays for protein binding microarray experiments
- PMID: 18651798
- PMCID: PMC3203512
- DOI: 10.1089/cmb.2007.0114
Design of compact, universal DNA microarrays for protein binding microarray experiments
Abstract
Our group has recently developed a compact, universal protein binding microarray (PBM) that can be used to determine the binding preferences of transcription factors (TFs). This design represents all possible sequence variants of a given length k (i.e., all k-mers) on a single array, allowing a complete characterization of the binding specificities of a given TF. Here, we present the mathematical foundations of this design based on de Bruijn sequences generated by linear feedback shift registers. We show that these sequences represent the maximum number of variants for any given set of array dimensions (i.e., number of spots and spot lengths), while also exhibiting desirable pseudo-randomness properties. Moreover, de Bruijn sequences can be selected that represent gapped sequence patterns, further increasing the coverage of the array. This design yields a powerful experimental platform that allows the binding preferences of TFs to be determined with unprecedented resolution.
Figures
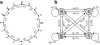
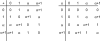
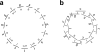
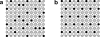
Similar articles
-
Compact, universal DNA microarrays to comprehensively determine transcription-factor binding site specificities.Nat Biotechnol. 2006 Nov;24(11):1429-35. doi: 10.1038/nbt1246. Epub 2006 Sep 24. Nat Biotechnol. 2006. PMID: 16998473 Free PMC article.
-
Universal protein-binding microarrays for the comprehensive characterization of the DNA-binding specificities of transcription factors.Nat Protoc. 2009;4(3):393-411. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2008.195. Nat Protoc. 2009. PMID: 19265799 Free PMC article.
-
Bayesian hierarchical model of protein-binding microarray k-mer data reduces noise and identifies transcription factor subclasses and preferred k-mers.Bioinformatics. 2013 Jun 1;29(11):1390-8. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt152. Epub 2013 Apr 4. Bioinformatics. 2013. PMID: 23559638 Free PMC article.
-
Protein binding microarrays for the characterization of DNA-protein interactions.Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2007;104:65-85. doi: 10.1007/10_025. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2007. PMID: 17290819 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Double-stranded DNA microarray: principal, techniques and applications].Yi Chuan. 2013 Mar;35(3):287-306. doi: 10.3724/sp.j.1005.2013.00287. Yi Chuan. 2013. PMID: 23575535 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Building the developmental oculome: systems biology in vertebrate eye development and disease.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2010 May-Jun;2(3):305-323. doi: 10.1002/wsbm.59. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2010. PMID: 20836031 Free PMC article. Review.
-
UniPROBE: an online database of protein binding microarray data on protein-DNA interactions.Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Jan;37(Database issue):D77-82. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn660. Epub 2008 Oct 8. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 18842628 Free PMC article.
-
High-resolution DNA-binding specificity analysis of yeast transcription factors.Genome Res. 2009 Apr;19(4):556-66. doi: 10.1101/gr.090233.108. Epub 2009 Jan 21. Genome Res. 2009. PMID: 19158363 Free PMC article.
-
Determining the specificity of protein-DNA interactions.Nat Rev Genet. 2010 Nov;11(11):751-60. doi: 10.1038/nrg2845. Epub 2010 Sep 28. Nat Rev Genet. 2010. PMID: 20877328 Review.
-
Rapid and systematic analysis of the RNA recognition specificities of RNA-binding proteins.Nat Biotechnol. 2009 Jul;27(7):667-70. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1550. Epub 2009 Jun 28. Nat Biotechnol. 2009. PMID: 19561594
References
-
- Ben-Dor A. Karp R. Schwikowski B., et al. Universal DNA tag systems: a combinatorial design scheme. J. Comput. Biol. 2000;7:503–519. - PubMed
-
- Benos P.V. Lapedes A.S. Stormo G.D. Is there a code for protein-DNA recognition? Probab(ilistical)ly. Bioessays. 2002;24:466–475. - PubMed
-
- Bulyk M.L. Gentalen E. Lockhart D.J., et al. Quantifying DNA-protein interactions by double-stranded DNA arrays. Nat. Biotechnol. 1999;17:573–577. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

