Identification of dopamine D1-D3 receptor heteromers. Indications for a role of synergistic D1-D3 receptor interactions in the striatum
- PMID: 18644790
- PMCID: PMC2533781
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M710349200
Identification of dopamine D1-D3 receptor heteromers. Indications for a role of synergistic D1-D3 receptor interactions in the striatum
Abstract
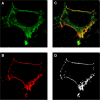
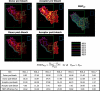
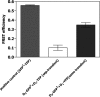
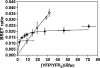
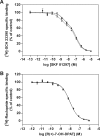
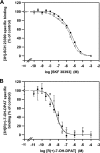
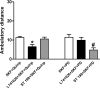
The function of dopamine D(3) receptors present in the striatum has remained elusive. In the present study evidence is provided for the existence of dopamine D(1)-D(3) receptor heteromers and for an intramembrane D(1)-D(3) receptor cross-talk in living cells and in the striatum. The formation of D(1)-D(3) receptor heteromers was demonstrated by fluorescence resonance energy transfer and bioluminescence resonance energy transfer techniques in transfected mammalian cells. In membrane preparations from these cells, a synergistic D(1)-D(3) intramembrane receptor-receptor interaction was observed, by which D(3) receptor stimulation enhances D(1) receptor agonist affinity, indicating that the D(1)-D(3) intramembrane receptor-receptor interaction is a biochemical characteristic of the D(1)-D(3) receptor heteromer. The same biochemical characteristic was also observed in membrane preparations from brain striatum, demonstrating the striatal co-localization and heteromerization of D(1) and D(3) receptors. According to the synergistic D(1)-D(3) intramembrane receptor-receptor interaction, experiments in reserpinized mice showed that D(3) receptor stimulation potentiates D(1) receptor-mediated behavioral effects by a different mechanism than D(2) receptor stimulation. The present study shows that a main functional significance of the D(3) receptor is to obtain a stronger dopaminergic response in the striatal neurons that co-express the two receptors.
Figures
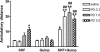
Similar articles
-
Biased G Protein-Independent Signaling of Dopamine D1-D3 Receptor Heteromers in the Nucleus Accumbens.Mol Neurobiol. 2019 Oct;56(10):6756-6769. doi: 10.1007/s12035-019-1564-8. Epub 2019 Mar 27. Mol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 30919214 Free PMC article.
-
Dimerization of dopamine D1 and D3 receptors in the regulation of striatal function.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2010 Feb;10(1):87-92. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2009.09.008. Epub 2009 Oct 17. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 19837631 Review.
-
Interactions between histamine H3 and dopamine D2 receptors and the implications for striatal function.Neuropharmacology. 2008 Aug;55(2):190-7. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2008.05.008. Epub 2008 May 16. Neuropharmacology. 2008. PMID: 18547596 Free PMC article.
-
Stronger Dopamine D1 Receptor-Mediated Neurotransmission in Dyskinesia.Mol Neurobiol. 2015 Dec;52(3):1408-1420. doi: 10.1007/s12035-014-8936-x. Epub 2014 Oct 26. Mol Neurobiol. 2015. PMID: 25344317
-
Dopamine receptors: homomeric and heteromeric complexes in L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2018 Aug;125(8):1187-1194. doi: 10.1007/s00702-018-1852-x. Epub 2018 Feb 7. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2018. PMID: 29417335 Review.
Cited by
-
Dopamine receptors - IUPHAR Review 13.Br J Pharmacol. 2015 Jan;172(1):1-23. doi: 10.1111/bph.12906. Br J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25671228 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhanced Natriuresis and Diuresis in Wistar Rats Caused by the Costimulation of Renal Dopamine D3 and Angiotensin II Type 2 Receptors.Am J Hypertens. 2015 Oct;28(10):1267-76. doi: 10.1093/ajh/hpv018. Epub 2015 Mar 13. Am J Hypertens. 2015. PMID: 25770092 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Statins on Neurotransmission and Their Neuroprotective Role in Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders.Molecules. 2021 May 11;26(10):2838. doi: 10.3390/molecules26102838. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34064670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adenosine-dopamine interactions in the pathophysiology and treatment of CNS disorders.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2010 Jun;16(3):e18-42. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2009.00126.x. Epub 2010 Mar 16. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2010. PMID: 20345970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential Dopamine D1 and D3 Receptor Modulation and Expression in the Spinal Cord of Two Mouse Models of Restless Legs Syndrome.Front Behav Neurosci. 2018 Sep 4;12:199. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2018.00199. eCollection 2018. Front Behav Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30233336 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Missale, C., Nash, S. R., Robinson, S. W., Jaber, M., and Caron, M. G. (1998) Physiol. Rev. 78 189-225 - PubMed
-
- Neve, K. A., Seamans, J. K., and Trantham-Davidson, H. (2004) J. Recept. Signal Transduct. Res. 24 165-205 - PubMed
-
- Gerfen, C. R. (2004) The Rat Nervous System (Paxinos, G., ed) pp. 445-508, Elsevier Academic Press, Amsterdam
-
- Gerfen, C. R., Engber, T. M., Mahan, L. C., Susel, Z., Chase, T. N., Monsma, F. J., Jr., and Sibley, D. R. (1990) Science 250 1429-1432 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

