The nucleotide receptor P2RX7 mediates ATP-induced CREB activation in human and murine monocytic cells
- PMID: 18625910
- PMCID: PMC2538603
- DOI: 10.1189/jlb.0907612
The nucleotide receptor P2RX7 mediates ATP-induced CREB activation in human and murine monocytic cells
Abstract
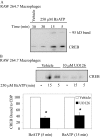
Nucleotide receptors serve as sensors of extracellular ATP and are important for immune function. The nucleotide receptor P2RX7 is a cell-surface, ligand-gated cation channel that has been implicated in many diseases, including arthritis, granuloma formation, sepsis, and tuberculosis. These disorders are often exacerbated by excessive mediator release from activated macrophages in the inflammatory microenvironment. Although P2RX7 activation can modulate monocyte/macrophage-induced inflammatory events, the relevant molecular mechanisms are poorly understood. Previous studies suggest that MAPK cascades and transcriptional control via CREB-linked pathways regulate the inflammatory capacity of monocytic cells. As P2RX7 promotes MAPK activation and inflammatory mediator production, we examined the involvement MAPK-induced CREB activation in P2RX7 action. Our data reveal that stimulation of multiple monocytic cell lines with P2RX7 agonists induces rapid CREB phosphorylation. In addition, we observed a lack of nucleotide-induced CREB phosphorylation in RAW 264.7 cells expressing nonfunctional P2RX7 and a gain of nucleotide-induced CREB phosphorylation in human embryonic kidney-293 cells that heterologously express human P2RX7. Furthermore, our results indicate that P2RX7 agonist-induced CREB phosphorylation is partly mediated via Ca(2+) fluxes and the MEK/ERK system. Mechanistic analyses revealed that macrophage stimulation with a P2RX7 agonist induces CREB/CREB-binding protein complex formation, which is necessary for CREB transcriptional activation. Also, we demonstrate that P2RX7 activation induces a known CREB-dependent gene (c-fos) and that dominant-negative CREB constructs attenuate this response. These studies support the idea that P2RX7 stimulation can directly regulate protein expression that is not dependent on costimulation with other immune modulators such as LPS.
Figures
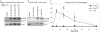



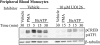
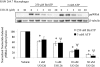
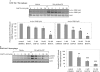
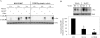
Similar articles
-
Activation of the transcription factor FosB/activating protein-1 (AP-1) is a prominent downstream signal of the extracellular nucleotide receptor P2RX7 in monocytic and osteoblastic cells.J Biol Chem. 2010 Oct 29;285(44):34288-98. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.142091. Epub 2010 Sep 2. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20813842 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular ATP may contribute to tissue repair by rapidly stimulating purinergic receptor X7-dependent vascular endothelial growth factor release from primary human monocytes.J Immunol. 2010 Sep 1;185(5):3028-34. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1001298. Epub 2010 Jul 28. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20668222 Free PMC article.
-
Purinergic receptor modulation of lipopolysaccharide signaling and inducible nitric-oxide synthase expression in RAW 264.7 macrophages.J Biol Chem. 1998 Oct 16;273(42):27170-5. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.42.27170. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9765236
-
Evidence for nucleotide receptor modulation of cross talk between MAP kinase and NF-kappa B signaling pathways in murine RAW 264.7 macrophages.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2004 Apr;286(4):C923-30. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00417.2003. Epub 2003 Dec 18. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2004. PMID: 14684387
-
P2RX7 Purinoceptor as a Therapeutic Target-The Second Coming?Front Chem. 2018 Jun 28;6:248. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2018.00248. eCollection 2018. Front Chem. 2018. PMID: 30003075 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epithelial extracellular ATP: an initiator of immunity to parasitic infections.Immunol Cell Biol. 2017 Feb;95(2):117-118. doi: 10.1038/icb.2016.106. Epub 2016 Nov 22. Immunol Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 27874014 No abstract available.
-
P2X7 receptor as the regulator of T-cell function in intestinal barrier disruption.World J Gastroenterol. 2022 Sep 28;28(36):5265-5279. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i36.5265. World J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36185635 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nucleotide receptor P2RX7 stimulation enhances LPS-induced interferon-β production in murine macrophages.J Leukoc Biol. 2013 Oct;94(4):759-68. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0712351. Epub 2013 Aug 2. J Leukoc Biol. 2013. PMID: 23911869 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional control mechanisms associated with the nucleotide receptor P2X7, a critical regulator of immunologic, osteogenic, and neurologic functions.Immunol Res. 2011 May;50(1):22-38. doi: 10.1007/s12026-011-8203-4. Immunol Res. 2011. PMID: 21298493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The second transmembrane domain of P2X7 contributes to dilated pore formation.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 17;8(4):e61886. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061886. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23613968 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gallucci S, Matzinger P. Danger signals: SOS to the immune system. Curr Opin Immunol. 2001;13:114–119. - PubMed
-
- Khakh B S, North R A. P2X receptors as cell-surface ATP sensors in health and disease. Nature. 2006;442:527–532. - PubMed
-
- Solle M, Labasi J, Perregaux D G, Stam E, Petrushova N, Koller B H, Griffiths R J, Gabel C A. Altered cytokine production in mice lacking P2X(7) receptors. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:125–132. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P50 HL056396/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI070503/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL088594-01A10003/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI050500/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI070503-030002/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HL056396-100004/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AI50500/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL088594/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5 T32 HL07899-09/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI070503-020002/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HL56396/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007899/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

