Limitations and lessons in the use of X-ray structural information in drug design
- PMID: 18617015
- PMCID: PMC7185550
- DOI: 10.1016/j.drudis.2008.06.006
Limitations and lessons in the use of X-ray structural information in drug design
Abstract
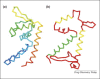
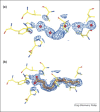
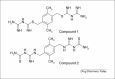
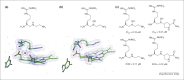
The use of X-ray crystal structure models continues to provide a strong stimulus to drug discovery, through the direct visualisation of ligand–receptor interactions. There is sometimes a limited appreciation of the uncertainties introduced during the process of deriving an atomic model from the experimentally observed electron density. Here, some of these uncertainties are highlighted with recent examples from the literature, together with snippets of advice for the medicinal chemist embarking on using X-ray crystal structure information in a drug discovery programme.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The rational design of inhibitors of nitric oxide formation by inducible nitric oxide synthase.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2007 May 1;17(9):2505-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2007.02.018. Epub 2007 Feb 9. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2007. PMID: 17336523
-
Heteroaromatic-aminomethyl quinolones: potent and selective iNOS inhibitors.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2012 Jan 15;22(2):1237-41. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2011.11.073. Epub 2011 Nov 25. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2012. PMID: 22182498
-
Discovery of highly potent and selective inhibitors of neuronal nitric oxide synthase by fragment hopping.J Med Chem. 2009 Feb 12;52(3):779-97. doi: 10.1021/jm801220a. J Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 19125620 Free PMC article.
-
Fragment-based drug discovery.J Med Chem. 2004 Jul 1;47(14):3463-82. doi: 10.1021/jm040031v. J Med Chem. 2004. PMID: 15214773 Review. No abstract available.
-
Inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibitors: A comprehensive update.Med Res Rev. 2020 May;40(3):823-855. doi: 10.1002/med.21636. Epub 2019 Sep 10. Med Res Rev. 2020. PMID: 31502681 Review.
Cited by
-
Prediction of the water content in protein binding sites.J Phys Chem B. 2009 Oct 8;113(40):13337-46. doi: 10.1021/jp9047456. J Phys Chem B. 2009. PMID: 19754086 Free PMC article.
-
MotiveValidator: interactive web-based validation of ligand and residue structure in biomolecular complexes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Jul;42(Web Server issue):W227-33. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku426. Epub 2014 May 21. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24848013 Free PMC article.
-
Case-controlled structure validation.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2009 Feb;65(Pt 2):140-7. doi: 10.1107/S0907444908041085. Epub 2009 Jan 20. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2009. PMID: 19171969 Free PMC article.
-
Estimation of the protein-ligand interaction energy for model building and validation.Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2017 Mar 1;73(Pt 3):195-202. doi: 10.1107/S2059798317003400. Epub 2017 Mar 6. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2017. PMID: 28291754 Free PMC article.
-
The solvent component of macromolecular crystals.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2015 May;71(Pt 5):1023-38. doi: 10.1107/S1399004715006045. Epub 2015 Apr 30. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2015. PMID: 25945568 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rowland P. Crystal structure of human cytochrome P450 2D6. J. Biol. Chem. 2006;281:7614–7622. - PubMed
-
- Yano J.K. The structure of human microsomal cytochrome P450 3A4 determined by X-ray crystallography to 2.05-A resolution. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:38091–38094. - PubMed
-
- Williams P.A. Crystal structures of human cytochrome P450 3A4 bound to metyrapone and progesterone. Science. 2004;305:683–686. - PubMed
-
- Williams P.A. Crystal structure of human cytochrome P450 2C9 with bound warfarin. Nature. 2003;424:464–468. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

