p66shc negatively regulates insulin-like growth factor I signal transduction via inhibition of p52shc binding to Src homology 2 domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase substrate-1 leading to impaired growth factor receptor-bound protein-2 membrane recruitment
- PMID: 18606861
- PMCID: PMC2631373
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2008-0079
p66shc negatively regulates insulin-like growth factor I signal transduction via inhibition of p52shc binding to Src homology 2 domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase substrate-1 leading to impaired growth factor receptor-bound protein-2 membrane recruitment
Abstract
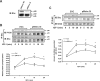
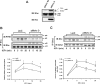
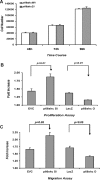
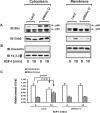
Our previous studies have indicated an essential role of p52shc in mediating IGF-I activation of MAPK in smooth muscle cells (SMC). However, the role of the p66 isoform of shc in IGF-I signal transduction is unclear. In the current study, two approaches were employed to investigate the role of p66shc in mediating IGF-I signaling. Knockdown p66shc by small interfering RNA enhanced IGF-I-stimulated p52shc tyrosine phosphorylation and growth factor receptor-bound protein-2 (Grb2) association, resulting in increased IGF-I-dependent MAPK activation. This was associated with enhanced IGF-I-stimulated cell proliferation. In contrast, knockdown of p66shc did not affect IGF-I-stimulated IGF-I receptor tyrosine phosphorylation. Overexpression of p66shc impaired IGF-I-stimulated p52shc tyrosine phosphorylation and p52shc-Grb2 association. In addition, IGF-I-dependent MAPK activation was also impaired, and SMC proliferation in response to IGF-I was inhibited. IGF-I-dependent cell migration was enhanced by p66shc knockdown and attenuated by p66shc overexpression. Mechanistic studies indicated that p66shc inhibited IGF-I signal transduction via competitively inhibiting the binding of Src homology 2 domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase-2 (SHP-2) to SHP substrate-1 (SHPS-1), leading to the disruption of SHPS-1/SHP-2/Src/p52shc complex formation, an event that has been shown previously to be essential for p52shc phosphorylation and Grb2 recruitment. These findings indicate that p66shc functions to negatively regulate the formation of a signaling complex that is required for p52shc activation in response to IGF-I, thus leading to attenuation of IGF-I-stimulated cell proliferation and migration.
Figures

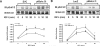

Similar articles
-
Role of SHPS-1 in the regulation of insulin-like growth factor I-stimulated Shc and mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in vascular smooth muscle cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Jul;16(7):3353-64. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-10-0918. Epub 2005 May 11. Mol Biol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15888547 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin-like growth factor-I-stimulated insulin receptor substrate-1 negatively regulates Src homology 2 domain-containing protein-tyrosine phosphatase substrate-1 function in vascular smooth muscle cells.J Biol Chem. 2010 May 21;285(21):15682-95. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.092270. Epub 2010 Mar 5. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20207740 Free PMC article.
-
p66shc inhibits insulin-like growth factor-I signaling via direct binding to Src through its polyproline and Src homology 2 domains, resulting in impairment of Src kinase activation.J Biol Chem. 2010 Mar 5;285(10):6937-51. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.069872. Epub 2010 Jan 4. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20048152 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction between insulin-like growth factor-I receptor and alphaVbeta3 integrin linked signaling pathways: cellular responses to changes in multiple signaling inputs.Mol Endocrinol. 2005 Jan;19(1):1-11. doi: 10.1210/me.2004-0376. Epub 2004 Nov 4. Mol Endocrinol. 2005. PMID: 15528274 Review.
-
The role of Src homology 2 containing protein tyrosine phosphatase 2 in vascular smooth muscle cell migration and proliferation.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2010 Oct;31(10):1277-83. doi: 10.1038/aps.2010.168. Epub 2010 Sep 27. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2010. PMID: 20871619 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
p66Shc in Cardiovascular Pathology.Cells. 2022 Jun 6;11(11):1855. doi: 10.3390/cells11111855. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35681549 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuronal Bmal1 regulates retinal angiogenesis and neovascularization in mice.Commun Biol. 2022 Aug 6;5(1):792. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03774-2. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 35933488 Free PMC article.
-
IGF-I and IGFBP-2 Stimulate AMPK Activation and Autophagy, Which Are Required for Osteoblast Differentiation.Endocrinology. 2016 Jan;157(1):268-81. doi: 10.1210/en.2015-1690. Epub 2015 Nov 10. Endocrinology. 2016. PMID: 26556533 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperglycemia enhances IGF-I-stimulated Src activation via increasing Nox4-derived reactive oxygen species in a PKCζ-dependent manner in vascular smooth muscle cells.Diabetes. 2012 Jan;61(1):104-13. doi: 10.2337/db11-0990. Epub 2011 Dec 6. Diabetes. 2012. PMID: 22148072 Free PMC article.
-
The adaptor proteins p66Shc and Grb2 regulate the activation of the GTPases ARF1 and ARF6 in invasive breast cancer cells.J Biol Chem. 2014 Feb 28;289(9):5687-703. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.516047. Epub 2014 Jan 9. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24407288 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Luzi L, Confalonieri S, Di Fiore PP, Pelicci PG 2000 Evolution of Shc functions from nematode to human. Curr Opin Genet Dev 10:668–674 - PubMed
-
- Pelicci G, Lanfrancone L, Grignani F, McGlade J, Cavallo F, Forni G, Nicoletti I, Pawson T, Pelicci PG 1992 A novel transforming protein (SHC) with an SH2 domain is implicated in mitogenic signal transduction. Cell 70:93–104 - PubMed
-
- Conti L, Sipione S, Magrassi L, Bonfanti L, Rigamonti D, Pettirossi V, Peschanski M, Haddad B, Pelicci P, Milanesi G, Pelicci G, Cattaneo E 2001 Shc signaling in differentiating neural progenitor cells. Nat Neurosci 4:579–586 - PubMed
-
- Ishihara H, Sasaoka T, Wada T, Ishiki M, Haruta T, Usui I, Iwata M, Takano A, Uno T, Ueno E, Kobayashi M 1998 Relative involvement of Shc tyrosine 239/240 and tyrosine 317 on insulin induced mitogenic signaling in rat1 fibroblasts expressing insulin receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 252:139–144 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

