FGF-16 is required for embryonic heart development
- PMID: 18565327
- PMCID: PMC5233434
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.06.029
FGF-16 is required for embryonic heart development
Abstract
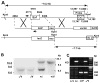
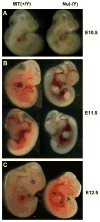
Fibroblast growth factor 16 (FGF-16) expression has previously been detected in mouse heart at mid-gestation in the endocardium and epicardium, suggesting a role in embryonic heart development. More specifically, exogenously applied FGF-16 has been shown to stimulate growth of embryonic myocardial cells in tissue explants. We have generated mice lacking FGF-16 by targeting the Fgf16 locus on the X chromosome. Elimination of Fgf16 expression resulted in embryonic death as early as day 11.5 (E11.5). External abnormalities, including hemorrhage in the heart and ventral body region as well as facial defects, began to appear in null embryos from E11.5. Morphological analysis of FGF-16 null hearts revealed cardiac defects including chamber dilation, thinning of the atrial and ventricular walls, and poor trabeculation, which were visible at E10.5 and more pronounced at E11.5. These findings indicate FGF-16 is required for embryonic heart development in mid-gestation through its positive effect on myocardial growth.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Embryonic survival and severity of cardiac and craniofacial defects are affected by genetic background in fibroblast growth factor-16 null mice.DNA Cell Biol. 2010 Aug;29(8):407-15. doi: 10.1089/dna.2010.1024. DNA Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20618076
-
Heart-specific expression of FGF-16 and a potential role in postnatal cardioprotection.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015 Feb;26(1):59-66. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2014.07.007. Epub 2014 Jul 21. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015. PMID: 25106133 Review.
-
Fgf16 is required for cardiomyocyte proliferation in the mouse embryonic heart.Dev Dyn. 2008 Oct;237(10):2947-54. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.21726. Dev Dyn. 2008. PMID: 18816849
-
Krüppel-like factor 2 is required for normal mouse cardiac development.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e54891. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054891. Epub 2013 Feb 14. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23457456 Free PMC article.
-
The Fgf families in humans, mice, and zebrafish: their evolutional processes and roles in development, metabolism, and disease.Biol Pharm Bull. 2007 Oct;30(10):1819-25. doi: 10.1248/bpb.30.1819. Biol Pharm Bull. 2007. PMID: 17917244 Review.
Cited by
-
Foxp1 coordinates cardiomyocyte proliferation through both cell-autonomous and nonautonomous mechanisms.Genes Dev. 2010 Aug 15;24(16):1746-57. doi: 10.1101/gad.1929210. Genes Dev. 2010. PMID: 20713518 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of three novel FGF16 mutations in X-linked recessive fusion of the fourth and fifth metacarpals and possible correlation with heart disease.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2014 Sep;2(5):402-11. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.81. Epub 2014 May 14. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2014. PMID: 25333065 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic regulation of the cerebral cavernous malformation pathway controls vascular stability and growth.Dev Cell. 2012 Aug 14;23(2):342-55. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2012.06.004. Dev Cell. 2012. PMID: 22898778 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast Growth Factors in Cardiovascular Disease.J Atheroscler Thromb. 2024 Nov 1;31(11):1496-1511. doi: 10.5551/jat.RV22025. Epub 2024 Aug 22. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2024. PMID: 39168622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fibroblast growth factors: from molecular evolution to roles in development, metabolism and disease.J Biochem. 2011 Feb;149(2):121-30. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvq121. Epub 2010 Oct 12. J Biochem. 2011. PMID: 20940169 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Miyake A, Konishi M, Martin FH, Hernday NA, Ozaki K, Yamamoto S, Mikami T, Arakawa T, Itoh N. Structure and expression of a novel member, FGF-16, on the fibroblast growth factor family. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998;243:148–152. - PubMed
-
- Ohmachi S, Watanabe Y, Mikami T, Kusu N, Ibi T, Akaike A, Itoh N. FGF-20, a novel neurotrophic factor, preferentially expressed in the substantia nigra pars compacta of rat brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000;277:355–360. - PubMed
-
- Lavine KJ, Yu K, White AC, Zhang X, Smith C, Partanen J, Ornitz DM. Endocardial and epicardial derived FGF signals regulate myocardial proliferation and differentiation in vivo. Dev Cell. 2005;8:85–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

