Misexpression of ELF5 disrupts lung branching and inhibits epithelial differentiation
- PMID: 18544451
- PMCID: PMC2586150
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.04.038
Misexpression of ELF5 disrupts lung branching and inhibits epithelial differentiation
Abstract
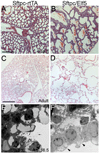
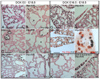
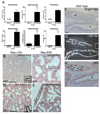
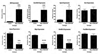
ELF5, an Ets family transcription factor found exclusively in epithelial cells, is expressed in the distal lung epithelium during embryogenesis, then becomes restricted to proximal airways at the end of gestation and postnatally. To test the hypothesis that ELF5 represses distal epithelial differentiation, we generated a transgenic mouse model in which a doxycycline inducible HA-tagged mouse Elf5 transgene was placed under the control of the lung epithelium-specific human SFTPC promoter. We found that expressing high levels of ELF5 during early lung development disrupted branching morphogenesis and produced a dilated epithelium. The effects of ELF5 on morphogenesis were stage-dependent, since inducing the transgene on E16.5 had no effect on branching. ELF5 reduced expression of the distal lung epithelial differentiation markers Erm, Napsa and Sftpc, and type II cell ultrastructural differentiation was immature. ELF5 overexpression did not induce the proximal airway epithelial markers Ccsp and Foxj1, but did induce expression of p63, a marker of basal cells in the trachea and esophagus. High ELF5 levels also induced the expression of genes found in other endodermal epithelia but not normally associated with the lung. These results suggest that precise levels of ELF5 regulate the specification and differentiation of epithelial cells in the lung.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Elf5 is an epithelium-specific, fibroblast growth factor-sensitive transcription factor in the embryonic lung.Dev Dyn. 2007 May;236(5):1175-92. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.21133. Dev Dyn. 2007. PMID: 17394208
-
Role for ETS domain transcription factors Pea3/Erm in mouse lung development.Dev Biol. 2003 Sep 1;261(1):10-24. doi: 10.1016/s0012-1606(03)00359-2. Dev Biol. 2003. PMID: 12941618
-
Sox2 is important for two crucial processes in lung development: branching morphogenesis and epithelial cell differentiation.Dev Biol. 2008 May 1;317(1):296-309. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.02.035. Epub 2008 Feb 29. Dev Biol. 2008. PMID: 18374910
-
Transcription factors in mouse lung development and function.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2001 May;280(5):L823-38. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.2001.280.5.L823. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11290504 Review.
-
ELF3, ELF5, EHF and SPDEF Transcription Factors in Tissue Homeostasis and Cancer.Molecules. 2018 Aug 30;23(9):2191. doi: 10.3390/molecules23092191. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30200227 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CPEB2-activated PDGFRα mRNA translation contributes to myofibroblast proliferation and pulmonary alveologenesis.J Biomed Sci. 2020 Apr 15;27(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s12929-020-00643-0. J Biomed Sci. 2020. PMID: 32295602 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy is required for lung development and morphogenesis.J Clin Invest. 2019 Jun 4;129(7):2904-2919. doi: 10.1172/JCI127307. eCollection 2019 Jun 4. J Clin Invest. 2019. PMID: 31162135 Free PMC article.
-
Semaphorin 3A contributes to distal pulmonary epithelial cell differentiation and lung morphogenesis.PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e27449. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027449. Epub 2011 Nov 11. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22096573 Free PMC article.
-
Pathway Regulation of p63, a Director of Epithelial Cell Fate.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2015 Apr 28;6:51. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2015.00051. eCollection 2015. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2015. PMID: 25972840 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential interactions between the TBX4-FGF10 and SHH-FOXF1 signaling during human lung development revealed using ChIP-seq.Respir Res. 2021 Jan 21;22(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s12931-021-01617-y. Respir Res. 2021. PMID: 33478486 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Avril-Delplanque A, et al. Aquaporin-3 expression in human fetal airway epithelial progenitor cells. Stem Cells. 2005;23:992–1001. - PubMed
-
- Bellusci S, et al. Fibroblast growth factor 10 (FGF10) and branching morphogenesis in the embryonic mouse lung. Development. 1997;124:4867–4878. - PubMed
-
- Blanpain C, Fuchs E. p63: revving up epithelial stem-cell potential. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9:731–733. - PubMed
-
- Brasch F, et al. Involvement of napsin A in the C- and N-terminal processing of surfactant protein B in type-II pneumocytes of the human lung. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:49006–49014. - PubMed
-
- Cangemi R, et al. Reduced expression and tumor suppressor function of the ETS transcription factor ESE-3 in prostate cancer. Oncogene. 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

