Transient reversal of RNA polymerase II active site closing controls fidelity of transcription elongation
- PMID: 18538654
- PMCID: PMC7243879
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.04.017
Transient reversal of RNA polymerase II active site closing controls fidelity of transcription elongation
Abstract
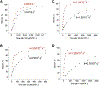
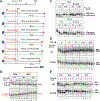
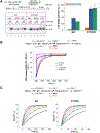
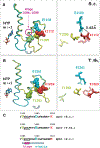
To study fidelity of RNA polymerase II (Pol II), we analyzed properties of the 6-azauracil-sensitive and TFIIS-dependent E1103G mutant of rbp1 (rpo21), the gene encoding the catalytic subunit of Pol II in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Using an in vivo retrotransposition-based transcription fidelity assay, we observed that rpb1-E1103G causes a 3-fold increase in transcription errors. This mutant showed a 10-fold decrease in fidelity of transcription elongation in vitro. The mutation does not appear to significantly affect translocation state equilibrium of Pol II in a stalled elongation complex. Primarily, it promotes NTP sequestration in the polymerase active center. Furthermore, pre-steady-state analyses revealed that the E1103G mutation shifted the equilibrium between the closed and the open active center conformations toward the closed form. Thus, open conformation of the active center emerges as an intermediate essential for preincorporation fidelity control. Similar mechanisms may control fidelity of DNA-dependent DNA polymerases and RNA-dependent RNA polymerases.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The fidelity of transcription: RPB1 (RPO21) mutations that increase transcriptional slippage in S. cerevisiae.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jan 25;288(4):2689-99. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.429506. Epub 2012 Dec 5. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23223234 Free PMC article.
-
Rpb9 subunit controls transcription fidelity by delaying NTP sequestration in RNA polymerase II.J Biol Chem. 2009 Jul 17;284(29):19601-12. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.006908. Epub 2009 May 13. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19439405 Free PMC article.
-
A genetic assay for transcription errors reveals multilayer control of RNA polymerase II fidelity.PLoS Genet. 2014 Sep 18;10(9):e1004532. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004532. eCollection 2014 Sep. PLoS Genet. 2014. PMID: 25232834 Free PMC article.
-
Basic mechanisms of RNA polymerase II activity and alteration of gene expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jan;1829(1):39-54. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.09.007. Epub 2012 Sep 26. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23022618 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isolation and characterization of transcription fidelity mutants.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Jul;1819(7):694-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.02.005. Epub 2012 Feb 16. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22366339 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cys-pair reporters detect a constrained trigger loop in a paused RNA polymerase.Mol Cell. 2013 Jun 27;50(6):882-93. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.05.015. Epub 2013 Jun 13. Mol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23769674 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of the mutation rate.Trends Genet. 2010 Aug;26(8):345-52. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2010.05.003. Epub 2010 Jun 30. Trends Genet. 2010. PMID: 20594608 Free PMC article.
-
Writing a wrong: Coupled RNA polymerase II transcription and RNA quality control.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2019 Jul;10(4):e1529. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1529. Epub 2019 Mar 7. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2019. PMID: 30848101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Templated nucleoside triphosphate binding to a noncatalytic site on RNA polymerase regulates transcription.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Apr 12;108(15):6079-84. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1011274108. Epub 2011 Mar 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21447716 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription bypass of DNA lesions enhances cell survival but attenuates transcription coupled DNA repair.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Dec 1;42(21):13242-53. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1150. Epub 2014 Nov 11. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 25389266 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anand VS, and Patel SS (2006). Transient state kinetics of transcription elongation by T7 RNA polymerase. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 35677–35685. - PubMed
-
- Bar-Nahum G, Epshtein V, Ruckenstein AE, Rafikov R, Mustaev A, and Nudler E (2005). A ratchet mechanism of transcription elongation and its control. Cell 120, 183–193. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

