Functional reconstitution of the human chemokine receptor CXCR4 with G(i)/G (o)-proteins in Sf9 insect cells
- PMID: 18523757
- PMCID: PMC2574856
- DOI: 10.1007/s00210-008-0313-8
Functional reconstitution of the human chemokine receptor CXCR4 with G(i)/G (o)-proteins in Sf9 insect cells
Abstract
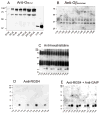
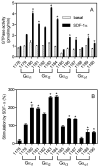
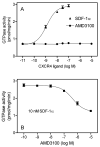
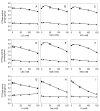
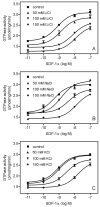
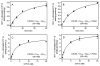
The chemokine stromal cell-derived factor-1alpha (SDF-1alpha) binds to the chemokine receptor CXCR4 that couples to pertussis toxin-sensitive G-proteins of the G(i)/G(o)-family. CXCR4 plays a role in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases, human immunodeficiency virus infection and various tumors, fetal development as well as endothelial progenitor and T-cell recruitment. To this end, most CXCR4 studies have focused on the cellular level. The aim of this study was to establish a reconstitution system for the human CXCR4 that allows for the analysis of receptor/G-protein coupling at the membrane level. We wished to study specifically constitutive CXCR4 activity and the G-protein-specificity of CXCR4. We co-expressed N- and C-terminally epitope-tagged human CXCR4 with various G(i)/G(o)-proteins and regulator of G-protein signaling (RGS)-proteins in Sf9 insect cells. Expression of CXCR4, G-proteins, and RGS-proteins was verified by immunoblotting. CXCR4 coupled more effectively to Galpha(i1) and Galpha(i2) than to Galpha(i3) and Galpha(o) and insect cell G-proteins as assessed by SDF-1alpha-stimulated high-affinity steady-state GTP hydrolysis. The RGS-proteins RGS4 and GAIP enhanced SDF-1alpha-stimulated GTP hydrolysis. SDF-1alpha stimulated [(35)S]guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate (GTPgammaS) binding to Galpha(i2). RGS4 did not enhance GTPgammaS binding. Na(+) salts of halides did not reduce basal GTPase activity. The bicyclam, 1-[[1,4,8,11-tetrazacyclotetradec-1-ylmethyl)phenyl]methyl]-1,4,8,11-tetrazacyclotetradecane (AMD3100), acted as CXCR4 antagonist but was devoid of inverse agonistic activity. Halides reduced the maximum SDF-1alpha-stimulated GTP hydrolysis in the order of efficacy I(-) > Br(-) > Cl(-). In addition, salts reduced the potency of SDF-1alpha at activating GTP hydrolysis. From our data, we conclude the following: (1) Sf9 cells are a suitable system for expression of functionally intact human CXCR4; (2) Human CXCR4 couples effectively to Galpha(i1) and Galpha(i2); (3) There is no evidence for constitutive activity of CXCR4; (4) RGS-proteins enhance agonist-stimulated GTP hydrolysis, showing that GTP hydrolysis becomes rate-limiting in the presence of SDF-1alpha; (5) By analogy to previous observations made for the beta(2)-adrenoceptor coupled to G(s), the inhibitory effects of halides on agonist-stimulated GTP hydrolysis may be due to increased GDP-affinity of G(i)-proteins, reducing the efficacy of CXCR4 at stimulating nucleotide exchange.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The human histamine H2-receptor couples more efficiently to Sf9 insect cell Gs-proteins than to insect cell Gq-proteins: limitations of Sf9 cells for the analysis of receptor/Gq-protein coupling.J Neurochem. 2002 Feb;80(4):678-96. doi: 10.1046/j.0022-3042.2001.00746.x. J Neurochem. 2002. PMID: 11841575
-
High constitutive activity and a G-protein-independent high-affinity state of the human histamine H(4)-receptor.Biochemistry. 2009 Feb 17;48(6):1424-38. doi: 10.1021/bi802050d. Biochemistry. 2009. PMID: 19166345
-
The CXCR4 agonist ligand stromal derived factor-1 maintains high affinity for receptors in both Galpha(i)-coupled and uncoupled states.Eur J Pharmacol. 2000 Dec 8;409(2):143-54. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(00)00846-3. Eur J Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 11104827
-
Sf9 cells: a versatile model system to investigate the pharmacological properties of G protein-coupled receptors.Pharmacol Ther. 2010 Dec;128(3):387-418. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2010.07.005. Epub 2010 Aug 10. Pharmacol Ther. 2010. PMID: 20705094 Review.
-
RGS-insensitive G-protein mutations to study the role of endogenous RGS proteins.Methods Enzymol. 2004;389:229-43. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(04)89014-1. Methods Enzymol. 2004. PMID: 15313569 Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetically silenced GNG4 inhibits SDF1α/CXCR4 signaling in mesenchymal glioblastoma.Genes Cancer. 2016 Mar;7(3-4):136-47. doi: 10.18632/genesandcancer.105. Genes Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27382437 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetic Analysis of the Early Signaling Steps of the Human Chemokine Receptor CXCR4.Mol Pharmacol. 2020 Aug;98(2):72-87. doi: 10.1124/mol.119.118448. Epub 2020 May 30. Mol Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32474443 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment of recombinant cannabinoid receptor assays and characterization of several natural and synthetic ligands.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2010 Aug;382(2):177-91. doi: 10.1007/s00210-010-0534-5. Epub 2010 Jul 9. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20617431
-
Role of the second and third extracellular loops of the histamine H(4) receptor in receptor activation.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2011 Sep;384(3):301-17. doi: 10.1007/s00210-011-0673-3. Epub 2011 Jul 29. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21800093
-
Modulation of GPCRs by monovalent cations and anions.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2015 Mar;388(3):363-80. doi: 10.1007/s00210-014-1073-2. Epub 2014 Nov 30. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25432095 Review.
References
-
- Bajetto A, Bonavia R, Barbero S, Florio T, Schettini G. Chemokines and their receptors in the central nervous system. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2001;22:147–184. - PubMed
-
- Birnbaumer L, Abramowitz J, Brown AM. Receptor-effector coupling by G proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990;1031:163–224. - PubMed
-
- Buckingham M. Myogenic progenitor cells and skeletal myogenesis in vertebrates. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2006;16:525–532. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

