CS23D: a web server for rapid protein structure generation using NMR chemical shifts and sequence data
- PMID: 18515350
- PMCID: PMC2447725
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkn305
CS23D: a web server for rapid protein structure generation using NMR chemical shifts and sequence data
Abstract
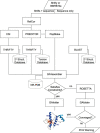
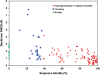
CS23D (chemical shift to 3D structure) is a web server for rapidly generating accurate 3D protein structures using only assigned nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) chemical shifts and sequence data as input. Unlike conventional NMR methods, CS23D requires no NOE and/or J-coupling data to perform its calculations. CS23D accepts chemical shift files in either SHIFTY or BMRB formats, and produces a set of PDB coordinates for the protein in about 10-15 min. CS23D uses a pipeline of several preexisting programs or servers to calculate the actual protein structure. Depending on the sequence similarity (or lack thereof) CS23D uses either (i) maximal subfragment assembly (a form of homology modeling), (ii) chemical shift threading or (iii) shift-aided de novo structure prediction (via Rosetta) followed by chemical shift refinement to generate and/or refine protein coordinates. Tests conducted on more than 100 proteins from the BioMagResBank indicate that CS23D converges (i.e. finds a solution) for >95% of protein queries. These chemical shift generated structures were found to be within 0.2-2.8 A RMSD of the NMR structure generated using conventional NOE-base NMR methods or conventional X-ray methods. The performance of CS23D is dependent on the completeness of the chemical shift assignments and the similarity of the query protein to known 3D folds. CS23D is accessible at http://www.cs23d.ca.
Figures
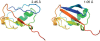
Similar articles
-
GeNMR: a web server for rapid NMR-based protein structure determination.Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Jul;37(Web Server issue):W670-7. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp280. Epub 2009 Apr 30. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 19406927 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid and reliable protein structure determination via chemical shift threading.J Biomol NMR. 2018 Jan;70(1):33-51. doi: 10.1007/s10858-017-0154-1. Epub 2017 Dec 1. J Biomol NMR. 2018. PMID: 29196969
-
CSI 3.0: a web server for identifying secondary and super-secondary structure in proteins using NMR chemical shifts.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Jul 1;43(W1):W370-7. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv494. Epub 2015 May 15. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25979265 Free PMC article.
-
Protein NMR structure determination with automated NOE assignment using the new software CANDID and the torsion angle dynamics algorithm DYANA.J Mol Biol. 2002 May 24;319(1):209-27. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(02)00241-3. J Mol Biol. 2002. PMID: 12051947
-
An overview of tools for the validation of protein NMR structures.J Biomol NMR. 2014 Apr;58(4):259-85. doi: 10.1007/s10858-013-9750-x. Epub 2013 Jul 23. J Biomol NMR. 2014. PMID: 23877928 Review.
Cited by
-
Utility of 1H NMR chemical shifts in determining RNA structure and dynamics.J Phys Chem B. 2013 Feb 21;117(7):2045-52. doi: 10.1021/jp310863c. Epub 2013 Feb 7. J Phys Chem B. 2013. PMID: 23320790 Free PMC article.
-
NMR paves the way for atomic level descriptions of sparsely populated, transiently formed biomolecular conformers.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Aug 6;110(32):12867-74. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1305688110. Epub 2013 Jul 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23868852 Free PMC article.
-
Transiently populated intermediate functions as a branching point of the FF domain folding pathway.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Oct 30;109(44):17777-82. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1201799109. Epub 2012 May 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22647611 Free PMC article.
-
A strong 13C chemical shift signature provides the coordination mode of histidines in zinc-binding proteins.J Biomol NMR. 2012 Jun;53(2):93-101. doi: 10.1007/s10858-012-9625-6. Epub 2012 Apr 17. J Biomol NMR. 2012. PMID: 22528293
-
Combining NMR ensembles and molecular dynamics simulations provides more realistic models of protein structures in solution and leads to better chemical shift prediction.J Biomol NMR. 2012 Mar;52(3):257-67. doi: 10.1007/s10858-012-9609-6. J Biomol NMR. 2012. PMID: 22314705
References
-
- Wuthrich K. NMR - this other method for protein and nucleic acid structure determination. Acta Crystallogr., D. 1995;51:249–270. - PubMed
-
- Wuthrich K. NMR of Proteins and Nucleic Acids. New York, NY: John Wiley & Sons; 1986.
-
- Schmidt JM, Löhr F, Rüterjans H. Heteronuclear relayed E.COSY applied to the determination of accurate 3J(HN,C') and 3J(H beta,C') coupling constants in Desulfovibrio vulgaris flavodoxin. J. Biomol. NMR. 1996;7:142–152. - PubMed
-
- Tjandra N, Bax A. Direct measurement of distances and angles in biomolecules by NMR in a dilute liquid crystalline medium. Science. 1997;278:1111–1114. - PubMed

