Toll-like receptor 2 acts as a natural innate immune receptor to clear amyloid beta 1-42 and delay the cognitive decline in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 18509040
- PMCID: PMC6670789
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1146-08.2008
Toll-like receptor 2 acts as a natural innate immune receptor to clear amyloid beta 1-42 and delay the cognitive decline in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
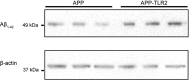
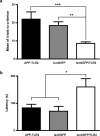
Microglia are the immune cells of the brain, they are activated in the brain of Alzheimer's disease (AD) patients and mouse models of AD, and they express the innate immune receptor toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2). The present study investigated role of this receptor in the progression of AD-like pathologies. Here we show that amyloid beta (A beta) stimulates TLR2 expression in a small proportion of microglia. We then generated triple transgenic mice that are deficient in TLR2 from mice that harbor a mutant human presenelin 1 and a chimeric mouse/human amyloid precursor protein (APP) genes. TLR2 deficiency accelerated spatial and contextual memory impairments, which correlated with increased levels of A beta(1-42) and transforming growth factor beta1 in the brain. NMDA receptors 1 and 2A expression levels were also lower in the hippocampus of APP-TLR2(-/-) mice. Gene therapy in cells of the bone marrow using lentivirus constructs expressing TLR2 rescued the cognitive impairment of APP-TLR2(-/-) mice. Indeed, lenti-green fluorescent protein/TLR2 treatment had beneficial effects by restoring the memory consolidation process disrupted by TLR2 deficiency in APP mice. These data suggest that TLR2 acts as an endogenous receptor for the clearance of toxic A beta by bone-marrow-derived immune cells. The cognitive decline is markedly accelerated in a context of TLR2 deficiency. Upregulating this innate immune receptor may then be considered as a potential new powerful therapeutic approach for AD.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CC chemokine receptor 2 deficiency aggravates cognitive impairments and amyloid pathology in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.J Neurosci. 2011 Apr 20;31(16):6208-20. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0299-11.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21508244 Free PMC article.
-
Amyloid generation and dysfunctional immunoproteasome activation with disease progression in animal model of familial Alzheimer's disease.Brain Pathol. 2012 Sep;22(5):636-53. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2011.00560.x. Epub 2012 Jan 13. Brain Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22188425 Free PMC article.
-
Hematopoietic CC-chemokine receptor 2 (CCR2) competent cells are protective for the cognitive impairments and amyloid pathology in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Mol Med. 2012 Mar 30;18(1):297-313. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2011.00306. Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22160221 Free PMC article.
-
Shared cognitive and behavioral impairments in epilepsy and Alzheimer's disease and potential underlying mechanisms.Epilepsy Behav. 2013 Mar;26(3):343-51. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2012.11.040. Epub 2013 Jan 13. Epilepsy Behav. 2013. PMID: 23321057 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipids and cognition.J Alzheimers Dis. 2010;20(3):737-47. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2010-091576. J Alzheimers Dis. 2010. PMID: 20413879 Review.
Cited by
-
Activation of epidermal growth factor receptor is required for NTHi-induced NF-κB-dependent inflammation.PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e28216. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028216. Epub 2011 Nov 23. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22132240 Free PMC article.
-
Animal Models of Alzheimer's Disease: Utilization of Transgenic Alzheimer's Disease Models in Studies of Amyloid Beta Clearance.Curr Transl Geriatr Exp Gerontol Rep. 2012 Mar;1(1):11-20. doi: 10.1007/s13670-011-0004-z. Epub 2012 Jan 19. Curr Transl Geriatr Exp Gerontol Rep. 2012. PMID: 23440676 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptors 1 and 2 cooperatively mediate immune responses to curli, a common amyloid from enterobacterial biofilms.Cell Microbiol. 2010 Oct;12(10):1495-505. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2010.01485.x. Cell Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20497180 Free PMC article.
-
CC chemokine receptor 2 deficiency aggravates cognitive impairments and amyloid pathology in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.J Neurosci. 2011 Apr 20;31(16):6208-20. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0299-11.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21508244 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2)-deficiency impairs male mouse recovery from a depression-like state.Brain Behav Immun. 2020 Oct;89:51-58. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2020.05.068. Epub 2020 May 29. Brain Behav Immun. 2020. PMID: 32479995 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell. 2006;124:783–801. - PubMed
-
- Akiyama H, Barger S, Barnum S, Bradt B, Bauer J, Cole GM, Cooper NR, Eikelenboom P, Emmerling M, Fiebich BL, Finch CE, Frautschy S, Griffin WS, Hampel H, Hull M, Landreth G, Lue L, Mrak R, Mackenzie IR, McGeer PL, et al. Inflammation and Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2000;21:383–421. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bi H, Sze CI. N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor subunit NR2A and NR2B messenger RNA levels are altered in the hippocampus and entorhinal cortex in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurol Sci. 2002;200:11–18. - PubMed
-
- Borchelt DR, Ratovitski T, van Lare J, Lee MK, Gonzales V, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG, Price DL, Sisodia SS. Accelerated amyloid deposition in the brains of transgenic mice coexpressing mutant presenilin 1 and amyloid precursor proteins. Neuron. 1997;19:939–945. - PubMed
-
- Brionne TC, Tesseur I, Masliah E, Wyss-Coray T. Loss of TGF-beta 1 leads to increased neuronal cell death and microgliosis in mouse brain. Neuron. 2003;40:1133–1145. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
