Chromatin remodeling complexes interact dynamically with a glucocorticoid receptor-regulated promoter
- PMID: 18508913
- PMCID: PMC2488306
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e08-02-0123
Chromatin remodeling complexes interact dynamically with a glucocorticoid receptor-regulated promoter
Abstract
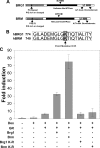
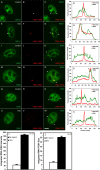
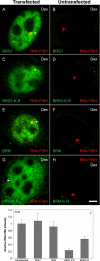
Brahma (BRM) and Brahma-related gene 1 (BRG1) are the ATP-dependent catalytic subunits of the SWI/SNF family of chromatin-remodeling complexes. These complexes are involved in essential processes such as cell cycle, growth, differentiation, and cancer. Using imaging approaches in a cell line that harbors tandem repeats of stably integrated copies of the steroid responsive MMTV-LTR (mouse mammary tumor virus-long terminal repeat), we show that BRG1 and BRM are recruited to the MMTV promoter in a hormone-dependent manner. The recruitment of BRG1 and BRM resulted in chromatin remodeling and decondensation of the MMTV repeat as demonstrated by an increase in the restriction enzyme accessibility and in the size of DNA fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) signals. This chromatin remodeling event was concomitant with an increased occupancy of RNA polymerase II and transcriptional activation at the MMTV promoter. The expression of ATPase-deficient forms of BRG1 (BRG1-K-R) or BRM (BRM-K-R) inhibited the remodeling of local and higher order MMTV chromatin structure and resulted in the attenuation of transcription. In vivo photobleaching experiments provided direct evidence that BRG1, BRG1-K-R, and BRM chromatin-remodeling complexes have distinct kinetic properties on the MMTV array, and they dynamically associate with and dissociate from MMTV chromatin in a manner dependent on hormone and a functional ATPase domain. Our data provide a kinetic and mechanistic basis for the BRG1 and BRM chromatin-remodeling complexes in regulating gene expression at a steroid hormone inducible promoter.
Figures

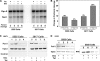

Similar articles
-
Chromatin remodeling during glucocorticoid receptor regulated transactivation.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Jul;1819(7):716-26. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.02.019. Epub 2012 Mar 6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22425674 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The activity of p53 is differentially regulated by Brm- and Brg1-containing SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complexes.J Biol Chem. 2007 Dec 28;282(52):37429-35. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M706039200. Epub 2007 Oct 15. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17938176
-
Reconstitution of glucocorticoid receptor-dependent transcription in vivo.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Apr;24(8):3347-58. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.8.3347-3358.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15060156 Free PMC article.
-
The HSA domain of BRG1 mediates critical interactions required for glucocorticoid receptor-dependent transcriptional activation in vivo.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Feb;28(4):1413-26. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01301-07. Epub 2007 Dec 17. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18086889 Free PMC article.
-
The BRG1 ATPase of human SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling enzymes as a driver of cancer.Epigenomics. 2017 Jun;9(6):919-931. doi: 10.2217/epi-2017-0034. Epub 2017 May 19. Epigenomics. 2017. PMID: 28521512 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The five Rs of glucocorticoid action during inflammation: ready, reinforce, repress, resolve, and restore.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2013 Mar;24(3):109-19. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2012.11.005. Epub 2013 Jan 8. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2013. PMID: 23312823 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effective dynamics of nucleosome configurations at the yeast PHO5 promoter.Elife. 2021 Mar 5;10:e58394. doi: 10.7554/eLife.58394. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33666171 Free PMC article.
-
DNA binding triggers tetramerization of the glucocorticoid receptor in live cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Jul 19;113(29):8236-41. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1606774113. Epub 2016 Jul 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27382178 Free PMC article.
-
Cell cycle phase regulates glucocorticoid receptor function.PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e22289. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022289. Epub 2011 Jul 29. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21829454 Free PMC article.
-
Single-molecule analysis of steroid receptor and cofactor action in living cells.Nat Commun. 2017 Jun 21;8:15896. doi: 10.1038/ncomms15896. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28635963 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agresti A., Scaffidi P., Riva A., Caiolfa V. R., Bianchi M. E. GR and HMGB1 interact only within chromatin and influence each other's residence time. Mol. Cell. 2005;18:109–121. - PubMed
-
- Belandia B., Parker M. G. Nuclear receptors: a rendezvous for chromatin remodeling factors. Cell. 2003;114:277–280. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

