Varicella-zoster virus open reading frame 66 protein kinase is required for efficient viral growth in primary human corneal stromal fibroblast cells
- PMID: 18495764
- PMCID: PMC2493351
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00311-08
Varicella-zoster virus open reading frame 66 protein kinase is required for efficient viral growth in primary human corneal stromal fibroblast cells
Abstract
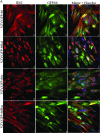
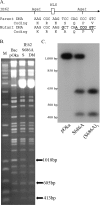
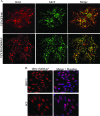
Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) open reading frame 66 (ORF66) encodes a serine/threonine protein kinase that is not required for VZV growth in most cell types but is needed for efficient growth in T cells. The ORF66 kinase affects nuclear import and virion packaging of IE62, the major regulatory protein, and is known to regulate apoptosis in T cells. Here, we further examined the importance of ORF66 using VZV recombinants expressing green fluorescent protein (GFP)-tagged functional and kinase-negative ORF66 proteins. VZV virions with truncated or kinase-inactivated ORF66 protein were marginally reduced for growth and progeny yields in MRC-5 fibroblasts but were severely growth and replication impaired in low-passage primary human corneal stromal fibroblasts (PCF). To determine if the growth impairment was due to ORF66 kinase regulation of IE62 nuclear import, recombinant VZVs that expressed IE62 with alanine residues at S686, the suspected target by which ORF66 kinase blocks IE62 nuclear import, were made. IE62 S686A expressed by the VZV recombinant remained nuclear throughout infection and was not packaged into virions. However, the mutant virus still replicated efficiently in PCF cells. We also show that inactivation of the ORF66 kinase resulted in only marginally increased levels of apoptosis in PCF cells, which could not fully account for the cell-specific growth requirement of ORF66 kinase. Thus, the unique short region VZV kinase has important cell-type-specific functions that are separate from those affecting IE62 and apoptosis.
Figures



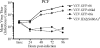
Similar articles
-
Phosphorylation of the varicella-zoster virus (VZV) major transcriptional regulatory protein IE62 by the VZV open reading frame 66 protein kinase.J Virol. 2006 Feb;80(4):1710-23. doi: 10.1128/JVI.80.4.1710-1723.2006. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16439528 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear accumulation of IE62, the varicella-zoster virus (VZV) major transcriptional regulatory protein, is inhibited by phosphorylation mediated by the VZV open reading frame 66 protein kinase.J Virol. 2000 Mar;74(5):2265-77. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.5.2265-2277.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10666257 Free PMC article.
-
Virion association of IE62, the varicella-zoster virus (VZV) major transcriptional regulatory protein, requires expression of the VZV open reading frame 66 protein kinase.J Virol. 2001 Oct;75(19):9106-13. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.19.9106-9113.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11533174 Free PMC article.
-
Varicella-zoster virus open reading frame 66 protein kinase and its relationship to alphaherpesvirus US3 kinases.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2010;342:79-98. doi: 10.1007/82_2009_7. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20186610 Free PMC article. Review.
-
VZV ORF47 serine protein kinase and its viral substrates.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2010;342:99-111. doi: 10.1007/82_2009_5. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20186612 Review.
Cited by
-
Varicella-zoster virus infects human embryonic stem cell-derived neurons and neurospheres but not pluripotent embryonic stem cells or early progenitors.J Virol. 2012 Mar;86(6):3211-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.06810-11. Epub 2012 Jan 11. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22238301 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of alphaherpesvirus protein via post-translational phosphorylation.Vet Res. 2022 Nov 17;53(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s13567-022-01115-z. Vet Res. 2022. PMID: 36397147 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide mutagenesis reveals that ORF7 is a novel VZV skin-tropic factor.PLoS Pathog. 2010 Jul 1;6(7):e1000971. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000971. PLoS Pathog. 2010. PMID: 20617166 Free PMC article.
-
Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) infection of neurons derived from human embryonic stem cells: direct demonstration of axonal infection, transport of VZV, and productive neuronal infection.J Virol. 2011 Jul;85(13):6220-33. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02396-10. Epub 2011 Apr 27. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21525353 Free PMC article.
-
The alphaherpesvirus US3/ORF66 protein kinases direct phosphorylation of the nuclear matrix protein matrin 3.J Virol. 2011 Jan;85(1):568-81. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01611-10. Epub 2010 Oct 20. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 20962082 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aubert, M., and J. A. Blaho. 2001. Modulation of apoptosis during herpes simplex virus infection in human cells. Microbes Infect. 3859-866. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

