Correlation between NK function and response to trastuzumab in metastatic breast cancer patients
- PMID: 18485193
- PMCID: PMC2415031
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-5876-6-25
Correlation between NK function and response to trastuzumab in metastatic breast cancer patients
Abstract
Background: Trastuzumab is a monoclonal antibody selectively directed against Her2 and approved for the treatment of Her2 overexpressing breast cancer patients. Its proposed mechanisms of action include mediation of antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) by triggering FcgammaRIII on natural killer (NK) cells. This study addresses the correlation between overall NK function and trastuzumab's clinical activity.
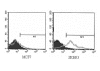
Subjects and methods: Clinical and immunological responses were assessed in 26 patients receiving trastuzumab monotherapy as maintenance management after chemotherapy (8 mg/kg load and then standard doses of 6 mg/kg every 3 weeks). Cytotoxic activity against the MHC class I-negative standard NK target K562 cell line and HER2-specific ADCC against a trastuzumab-coated Her2-positive SKBR3 cell line were assessed in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) harvested after the first standard dose. After six months, seventeen patients were scored as responders and nine as non-responders according to the RECIST criteria, while Progression-Free Survival (PFS) was calculated during a 12 months follow-up.
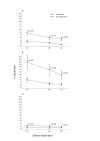
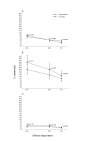
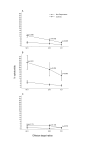
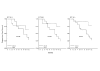
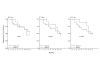
Results: The responders had significantly higher levels of both NK and ADCC activities (p < 0.05) that were not different from those of eleven normal controls. The NK activity of the non-responders was significantly (p < 0.05) lower than that of the normal controls. At twelve months, there was a marked correlation between PFS and NK activity only. PFS was significantly longer in patients with high levels of NK activity, whereas its pattern was unrelated to high or low ADCC activity.
Conclusion: One of the mechanisms of action of trastuzumab is NK cell-mediated ADCC lysis of the Her2-positve target cell. We show here that its potency is correlated with the short-term response to treatment, whereas longer protection against tumor expansion seems to be mediated by pure NK activity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Elements related to heterogeneity of antibody-dependent cell cytotoxicity in patients under trastuzumab therapy for primary operable breast cancer overexpressing Her2.Cancer Res. 2007 Dec 15;67(24):11991-9. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-2068. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 18089830 Clinical Trial.
-
Trastuzumab and interleukin-2 in HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer: a pilot study.Clin Cancer Res. 2003 Jul;9(7):2440-6. Clin Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 12855616 Clinical Trial.
-
Paclitaxel enhances antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity of trastuzumab by rapid recruitment of natural killer cells in HER2-positive breast cancer.J Nippon Med Sch. 2014;81(4):211-20. doi: 10.1272/jnms.81.211. J Nippon Med Sch. 2014. PMID: 25186575
-
[Human recombinant anti-HER2 monoclonal antibody--a new targeted treatment in breast cancer].Orv Hetil. 2001 Nov 18;142(46):2563-8. Orv Hetil. 2001. PMID: 11770175 Review. Hungarian.
-
Trastuzumab: a review of its use in the treatment of metastatic breast cancer overexpressing HER2.Drugs. 2002;62(1):209-43. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200262010-00008. Drugs. 2002. PMID: 11790161 Review.
Cited by
-
Three-Dimensional Model Analysis Revealed Differential Cytotoxic Effects of the NK-92 Cell Line and Primary NK Cells on Breast and Ovarian Carcinoma Cell Lines Mediated by Variations in Receptor-Ligand Interactions and Soluble Factor Profiles.Biomedicines. 2024 Oct 20;12(10):2398. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12102398. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39457710 Free PMC article.
-
Association studies of Fcγ receptor polymorphisms with outcome in HER2+ breast cancer patients treated with trastuzumab in NCCTG (Alliance) Trial N9831.Cancer Immunol Res. 2014 Oct;2(10):962-9. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-14-0059. Epub 2014 Jul 2. Cancer Immunol Res. 2014. PMID: 24989892 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
PD-L1 (B7-H1) and PD-1 pathway blockade for cancer therapy: Mechanisms, response biomarkers, and combinations.Sci Transl Med. 2016 Mar 2;8(328):328rv4. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aad7118. Sci Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 26936508 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interplay between Natural Killer Cells and Anti-HER2 Antibodies: Perspectives for Breast Cancer Immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2017 Nov 13;8:1544. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01544. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29181007 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Improved Natural Killer cell activity and retained anti-tumor CD8(+) T cell responses contribute to the induction of a pathological complete response in HER2-positive breast cancer patients undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy.J Transl Med. 2015 Jun 27;13:204. doi: 10.1186/s12967-015-0567-0. J Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 26116238 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Owens MA, Horten BC, Da Silva MM. HER2 amplification ratios by fluorescence in situ hybridization and correlation with immunohistochemistry in a cohort of 6556 breast cancer tissues. Clin Breast Cancer. 2004;5:63–69. - PubMed
-
- Gusterson BA, Gelber RD, Goldhirsch A, Price KN, Säve-Söderborgh J, Anbazhagan R, Styles J, Rudenstam CM, Golouh R, Reed R. Prognostic importance of c-erbB-2 expression in breast cancer. International (Ludwig) Breast Cancer Study Group J Clin Oncol. 1992;10:1049–1056. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

