Chemoselection as a strategy for organ preservation in advanced oropharynx cancer: response and survival positively associated with HPV16 copy number
- PMID: 18474879
- PMCID: PMC2742158
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2007.12.7597
Chemoselection as a strategy for organ preservation in advanced oropharynx cancer: response and survival positively associated with HPV16 copy number
Abstract
Purpose: To test induction chemotherapy (IC) followed by concurrent chemoradiotherapy (CRT) or surgery/radiotherapy (RT) for advanced oropharyngeal cancer and to assess the effect of human papilloma virus (HPV) on response and outcome.
Patients and methods: Sixty-six patients (51 male; 15 female) with stage III to IV squamous cell carcinoma of the oropharynx (SCCOP) were treated with one cycle of cisplatin (100 mg/m(2)) or carboplatin (AUC 6) and with fluorouracil (1,000 mg/m(2)/d for 5 days) to select candidates for CRT. Those achieving a greater than 50% response at the primary tumor received CRT (70 Gy; 35 fractions with concurrent cisplatin 100 mg/m(2) or carboplatin (AUC 6) every 21 days for three cycles). Adjuvant paclitaxel was given to patients who were complete histologic responders. Patients with a response of 50% or less underwent definitive surgery and postoperative radiation. Pretreatment biopsies from 42 patients were tested for high-risk HPV.
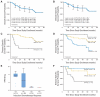
Results: Fifty-four of 66 patients (81%) had a greater than 50% response after IC. Of these, 53 (98%) received CRT, and 49 (92%) obtained complete histologic response with a 73.4% (47 of 64) rate of organ preservation. The 4-year overall survival (OS) was 70.4%, and the disease-specific survival (DSS) was 75.8% (median follow-up, 64.1 months). HPV16, found in 27 of 42 (64.3%) biopsies, was associated with younger age (median, 55 v 63 years; P = .016), sex (22 of 30 males [73.3%] and five of 12 females [41.7%]; P = .08), and nonsmoking status (P = .037). HPV titer was significantly associated with IC response (P = .001), CRT response (P = .005), OS (P = .007), and DSS (P = .008).
Conclusion: Although the numbers in this study are small, IC followed by CRT is an effective treatment for SCCOP, especially in patients with HPV-positive tumors; however, for patients who do not respond to treatment, alternative treatments must be developed.
Figures
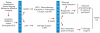

Comment in
-
Redefining the role of induction chemotherapy in head and neck cancer.J Clin Oncol. 2008 Jul 1;26(19):3117-9. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.15.2256. Epub 2008 May 12. J Clin Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18474875 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Weekly chemotherapy with radiation versus high-dose cisplatin with radiation as organ preservation for patients with HPV-positive and HPV-negative locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the oropharynx.Head Neck. 2014 May;36(5):617-23. doi: 10.1002/hed.23339. Epub 2013 Jul 2. Head Neck. 2014. PMID: 23596055 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Phase 1 study of nab-paclitaxel, cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil as induction chemotherapy followed by concurrent chemoradiotherapy in locoregionally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the oropharynx.Eur J Cancer. 2014 Sep;50(13):2263-70. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2014.05.021. Epub 2014 Jun 19. Eur J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24953566 Clinical Trial.
-
Reduced-dose radiotherapy for human papillomavirus-associated squamous-cell carcinoma of the oropharynx: a single-arm, phase 2 study.Lancet Oncol. 2017 Jun;18(6):803-811. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30246-2. Epub 2017 Apr 20. Lancet Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28434660 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Chemoselection as a strategy for organ preservation in patients with T4 laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma with cartilage invasion.Laryngoscope. 2009 Aug;119(8):1510-7. doi: 10.1002/lary.20294. Laryngoscope. 2009. PMID: 19504552 Free PMC article.
-
Utility of PET, CT, and EUS to identify pathologic responders in esophageal cancer.Ann Thorac Surg. 2004 Oct;78(4):1152-60; discussion 1152-60. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2004.04.046. Ann Thorac Surg. 2004. PMID: 15464463 Review.
Cited by
-
Technical guidelines for head and neck cancer IMRT on behalf of the Italian association of radiation oncology - head and neck working group.Radiat Oncol. 2014 Dec 29;9:264. doi: 10.1186/s13014-014-0264-9. Radiat Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25544268 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the impact of high-risk human papillomavirus on oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinomas in Taiwan: A retrospective cohort study.PLoS One. 2021 Apr 23;16(4):e0250530. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0250530. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33891627 Free PMC article.
-
Human papillomavirus: changing paradigms in oropharyngeal cancer.Curr Oncol Rep. 2010 Mar;12(2):115-20. doi: 10.1007/s11912-010-0084-5. Curr Oncol Rep. 2010. PMID: 20425596
-
The clinical impact of HPV tumor status upon head and neck squamous cell carcinomas.Oral Oncol. 2014 Jun;50(6):565-74. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2013.09.008. Epub 2013 Oct 14. Oral Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24134947 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes predict for outcome in HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancer.Br J Cancer. 2014 Jan 21;110(2):489-500. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2013.639. Epub 2013 Oct 29. Br J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24169344 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shiboski CH, Schmidt BL, Jordan RC. Tongue and tonsil carcinoma: Increasing trends in the US population ages 20-44 years. Cancer. 2005;103:1843–1849. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al. Cancer statistics, 2007. CA Cancer J Clin. 2007;57:43–66. - PubMed
-
- Lewin F, Norell SE, Johansson H, et al. Smoking tobacco, oral snuff, and alcohol in the etiology of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: A population-based case-referent study in Sweden. Cancer. 1998;82:1367–1375. - PubMed
-
- D'Souza G, Kreimer AR, Viscidi R, et al. Case-control study of human papillomavirus and oropharyngeal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:1944–1956. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DE013346/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA046592/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA097248-06A1/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DC005188/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE13346/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA046592-21/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA97248/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DC 05188/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA097248/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE019126/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DC005188-07/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE013346-05/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

