Development of an immunochromatographic lateral-flow device for rapid serodiagnosis of invasive aspergillosis
- PMID: 18463222
- PMCID: PMC2446636
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00068-08
Development of an immunochromatographic lateral-flow device for rapid serodiagnosis of invasive aspergillosis
Abstract
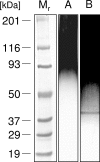
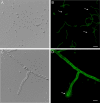
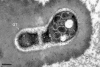
Aspergillus fumigatus is a cosmopolitan saprotrophic fungus that is second only to Candida species as a cause of invasive fungal infections in immunocompromised humans. Current immunodiagnostic tests for invasive aspergillosis (IA) are based on the detection of circulating galactomannan (GM) in a patient's serum by using a rat monoclonal antibody (MAb), EB-A2, that binds to tetra (1-->5)-beta-D-galactofuranoside, the immunodominant epitope in GM. The potential cross-reactivity of MAb EB-A2 with non-Aspergillus fungi, with contaminating GM in beta-lactam antibiotics and foodstuffs, and with bacterial lipoteichoic acids has prompted efforts to discover non-GM antigens that can act as surrogate markers for the diagnosis of IA. This paper describes the development of a mouse MAb, JF5, that binds to a protein epitope present on an extracellular glycoprotein antigen secreted constitutively during the active growth of A. fumigatus. The MAb was used to develop an immunochromatographic lateral-flow device (LFD) for the rapid (15-min) detection of Aspergillus antigens in human serum. The test is highly specific, reacting with antigens from Aspergillus species but not with antigens from a large number of clinically important fungi, including Candida species, Cryptococcus neoformans, Fusarium solani, Penicillium marneffei, Pseudallescheria boydii, and Rhizopus oryzae. The LFD was able to detect circulating antigen in serum samples from patients suspected of having or shown to have IA on the basis of their clinical symptoms and results from tests for GM and fungal (1-->3)-beta-D-glucan. The ease of use of the LFD provides a diagnostic platform for the routine testing of vulnerable patients who have an elevated risk of IA.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Monoclonal Antibody AP3 Binds Galactomannan Antigens Displayed by the Pathogens Aspergillus flavus, A. fumigatus, and A. parasiticus.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 Jul 16;9:234. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00234. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31380292 Free PMC article.
-
Well-characterized monoclonal antibodies against cell wall antigen of Aspergillus species improve immunoassay specificity and sensitivity.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2008 Feb;15(2):194-202. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00362-07. Epub 2007 Nov 21. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18032591 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of cell wall galactomannoprotein Afmp1p in culture supernatants of Aspergillus fumigatus and in sera of aspergillosis patients.J Clin Microbiol. 2002 Nov;40(11):4382-7. doi: 10.1128/JCM.40.11.4382-4387.2002. J Clin Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 12409437 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of invasive aspergillosis.Adv Appl Microbiol. 2010;70:187-216. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2164(10)70006-X. Epub 2010 Mar 6. Adv Appl Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20359458 Review.
-
[Mycoserology--did we move on? Aspergillus].Mycoses. 2010 May;53 Suppl 1:26-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0507.2009.01839.x. Mycoses. 2010. PMID: 20433653 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Rapid Detection of Azole-Resistant Aspergillus fumigatus in Clinical and Environmental Isolates by Use of a Lab-on-a-Chip Diagnostic System.J Clin Microbiol. 2020 Oct 21;58(11):e00843-20. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00843-20. Print 2020 Oct 21. J Clin Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32907990 Free PMC article.
-
The clinical spectrum of aspergillosis in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Infection. 2023 Aug;51(4):813-829. doi: 10.1007/s15010-022-01960-2. Epub 2023 Jan 20. Infection. 2023. PMID: 36662439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monoclonal Antibodies and Invasive Aspergillosis: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Perspectives.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 16;23(10):5563. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105563. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35628374 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of a Monoclonal Antibody and a Serodiagnostic Lateral-Flow Device Specific to Rhizopus arrhizus (Syn. R. oryzae), the Principal Global Agent of Mucormycosis in Humans.J Fungi (Basel). 2022 Jul 21;8(7):756. doi: 10.3390/jof8070756. J Fungi (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35887511 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid clinical bacteriology and its future impact.Ann Lab Med. 2013 Jan;33(1):14-27. doi: 10.3343/alm.2013.33.1.14. Epub 2012 Dec 17. Ann Lab Med. 2013. PMID: 23301218 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ansorg, R., R. Van den Boom, and P. M. Rath. 1997. Detection of Aspergillus galactomannan antigen in foods and antibiotics. Mycoses 40:353-357. - PubMed
-
- Aubry, A., R. Porcher, J. Bottero, S. Touratier, T. Leblanc, B. Brethon, P. Rousselot, E. Raffoux, J. Menotti, F. Derouin, P. Ribaud, and A. Sulahian. 2006. Occurrence and kinetics of false-positive Aspergillus galactomannan test results following treatment with β-lactam antibiotics in patients with hematological disorders. J. Clin. Microbiol. 44:389-394. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bleddyn Hughes, H., R. Carzaniga, S. L. Rawlings, J. R. Green, and R. J. O'Connell. 1999. Spore surface glycoproteins of Colletotrichum lindemuthianum are recognized by a monoclonal antibody which inhibits binding to polystyrene. Microbiology 145:1927-1936. - PubMed
-
- Brakhage, A. A., and K. Langfelder. 2002. Menacing mold: the molecular biology of Aspergillus fumigatus. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 56:433-455. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

