FFPred: an integrated feature-based function prediction server for vertebrate proteomes
- PMID: 18463141
- PMCID: PMC2447771
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkn193
FFPred: an integrated feature-based function prediction server for vertebrate proteomes
Abstract
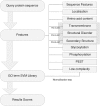
One of the challenges of the post-genomic era is to provide accurate function annotations for large volumes of data resulting from genome sequencing projects. Most function prediction servers utilize methods that transfer existing database annotations between orthologous sequences. In contrast, there are few methods that are independent of homology and can annotate distant and orphan protein sequences. The FFPred server adopts a machine-learning approach to perform function prediction in protein feature space using feature characteristics predicted from amino acid sequence. The features are scanned against a library of support vector machines representing over 300 Gene Ontology (GO) classes and probabilistic confidence scores returned for each annotation term. The GO term library has been modelled on human protein annotations; however, benchmark performance testing showed robust performance across higher eukaryotes. FFPred offers important advantages over traditional function prediction servers in its ability to annotate distant homologues and orphan protein sequences, and achieves greater coverage and classification accuracy than other feature-based prediction servers. A user may upload an amino acid and receive annotation predictions via email. Feature information is provided as easy to interpret graphics displayed on the sequence of interest, allowing for back-interpretation of the associations between features and function classes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
FFPred 2.0: improved homology-independent prediction of gene ontology terms for eukaryotic protein sequences.PLoS One. 2013 May 22;8(5):e63754. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063754. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23717476 Free PMC article.
-
JAFA: a protein function annotation meta-server.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006 Jul 1;34(Web Server issue):W379-81. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl045. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16845030 Free PMC article.
-
Bioverse: Functional, structural and contextual annotation of proteins and proteomes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2003 Jul 1;31(13):3736-7. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg550. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003. PMID: 12824406 Free PMC article.
-
An Experimental Approach to Genome Annotation: This report is based on a colloquium sponsored by the American Academy of Microbiology held July 19-20, 2004, in Washington, DC.Washington (DC): American Society for Microbiology; 2004. Washington (DC): American Society for Microbiology; 2004. PMID: 33001599 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Servers for protein structure prediction.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2006 Apr;16(2):178-82. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2006.03.004. Epub 2006 Mar 20. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2006. PMID: 16546376 Review.
Cited by
-
PROSPER: an integrated feature-based tool for predicting protease substrate cleavage sites.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e50300. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050300. Epub 2012 Nov 29. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23209700 Free PMC article.
-
Classification of intrinsically disordered regions and proteins.Chem Rev. 2014 Jul 9;114(13):6589-631. doi: 10.1021/cr400525m. Epub 2014 Apr 29. Chem Rev. 2014. PMID: 24773235 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Three-level prediction of protein function by combining profile-sequence search, profile-profile search, and domain co-occurrence networks.BMC Bioinformatics. 2013;14 Suppl 3(Suppl 3):S3. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-14-S3-S3. Epub 2013 Feb 28. BMC Bioinformatics. 2013. PMID: 23514381 Free PMC article.
-
Sequence-based feature prediction and annotation of proteins.Genome Biol. 2009 Feb 2;10(2):206. doi: 10.1186/gb-2009-10-2-206. Genome Biol. 2009. PMID: 19226438 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting human protein function with multi-task deep neural networks.PLoS One. 2018 Jun 11;13(6):e0198216. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0198216. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29889900 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ofran Y, Punta M, Schneider R, Rost B. Beyond annotation transfer by homology: novel protein function prediction methods to assist drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today. 2005;10:1475–1482. - PubMed
-
- Rost B. Enzyme function less conserved than anticipated. J. Mol. Biol. 2002;318:595–608. - PubMed
-
- Tian W, Skolnick J. How well is enzyme function conserved as a function of pairwise sequence identity? 2003;333:863–882. - PubMed
-
- Dobson PD, Doig AJ. Predicting enzyme class from protein structure without alignments. 2004;345:187–199. - PubMed
-
- Jensen LJ, Stærfeldt H-H, Brunak S. Prediction of human protein function according to Gene Ontology categories. Bioinformatics. 2003;19:635–642. - PubMed