The human lipodystrophy gene BSCL2/seipin may be essential for normal adipocyte differentiation
- PMID: 18458148
- PMCID: PMC2494687
- DOI: 10.2337/db08-0184
The human lipodystrophy gene BSCL2/seipin may be essential for normal adipocyte differentiation
Abstract
Objective: Berardinelli-Seip congenital lipodystrophy type 2 (BSCL2) is a recessive disorder featuring near complete absence of adipose tissue. Remarkably, although the causative gene, BSCL2, has been known for several years, its molecular function and its role in adipose tissue development have not been elucidated. Therefore, we examined whether BSCL2 is involved in the regulation of adipocyte differentiation and the mechanism whereby pathogenic mutations in BSCL2 cause lipodystrophy.
Research design and methods: Following the characterization of BSCL2 expression in developing adipocytes, C3H10T1/2 mesenchymal stem cells were generated in which BSCL2 expression was knocked down using short hairpin RNA (shRNA). These cells were used to investigate whether BSCL2 is required for adipogenesis. BSCL2 constructs harboring pathogenic mutations known to cause lipodystrophy were also generated and characterized.
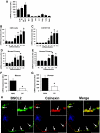
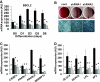
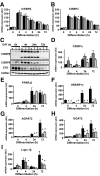
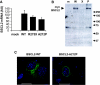
Results: BSCL2 expression was strongly induced during adipocyte differentiation, and the induction of BSCL2 expression was essential for adipogenesis to occur. The initial induction of key adipogenic transcription factors, including peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)gamma and CAAT/enhancer-binding protein-alpha, was preserved in cells lacking BSCL2. However, the expression of these critical factors was not sustained, suggesting that the activity of PPARgamma was impaired. Moreover, expression of key genes mediating triglyceride synthesis, including AGPAT2, lipin 1, and DGAT2, was persistently reduced and lipid accumulation was inhibited. Analysis of pathogenic missense mutants of BSCL2 revealed that the amino acid substitution A212P causes aberrant targeting of BSCL2 within the cell, suggesting that subcellular localization of BSCL2 may be critical to its function.
Conclusions: This study demonstrates that BSCL2 is an essential, cell-autonomous regulator of adipogenesis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Berardinelli-seip congenital lipodystrophy 2/seipin is a cell-autonomous regulator of lipolysis essential for adipocyte differentiation.Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Mar;32(6):1099-111. doi: 10.1128/MCB.06465-11. Epub 2012 Jan 23. Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22269949 Free PMC article.
-
The human lipodystrophy gene product Berardinelli-Seip congenital lipodystrophy 2/seipin plays a key role in adipocyte differentiation.Endocrinology. 2009 Oct;150(10):4552-61. doi: 10.1210/en.2009-0236. Epub 2009 Jul 2. Endocrinology. 2009. PMID: 19574402 Free PMC article.
-
Berardinelli-Seip congenital lipodystrophy 2/SEIPIN determines brown adipose tissue maintenance and thermogenic programing.Mol Metab. 2020 Jun;36:100971. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2020.02.014. Epub 2020 Mar 4. Mol Metab. 2020. PMID: 32246911 Free PMC article.
-
Towards a mechanistic understanding of lipodystrophy and seipin functions.Biosci Rep. 2014 Oct 2;34(5):e00141. doi: 10.1042/BSR20140114. Biosci Rep. 2014. PMID: 25195639 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Function of seipin: new insights from Bscl2/seipin knockout mouse models.Biochimie. 2014 Jan;96:166-72. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2013.06.022. Epub 2013 Jul 2. Biochimie. 2014. PMID: 23831461 Review.
Cited by
-
Celia's Encephalopathy (BSCL2-Gene-Related): Current Understanding.J Clin Med. 2021 Apr 1;10(7):1435. doi: 10.3390/jcm10071435. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 33916074 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reep1 null mice reveal a converging role for hereditary spastic paraplegia proteins in lipid droplet regulation.Hum Mol Genet. 2016 Dec 1;25(23):5111-5125. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddw315. Hum Mol Genet. 2016. PMID: 27638887 Free PMC article.
-
Berardinelli-seip congenital lipodystrophy 2/seipin is a cell-autonomous regulator of lipolysis essential for adipocyte differentiation.Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Mar;32(6):1099-111. doi: 10.1128/MCB.06465-11. Epub 2012 Jan 23. Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22269949 Free PMC article.
-
Congenital generalized lipodystrophy: identification of novel variants and expansion of clinical spectrum.Clin Genet. 2016 Apr;89(4):434-441. doi: 10.1111/cge.12623. Epub 2015 Jul 20. Clin Genet. 2016. PMID: 26072926 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of genes involved in lipid droplet formation (BSCL2, SNAP23 and COPA) during porcine in vitro adipogenesis.J Appl Genet. 2016 Nov;57(4):505-510. doi: 10.1007/s13353-016-0350-9. Epub 2016 Apr 23. J Appl Genet. 2016. PMID: 27108337 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agarwal AK, Garg A: Genetic disorders of adipose tissue development, differentiation, and death. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 7: 175–199, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Boguslavsky RL, Stewart CL, Worman HJ: Nuclear lamin A inhibits adipocyte differentiation: implications for Dunnigan-type familial partial lipodystrophy. Hum Mol Genet 15: 653–663, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Agarwal AK, Simha V, Oral EA, Moran SA, Gorden P, O'Rahilly S, Zaidi Z, Gurakan F, Arslanian SA, Klar A, Ricker A, White NH, Bindl L, Herbst K, Kennel K, Patel SB, Al-Gazali L, Garg A: Phenotypic and genetic heterogeneity in congenital generalized lipodystrophy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88: 4840–4847, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Magre J, Delepine M, Khallouf E, Gedde-Dahl T, Jr, Van Maldergem L, Sobel E, Papp J, Meier M, Megarbane A, Bachy A, Verloes A, d'Abronzo FH, Seemanova E, Assan R, Baudic N, Bourut C, Czernichow P, Huet F, Grigorescu F, de Kerdanet M, Lacombe D, Labrune P, Lanza M, Loret H, Matsuda F, Navarro J, Nivelon-Chevalier A, Polak M, Robert JJ, Tric P, Tubiana-Rufi N, Vigouroux C, Weissenbach J, Savasta S, Maassen JA, Trygstad O, Bogalho P, Freitas P, Medina JL, Bonnicci F, Joffe BI, Loyson G, Panz VR, Raal FJ, O'Rahilly S, Stephenson T, Kahn CR, Lathrop M, Capeau J: Identification of the gene altered in Berardinelli-Seip congenital lipodystrophy on chromosome 11q13. Nat Genet 28: 365–370, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Agarwal AK, Garg A: Seipin: a mysterious protein. Trends Mol Med 10: 440–444, 2004 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

