Functional roles for C5a receptors in sepsis
- PMID: 18454156
- PMCID: PMC2753858
- DOI: 10.1038/nm1753
Functional roles for C5a receptors in sepsis
Abstract
The function of the C5a receptors, C5ar (encoded by C5ar) and C5l2 (encoded by Gpr77), especially of C5l2, which was originally termed a 'default receptor', remains a controversial topic. Here we investigated the role of each receptor in the setting of cecal ligation and puncture-induced sepsis by using antibody-induced blockade of C5a receptors and knockout mice. In 'mid-grade' sepsis (30-40% survival), blockade or absence of either C5ar or C5l2 greatly improved survival and attenuated the buildup of proinflammatory mediators in plasma. In vivo appearance or in vitro release of high mobility group box 1 protein (HMGB1) required C5l2 but not C5ar. In 'high-grade' sepsis (100% lethality), the only protective condition was the combined blockade of C5l2 and C5ar. These data suggest that C5ar and C5l2 contribute synergistically to the harmful consequences in sepsis and that C5l2 is required for the release of HMGB1. Thus, contrary to earlier speculation, C5l2 is a functional receptor rather than merely a default receptor.
Figures
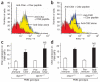
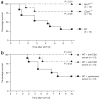

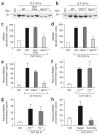

Similar articles
-
The interaction between C5a and both C5aR and C5L2 receptors is required for production of G-CSF during acute inflammation.Eur J Immunol. 2013 Jul;43(7):1907-13. doi: 10.1002/eji.201243075. Epub 2013 May 13. Eur J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23575697 Free PMC article.
-
C5L2: a controversial receptor of complement anaphylatoxin, C5a.FASEB J. 2013 Mar;27(3):855-64. doi: 10.1096/fj.12-220509. Epub 2012 Dec 13. FASEB J. 2013. PMID: 23239822 Review.
-
Complement dependency of cardiomyocyte release of mediators during sepsis.FASEB J. 2011 Jul;25(7):2500-8. doi: 10.1096/fj.11-183236. Epub 2011 Apr 8. FASEB J. 2011. PMID: 21478262 Free PMC article.
-
C5L2 is required for C5a-triggered receptor internalization and ERK signaling.Cell Signal. 2014 Jul;26(7):1409-19. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.02.021. Epub 2014 Mar 12. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24631530
-
Receptors for complement C5a. The importance of C5aR and the enigmatic role of C5L2.Immunol Cell Biol. 2008 Feb;86(2):153-60. doi: 10.1038/sj.icb.7100166. Epub 2008 Jan 29. Immunol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18227853 Review.
Cited by
-
A Pathophysiological Insight into Sepsis and Its Correlation with Postmortem Diagnosis.Mediators Inflamm. 2016;2016:4062829. doi: 10.1155/2016/4062829. Epub 2016 Apr 27. Mediators Inflamm. 2016. PMID: 27239102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neutrophil migration under normal and sepsis conditions.Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 2015;15(1):19-28. doi: 10.2174/1871529x15666150108113236. Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 2015. PMID: 25567338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Danger signals activating the immune response after trauma.Mediators Inflamm. 2012;2012:315941. doi: 10.1155/2012/315941. Epub 2012 Jun 19. Mediators Inflamm. 2012. PMID: 22778496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
C5aR2 Deficiency Lessens C5aR1 Distribution and Expression in Neutrophils and Macrophages.J Immunol Res. 2024 Jul 10;2024:2899154. doi: 10.1155/2024/2899154. eCollection 2024. J Immunol Res. 2024. PMID: 39021433 Free PMC article.
-
C5a promotes migration, proliferation, and vessel formation in endothelial cells.Inflamm Res. 2010 Aug;59(8):659-66. doi: 10.1007/s00011-010-0178-4. Epub 2010 Mar 9. Inflamm Res. 2010. PMID: 20217457 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Czermak BJ, et al. Protective effects of C5a blockade in sepsis. Nat. Med. 1999;5:788–792. - PubMed
-
- Gerard NP, Gerard C. The chemotactic receptor for human C5a anaphylatoxin. Nature. 1991;349:614–617. - PubMed
-
- Gerard C, Gerard NP. C5A anaphylatoxin and its seven transmembrane-segment receptor. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1994;12:775–808. - PubMed
-
- Cain SA, Monk PN. The orphan receptor C5L2 has high affinity binding sites for complement fragments C5a and C5a des-Arg74. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:7165–7169. - PubMed
-
- Johswich K, et al. Ligand specificity of the anaphylatoxin C5L2 receptor and its regulation on myeloid and epithelial cell lines. J. Biol. Chem. 2006;281:39088–39095. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AI057839/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL031963/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-69511/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM061656-07/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL031963-250001/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL069511/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM029507-27/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 GM029507/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM061656/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- AI-057839/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- GM-29507/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM029507/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM-61656/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HL-31963/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

