A mechanism for SRC kinase-dependent signaling by noncatalytic receptors
- PMID: 18444664
- PMCID: PMC2614901
- DOI: 10.1021/bi8003044
A mechanism for SRC kinase-dependent signaling by noncatalytic receptors
Abstract
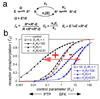
A fundamental issue in cell biology is how signals are transmitted across membranes. A variety of transmembrane receptors, including multichain immune recognition receptors, lack catalytic activity and require Src family kinases (SFKs) for signal transduction. However, many receptors only bind and activate SFKs after ligand-induced receptor dimerization. This presents a conundrum: How do SFKs sense the dimerization of receptors to which they are not already bound? Most proposals for resolving this enigma invoke additional players, such as lipid rafts or receptor conformational changes. Here we used simple thermodynamics to show that SFK activation is a natural outcome of clustering of receptors with SFK phosphorylation sites, provided that there is phosphorylation-dependent receptor-SFK association and an SFK bound to one receptor can phosphorylate the second receptor or its associated SFK in a dimer. A simple system of receptor, SFK, and an unregulated protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) can account for ligand-induced changes in phosphorylation observed in cells. We suggest that a core signaling system comprising a receptor with SFK phosphorylation sites, an SFK, and an unregulated PTP provides a robust mechanism for transmembrane signal transduction. Other events that regulate signaling in specific cases may have evolved for fine-tuning of this basic mechanism.
Figures



Similar articles
-
SRC family kinases and receptors: analysis of three activation mechanisms by dynamic systems modeling.Biophys J. 2008 Mar 15;94(6):1995-2006. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.107.115022. Epub 2007 Nov 30. Biophys J. 2008. PMID: 18055537 Free PMC article.
-
EphrinB phosphorylation and reverse signaling: regulation by Src kinases and PTP-BL phosphatase.Mol Cell. 2002 Apr;9(4):725-37. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(02)00488-4. Mol Cell. 2002. PMID: 11983165
-
Src family kinase tyrosine phosphorylates Toll-like receptor 4 to dissociate MyD88 and Mal/Tirap, suppressing LPS-induced inflammatory responses.Biochem Pharmacol. 2018 Jan;147:119-127. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2017.11.015. Epub 2017 Nov 23. Biochem Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29175418 Free PMC article.
-
The regulation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors by Src kinase.FEBS J. 2012 Jan;279(1):20-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08413.x. Epub 2011 Dec 5. FEBS J. 2012. PMID: 22060915 Review.
-
Endogenous and synthetic inhibitors of the Src-family protein tyrosine kinases.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005 Dec 30;1754(1-2):210-20. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2005.07.027. Epub 2005 Sep 8. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005. PMID: 16198159 Review.
Cited by
-
CD44/CD44v6 a Reliable Companion in Cancer-Initiating Cell Maintenance and Tumor Progression.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2018 Aug 28;6:97. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2018.00097. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2018. PMID: 30211160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms for T cell receptor triggering.Nat Rev Immunol. 2011 Jan;11(1):47-55. doi: 10.1038/nri2887. Epub 2010 Dec 3. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21127503 Review.
-
Lipid rafts control P2X3 receptor distribution and function in trigeminal sensory neurons of a transgenic migraine mouse model.Mol Pain. 2011 Sep 29;7:77. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-7-77. Mol Pain. 2011. PMID: 21958474 Free PMC article.
-
The SCHOOL of nature: III. From mechanistic understanding to novel therapies.Self Nonself. 2010 Jul;1(3):192-224. doi: 10.4161/self.1.3.12794. Epub 2010 Jun 11. Self Nonself. 2010. PMID: 21487477 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody mediated CDCP1 degradation as mode of action for cancer targeted therapy.Mol Oncol. 2013 Dec;7(6):1142-51. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2013.08.009. Epub 2013 Sep 3. Mol Oncol. 2013. PMID: 24055141 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tamir I, Cambier JC. Antigen receptor signaling: integration of protein tyrosine kinase functions. Oncogene. 1998;17:1353–1364. - PubMed
-
- Sigalov A. Multi-chain immune recognition receptors: spatial organization and signal transduction. Semin. Immunol. 2005;17:51–64. - PubMed
-
- Germain RN. T-cell signaling: the importance of receptor clustering. Curr. Biol. 1997;7:R640–R644. - PubMed
-
- Veillette A, Latour S, Davidson D. Negative regulation of immunoreceptor signaling. Annu. Rev. Immuno. 2002;20:669–707. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

